SLVS927F March 2009 – July 2018 TPS65023-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1 VERSION Register (address: 00h) Read-Only
- 8.6.2 PGOODZ Register (address: 01h) Read-Only
- 8.6.3 MASK Register (address: 02h)
- 8.6.4 REG_CTRL Register (address: 03h)
- 8.6.5 CON_CTRL Register (address: 04h)
- 8.6.6 CON_CTRL2 Register (address: 05h)
- 8.6.7 DEFCORE Register (address: 06h)
- 8.6.8 DEFSLEW Register (address: 07h)
- 8.6.9 LDO_CTRL Register (address: 08h)
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
9.2.2.1 Inductor Selection for the DC-DC Converters
Each of the converters in the TPS65023-Q1 typically uses a 2.2-μH output inductor. Larger or smaller inductor values are used to optimize the performance of the device for specific operation conditions. The selected inductor must be rated for its DC resistance and saturation current. The DC resistance of the inductance influences directly the efficiency of the converter. Therefore, an inductor with lowest DC resistance should be selected for highest efficiency.
For a fast transient response, TI recommends a 2.2-μH inductor in combination with a 22-μF output capacitor.
Equation 4 calculates the maximum inductor current under static load conditions. The saturation current of the inductor should be rated higher than the maximum inductor current as calculated with Equation 4. This is needed because during a heavy load transient the inductor current rises above the value calculated under Equation 4.
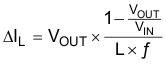
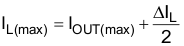
where
- f = Switching frequency (2.25 MHz typical)
- L = Inductor value
- ΔIL = Peak-to-peak inductor ripple current
- ILMAX = Maximum inductor current
The highest inductor current occurs at maximum VIN.
Open-core inductors have a soft saturation characteristic, and they can usually handle higher inductor currents versus a comparable shielded inductor.
A more-conservative approach is to select the inductor current rating just for the maximum switch current of the TPS65023-Q1 (2 A for the VDCDC1 and VDCDC2 converters, and 1.5 A for the VDCDC3 converter). The core material from inductor to inductor differs and has an impact on the efficiency, especially at high switching frequencies.
See Table 12 and the typical applications for possible inductors.
Table 12. Tested Inductors
| DEVICE | INDUCTOR VALUE | TYPE | COMPONENT SUPPLIER |
|---|---|---|---|
| All converters | 2.2 μH | LPS4012-222LMB | Coilcraft |
| 2.2 μH | VLCF4020T-2R2N1R7 | TDK |