JAJSQZ4B March 2023 – September 2023 AM62A3 , AM62A3-Q1 , AM62A7 , AM62A7-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Device Comparison
-
5 Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 5.1 Pin Diagrams
- 5.2 Pin Attributes
- 5.3
Signal Descriptions
- 14
- 5.3.1 CPSW3G
- 5.3.2 CPTS
- 5.3.3 CSI-2
- 5.3.4 DDRSS
- 5.3.5 DSS
- 5.3.6 ECAP
- 5.3.7 Emulation and Debug
- 5.3.8 EPWM
- 5.3.9 EQEP
- 5.3.10 GPIO
- 5.3.11 GPMC
- 5.3.12 I2C
- 5.3.13 MCAN
- 5.3.14 MCASP
- 5.3.15 MCSPI
- 5.3.16 MDIO
- 5.3.17 MMC
- 5.3.18 OSPI
- 5.3.19 Power Supply
- 5.3.20 Reserved
- 5.3.21 System and Miscellaneous
- 5.3.22 TIMER
- 5.3.23 UART
- 5.3.24 USB
- 5.4 Pin Connectivity Requirements
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings for Devices which are not AEC - Q100 Qualified
- 6.3 ESD Ratings for AEC - Q100 Qualified Devices
- 6.4 Power-On Hours (POH)
- 6.5 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.6 Operating Performance Points
- 6.7 Power Consumption Summary
- 6.8
Electrical
Characteristics
- 6.8.1 I2C Open-Drain, and Fail-Safe (I2C OD FS) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8.2 Fail-Safe Reset (FS RESET) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8.3 High-Frequency Oscillator (HFOSC) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8.4 Low-Frequency Oscillator (LFXOSC) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8.5 SDIO Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8.6 LVCMOS Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8.7 CSI-2 (D-PHY) Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8.8 USB2PHY Electrical Characteristics
- 6.8.9 DDR Electrical Characteristics
- 6.9 VPP Specifications for One-Time Programmable (OTP) eFuses
- 6.10 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 6.11
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 6.11.1 Timing Parameters and Information
- 6.11.2 Power Supply Requirements
- 6.11.3 System Timing
- 6.11.4
Clock Specifications
- 6.11.4.1 Input Clocks / Oscillators
- 6.11.4.2 Output Clocks
- 6.11.4.3 PLLs
- 6.11.4.4 Recommended System Precautions for Clock and Control Signal Transitions
- 6.11.5
Peripherals
- 6.11.5.1 CPSW3G
- 6.11.5.2 CPTS
- 6.11.5.3 CSI-2
- 6.11.5.4 DDRSS
- 6.11.5.5 DSS
- 6.11.5.6 ECAP
- 6.11.5.7 Emulation and Debug
- 6.11.5.8 EPWM
- 6.11.5.9 EQEP
- 6.11.5.10 GPIO
- 6.11.5.11 GPMC
- 6.11.5.12 I2C
- 6.11.5.13 MCAN
- 6.11.5.14 MCASP
- 6.11.5.15 MCSPI
- 6.11.5.16
MMCSD
- 6.11.5.16.1
MMC0 - eMMC/SD/SDIO Interface
- 6.11.5.16.1.1 Legacy SDR Mode
- 6.11.5.16.1.2 High Speed SDR Mode
- 6.11.5.16.1.3 HS200 Mode
- 6.11.5.16.1.4 Default Speed Mode
- 6.11.5.16.1.5 High Speed Mode
- 6.11.5.16.1.6 UHS–I SDR12 Mode
- 6.11.5.16.1.7 UHS–I SDR25 Mode
