SLVSD38C November 2015 – August 2021 TPS61089
PRODMIX
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RNR|11
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
11.2.1 Thermal Considerations
The maximum IC junction temperature should be restricted to 125°C under normal operating conditions. Calculate the maximum allowable dissipation, PD(max), and keep the actual power dissipation less than or equal to PD(max). The maximum-power-dissipation limit is determined using Equation 20.
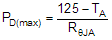
where
- TA is the maximum ambient temperature for the application
- RθJA is the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance given in the Thermal Information table
The TPS61089x comes in a thermally-enhanced VQFN package. The pads underneath the package improve the thermal capabilities of the package. The real junction-to-ambient thermal resistance of the package greatly depends on the PCB type, layout, and pad connection. Using thick PCB copper and soldering the SW pin, VOUT pin, and GND pin to large copper plate enhances the thermal performance. Using more vias connects the ground plate on the top layer and bottom layer around the IC without solder mask also improves the thermal capability.