SLUS964D NOVEMBER 2009 – March 2018 TPS40303 , TPS40304 , TPS40305
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Using the TPS40305 for a 12-V to 1.8-V Point-of-Load Synchronous Buck Regulator
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.1.2.2 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.1.2.3 Inductor Selection (L1)
- 8.2.1.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection (C12)
- 8.2.1.2.5 Peak Current Rating of Inductor
- 8.2.1.2.6 Input Capacitor Selection (C8)
- 8.2.1.2.7 MOSFET Switch Selection (Q1 and Q2)
- 8.2.1.2.8 Bootstrap Capacitor (C6)
- 8.2.1.2.9 VDD Bypass Capacitor (C7)
- 8.2.1.2.10 BP Bypass Capacitor (C5)
- 8.2.1.2.11 Short-Circuit Protection (R11)
- 8.2.1.2.12 Feedback Divider (R4, R5)
- 8.2.1.2.13 Compensation: (C2, C3, C4, R3, R6)
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2
A High-Current, Low-Voltage Design Using the TPS40304
- 8.2.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.2.1 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2.2 Inductor Selection (L1)
- 8.2.2.2.3 Output Capacitor Selection (C12)
- 8.2.2.2.4 Peak Current Rating of Inductor
- 8.2.2.2.5 Input Capacitor Selection (C8)
- 8.2.2.2.6 MOSFET Switch Selection (Q1 and Q2)
- 8.2.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor (C6)
- 8.2.2.2.8 VDD Bypass Capacitor (C7)
- 8.2.2.2.9 BP Bypass Capacitor (C5)
- 8.2.2.2.10 Short-Circuit Protection (R11)
- 8.2.2.2.11 Feedback Divider (R4, R5)
- 8.2.2.2.12 Compensation: (C2, C3, C4, R3, R6)
- 8.2.2.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.3
A Synchronous Buck Application Using the TPS40303
- 8.2.3.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.3.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.3.2.1 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.3.2.2 Inductor Selection (L1)
- 8.2.3.2.3 Output Capacitor Selection (C12)
- 8.2.3.2.4 Peak Current Rating of Inductor
- 8.2.3.2.5 Input Capacitor Selection (C8)
- 8.2.3.2.6 MOSFET Switch Selection (Q1 and Q2)
- 8.2.3.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor (C6)
- 8.2.3.2.8 VDD Bypass Capacitor (C7)
- 8.2.3.2.9 BP Bypass Capacitor (C5)
- 8.2.3.2.10 Short-Circuit Protection (R11)
- 8.2.3.2.11 Feedback Divider (R4, R5)
- 8.2.3.2.12 Compensation: (C2, C3, C4, R3, R6)
- 8.2.3.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
Using the TPS40305 for a 12-V to 1.8-V Point-of-Load Synchronous Buck Regulator
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Orderable Information
8.2.2.2.5 Input Capacitor Selection (C8)
The input voltage ripple is divided between capacitance and ESR. For this design VRIPPLE(cap) = 150 mV and VRIPPLE(esr) = 150 mV. The minimum capacitance and maximum ESR are estimated by Equation 27.
Equation 27. 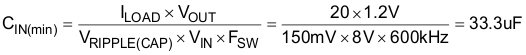
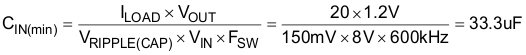
Equation 28. 

The RMS current in the input capacitors is estimated by Equation 29.
Equation 29. 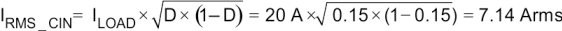
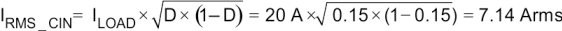
Three 1210, 10-µF, 25-V, X5R ceramic capacitors are selected. Higher voltage capacitors are selected to minimize capacitance loss at the DC bias voltage to ensure the capacitors allow sufficient capacitance at the working voltage.