SLVSB50C December 2011 – June 2020 TPS61087-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Orderable Information
8.2.1.2.1 Inductor Selection
The TPS61087-Q1 is designed to work with a wide range of inductors. The main parameter for the inductor selection is the saturation current of the inductor, which must be higher than the peak switch current as calculated in Equation 3 with additional margin to cover for heavy load transients. A more conservative alternative is to choose an inductor with a saturation current at least as high as the maximum switch current limit of 4.8 A. The other important parameter is the inductor DC resistance. As the DC resistance decreases, the efficiency usually increases. It is important to note that the inductor DC resistance is not the only parameter determining the efficiency. Especially for a boost converter where the inductor is the energy storage element, the type and core material of the inductor influences the efficiency as well. At high switching frequencies of 1.2 MHz, inductor core losses, proximity effects, and skin effects become more important. An inductor with a larger form factor usually gives higher efficiency. The efficiency difference between different inductors can vary from 2% to 10%. For the TPS61087-Q1, inductor values from 3 μH to 6 μH are a good choice with a switching frequency of 1.2 MHz, typically 3.3 μH. At 650 kHz, TI recommends inductors from 6 μH to 13 μH, typically 6.8 μH. See Table 3 for inductor selection. Customers must verify and validate selected components for suitability with their application.
TI recommends that the inductor current ripple is below 35% of the average inductor current. Equation 5 can be used to calculate the inductor value (L).
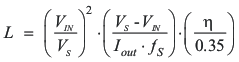
where
- Iout is the maximum output current in the application.
Table 3. Inductor Selection
| INDUCTOR VALUE | TYPICAL DCR | Isat | SUPPLIER | SIZE (L × W × H mm) | COMPONENT CODE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2 MHz | |||||
| 4.2 µH | 23 mΩ | 2.2 A | Sumida | 5.7 × 5.7 × 3 | CDRH5D28 |
| 4.7 µH | 60 mΩ | 2.5 A | Wurth Elektronik | 5.9 × 6.2 × 3.3 | 7447785004 |
| 5 µH | 24 mΩ | 2.9 A | Coilcraft | 7.3 × 7.3 × 4.1 | MSS7341 |
| 5 µH | 23 mΩ | 2.4 A | Sumida | 7 × 7 × 3 | CDRH6D28 |
| 4.6 µH | 38 mΩ | 3.15 A | Sumida | 7.6 × 7.6 × 3 | CDR7D28 |
| 4.7 µH | 33 mΩ | 3.9 A | Wurth Elektronik | 7.3 × 7.3 × 3.2 | 7447789004 |
| 3.3 µH | 30 mΩ | 4.2 A | Wurth Elektronik | 7.3 × 7.3 × 3.2 | 7447789003 |
| 650 kHz | |||||
| 10 µH | 51 mΩ | 2.2 A | Wurth Elektronik | 7.3 × 7.3 × 3.2 | 744778910 |
| 10 µH | 36 mΩ | 2.7 A | Sumida | 8.3 × 8.3 × 3 | CDRH8D28 |
| 6.8 µH | 52 mΩ | 2.9 A | Sumida | 7 × 7 × 2.8 | CDRH6D26HPNP |
| 6.2 µH | 25 mΩ | 3.3 A | Sumida | 8.3 × 8.3 × 6 | CDRH8D58 |
| 10 µH | 80 mΩ | 3.5 A | Coilcraft | 12.95 × 9.4 × 5.08 | DS3316P |
| 10 µH | 29 mΩ | 4 A | Sumida | 8.3 × 8.3 × 4.5 | CDRH8D43 |
| 6.8 µH | 55 mΩ | 4.1 A | Wurth Elektronik | 12.7 × 10 × 4.9 | 74454068 |