SLVSEQ0A May 2019 – March 2020 TPS54A24
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 7.3.2 Continuous Conduction Mode Operation (CCM)
- 7.3.3 VIN Pins and VIN UVLO
- 7.3.4 Voltage Reference and Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.6 Enable and Adjustable UVLO
- 7.3.7 Soft Start and Tracking
- 7.3.8 Safe Start-Up Into Prebiased Outputs
- 7.3.9 Power Good
- 7.3.10 Sequencing (SS/TRK)
- 7.3.11 Adjustable Switching Frequency (RT Mode)
- 7.3.12 Synchronization (CLK Mode)
- 7.3.13 Bootstrap Voltage and 100% Duty Cycle Operation (BOOT)
- 7.3.14 Output Overvoltage Protection (OVP)
- 7.3.15 Overcurrent Protection
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 8.2.2.2 Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Output Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.6 Output Voltage Resistors Selection
- 8.2.2.7 Soft-Start Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Undervoltage Lockout Setpoint
- 8.2.2.9 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.10 PGOOD Pullup Resistor
- 8.2.2.11 Compensation
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTW|24
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTW|24
Orderable Information
7.3.13 Bootstrap Voltage and 100% Duty Cycle Operation (BOOT)
The device provides an integrated bootstrap-voltage regulator. A small capacitor between the BOOT and SW pins provides the gate-drive voltage for the high-side MOSFET. The BOOT capacitor is refreshed when the low-side MOSFET is on. The recommended value of the BOOT capacitor is 0.1 μF. A ceramic capacitor with an X7R or X5R grade dielectric with a voltage rating of 10 V or higher is recommended for stable performance over temperature and voltage.
When operating with a low voltage difference from input to output, the high-side MOSFET of the device operate at 100% duty cycle as long as the BOOT to SW pin voltage is greater than 2.2 V. The device begins to transition to 100% duty cycle operation when the high-side MOSFET off-time is less than 200 ns typical. Equation 12 can be used to estimate the input voltage the switching frequency begins to decrease. When the switching frequency decreases the BOOT to SW capacitor is not recharged as often so the BOOT to SW voltage will start to decrease. If the voltage from BOOT to SW drops below 2.2 V, the high-side MOSFET is turned off due to BOOT UVLO and the low-side MOSFET pulls SW low to recharge the BOOT capacitor. When operating at 100% duty cycle the high-side MOSFET can remain on for many switching cycles before the MOSFET is turned off to refresh the capacitor because the gate drive current sourced by the BOOT capacitor is small. The effective switching frequency reduced and the effective maximum duty cycle of the switching regulator is near 100%. The output voltage of the converter during dropout is mainly influenced by the voltage drops across the power MOSFET, the inductor resistance, and the printed circuit board resistance.
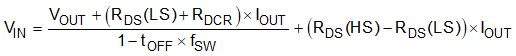
where
- RDS(LS) = low-side MOSFET RDS(on)
- RDS(HS) = high-side MOSFET RDS(on)
- RDCR = DC resistance of inductor
- tOFF = off-time that 100% duty cycle operation begins