- 6.11.5.16.1.8 UHS–I SDR50 Mode
- 6.11.5.16.1.9 UHS–I DDR50 Mode
- 6.11.5.16.1.10 UHS–I SDR104 Mode
- 6.11.5.16.2 MMC1/MMC2 - SD/SDIO Interface
- 6.11.5.16.1
MMC0 - eMMC/SD/SDIO Interface
- 6.11.5.17 OSPI
- 6.11.5.18 Timers
- 6.11.5.19 UART
- 6.11.5.20 USB
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Processor Subsystems
- 7.3 Accelerators and Coprocessors
- 7.4 Other Subsystems
- 7.5
Peripherals
- 7.5.1 Gigabit Ethernet Switch (CPSW3G)
- 7.5.2 Camera Serial Interface Receiver (CSI_RX_IF)
- 7.5.3 Display Subsystem (DSS)
- 7.5.4 Enhanced Capture (ECAP)
- 7.5.5 Error Location Module (ELM)
- 7.5.6 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulation (EPWM)
- 7.5.7 Error Signaling Module (ESM)
- 7.5.8 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse (EQEP)
- 7.5.9 General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 7.5.10 General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 7.5.11 Global Timebase Counter (GTC)
- 7.5.12 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 7.5.13 Modular Controller Area Network (MCAN)
- 7.5.14 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (MCASP)
- 7.5.15 Multichannel Serial Peripheral Interface (MCSPI)
- 7.5.16 Multi-Media Card Secure Digital (MMCSD)
- 7.5.17 Octal Serial Peripheral Interface (OSPI)
- 7.5.18 Timers
- 7.5.19 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 7.5.20 Universal Serial Bus Subsystem (USBSS)
-
8 Applications,
Implementation, and Layout
- 8.1 Device Connection and Layout Fundamentals
- 8.2 Peripheral- and Interface-Specific Design Information
- 8.3 Clock Routing Guidelines
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Revision History
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- AMB|484
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
6.11.5.17.1.1 OSPI0 With PHY Data Training
Read and write data valid windows will shift due to variation in process, voltage, temperature, and operating frequency. A data training method may be implemented to dynamically configure optimal read and write timing. Implementing data training enables proper operation across temperature with a specific process, voltage, and frequency operating condition, while achieving a higher operating frequency.
Data transmit and receive timing parameters are not defined for the data training use case since they are dynamically adjusted based on the operating condition.
Table 6-111 defines DLL delays required for OSPI0 with Data Training. Table 6-112, Figure 6-94, Figure 6-95, Table 6-113, Figure 6-96, and Figure 6-97 present timing requirements and switching characteristics for OSPI0 with Data Training.
| MODE | OSPI_PHY_CONFIGURATION_REG BIT FIELD | DELAY VALUE |
