SLVS979C October 2009 – May 2018 TPS65720 , TPS65721
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Options
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Battery Charger and Power Path
- 8.3.2 Power-Path Management
- 8.3.3 Battery Charging
- 8.3.4 Thermal Regulation and Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.5 Battery Pack Temperature Monitoring
- 8.3.6 DCDC1 Converter
- 8.3.7 Power Save Mode
- 8.3.8 Short-Circuit Protection
- 8.3.9 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.10 LDO1
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1 CHGSTATUS Register Address: 01h (read only)
- 8.6.2 CHGCONFIG0 Register Address: 02h (read/write)
- 8.6.3 CHGCONFIG1 Register Address: 03h (read/write)
- 8.6.4 CHGCONFIG2 Register Address: 04h (read/write)
- 8.6.5 CHGCONFIG3 Register Address: 05h (read/write)
- 8.6.6 CHGSTATE Register Address: 06h (read only)
- 8.6.7 DEFDCDC1 Register Address: 07h (read/write)
- 8.6.8 LDO_CTRL Register Address: 08h (read/write)
- 8.6.9 CONTROL0 Register Address: 09h (read/write)
- 8.6.10 CONTROL1 Register Address: 0Ah (read/write)
- 8.6.11 GPIO_SSC Register Address: 0Bh (read/write)
- 8.6.12 GPIODIR Register Address: 0Ch (read/write)
- 8.6.13 IRMASK0 Register Address: 0Dh (read/write)
- 8.6.14 IRMASK1 Register Address: 0Eh (read/write)
- 8.6.15 IRMASK2 Register Address: 0Fh (read/write)
- 8.6.16 IR0 Register Address: 10h (read only)
- 8.6.17 IR1 Register Address: 11h (read)
- 8.6.18 IR2 Register Address: 12h (read)
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RSN|32
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RSN|32
Orderable Information
8.3.10.6.2 PB_IN Input
Enables DCDC1 and LDO1 if pulled to GND. Disables DCDC1 and LDO1 if pulled high. There is no internal pull-up resistor, so a resistor is needed externally to SYS. SYS is preferred over BAT because it is powered by either AC or BAT (whichever is higher). If BAT is used, the device may not get a valid HIGH signal if the battery is deeply discharged even when there is voltage at AC.
The input signal is debounced internally by 50 ms. When PB_IN is pulled low, the DCDC1 converter and LDO1 will power up simultaneously. When PB_IN is deasserted, both converters are turned off. To leave the converters on, the HOLD_DCDC1 and HOLD_LDO1 pin need to be asserted high. The HOLD register Bit <CONTROL1:B5> will keep both, DCDC1 and LDO1 enabled if set to 1. For proper operation the PB_IN, HOLD_DCDC1 and HOLD_LDO1 pins must be terminated and must not be left floating.
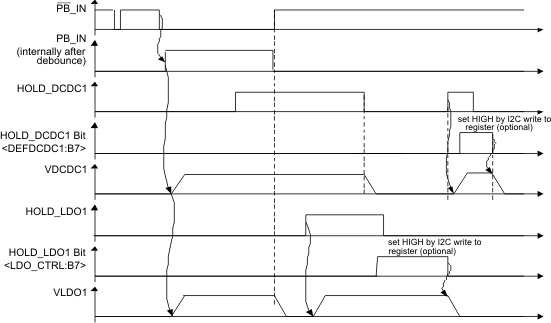 Figure 17. PB_IN Timing
Figure 17. PB_IN Timing