SLVSAV1D May 2011 – July 2016 TPS54062
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed-Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Slope Compensation Output Current
- 7.3.3 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.4 Voltage Reference
- 7.3.5 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.6 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 7.3.7 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK Pin)
- 7.3.8 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 7.3.9 How to Interface to RT/CLK Pin
- 7.3.10 Overvoltage Transient Protection
- 7.3.11 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Applications and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM) Switching Regulator
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.1.2.2 Output Inductor Selection (LO)
- 8.2.1.2.3 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.4 Input capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.5 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.6 Under Voltage Lock Out Set Point
- 8.2.1.2.7 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 8.2.1.2.8 Closing the Loop
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 DCM Application
- 8.2.1
Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM) Switching Regulator
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRB|8
Orderable Information
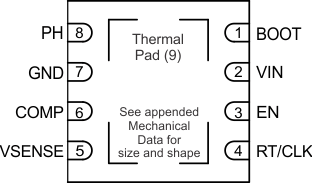
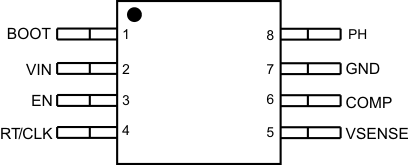
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
MSOP PACKAGE
8 PINS
TOP VIEW
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NUMBER | ||
| BOOT | 1 | O | A bootstrap capacitor is required between BOOT and PH. If the voltage on this capacitor is below the minimum required by the output device, the output is forced to switch off until the capacitor is refreshed. |
| VIN | 2 | I | Input supply voltage, 4.7 V to 60 V. |
| EN | 3 | I | Enable pin, internal pull-up current source. Pull below 1.14 V to disable. Float to enable. Adjust the input undervoltage lockout with two resistors, see the Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout section. |
| RT/CLK | 4 | I | Resistor Timing and External Clock. An internal amplifier holds this pin at a fixed voltage when using an external resistor to ground to set the switching frequency. If the pin is pulled above the PLL upper threshold, a mode change occurs and the pin becomes a synchronization input. The internal amplifier is disabled and the pin is a high impedance clock input to the internal PLL. If clocking edges stop, the internal amplifier is re-enabled and the mode returns to a resistor frequency programming. |
| VSENSE | 5 | I | Inverting input of the transconductance (gm) error amplifier. |
| COMP | 6 | O | Error amplifier output, and input to the output switch current comparator. Connect frequency compensation components to this pin. |
| GND | 7 | – | Ground |
| PH | 8 | O | The source of the internal high-side power MOSFET and drain of the internal low side MOSFET |
| Thermal Pad | 9 | – | GND pin must be electrically connected to the exposed pad on the printed circuit board for proper operation. VSON-8 package only. |