|---|---|---|
| Transmit | ||
| All modes | PHY_CONFIG_TX_DLL_DELAY_FLD, | (1) |
| Receive | ||
| All modes | PHY_CONFIG_RX_DLL_DELAY_FLD | (2) |
| NO. | MODE | MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O15 | tsu(D-LBCLK) | Setup time, OSPI0_D[7:0] valid before active OSPI0_DQS edge | DDR with DQS | (1) | ns | |
| O16 | th(LBCLK-D) | Hold time, OSPI0_D[7:0] valid after active OSPI0_DQS edge | DDR with DQS | (1) | ns | |
| O21 | tsu(D-LBCLK) | Setup time, OSPI0_D[7:0] valid before active OSPI0_DQS edge | SDR with External Board Loopback | (1) | ns | |
| O22 | th(LBCLK-D) | Hold time, OSPI0_D[7:0] valid after active OSPI0_DQS edge | SDR with External Board Loopback | (1) | ns | |
| tDVW | Data valid window (O15 + O16) | 1.8V, DDR with DQS | 1.6 | ns | ||
| 3.3V, DDR with DQS | 2.2 | ns | ||||
| Data valid window (O21 + O22) | 1.8V, SDR with External Board Loopback | 2.3 | ns | |||
| 3.3V, SDR with External Board Loopback | 2.9 | ns | ||||
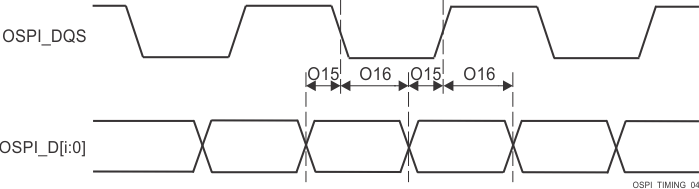 Figure 6-94 OSPI0
Timing Requirements – PHY Data Training, DDR with DQS
Figure 6-94 OSPI0
Timing Requirements – PHY Data Training, DDR with DQS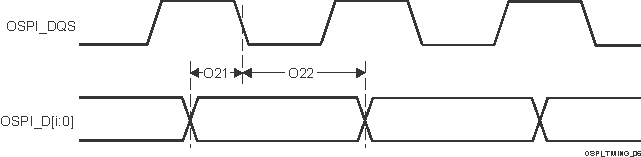 Figure 6-95 OSPI0
Timing Requirements – PHY Data Training, SDR with External Board
Loopback
Figure 6-95 OSPI0
Timing Requirements – PHY Data Training, SDR with External Board
Loopback| NO. | PARAMETER | MODE | MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | tc(CLK) | Cycle time, OSPI0_CLK | 1.8V, DDR | 6.0 | 10 | ns |
| 3.3V, DDR | 7.5 | 10 | ns | |||
| O7 | 1.8V, SDR | 6.0 | 10 | ns | ||
| 3.3V, SDR | 7.5 | 10 | ns | |||
| O2 | tw(CLKL) | Pulse duration, OSPI0_CLK low | DDR | ((0.475P(1)) - 0.3) | ns | |
| O8 | SDR | |||||
| O3 | tw(CLKH) | Pulse duration, OSPI0_CLK high | DDR | ((0.475P(1)) - 0.3) | ns | |
| O9 | SDR | |||||
| O4 | td(CSn-CLK) | Delay time, OSPI0_CSn[3:0] active edge to OSPI0_CLK rising edge | DDR | ((0.475P(1)) + (0.975M(2)R(4)) + (0.04TD(5)) - 1) | ((0.525P(1)) + (1.025M(2)R(4)) + (0.11TD(5)) + 1) | ns |
| O10 | SDR | |||||
| O5 | td(CLK-CSn) | Delay time, OSPI0_CLK rising edge to OSPI0_CSn[3:0] inactive edge | DDR | ((0.475P(1)) + (0.975N(3)R(4)) - (0.04TD(5)) - 1) | ((0.525P(1)) + (1.025N(3)R(4)) - (0.11TD(5)) + 1) | ns |
| O11 | SDR | |||||
| O6 | td(CLK-D) | Delay time, OSPI0_CLK active edge to OSPI0_D[7:0] transition | DDR | (6) | (6) | ns |
| O12 | SDR | |||||
| tDIVW | Data invalid window (O6 Max - Min) | DDR | 1.6 | ns | ||
| Data invalid window (O12 Max - Min) | SDR | |||||
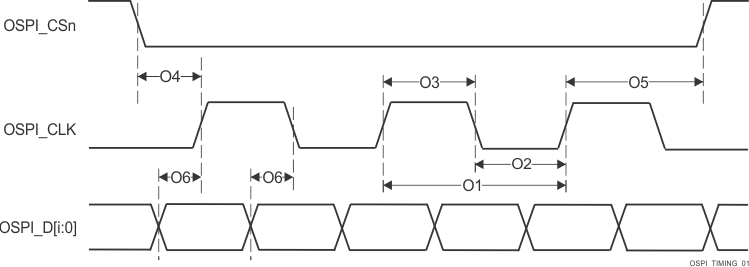 Figure 6-96 OSPI0 Switching Characteristics – PHY DDR Data
Training
Figure 6-96 OSPI0 Switching Characteristics – PHY DDR Data
Training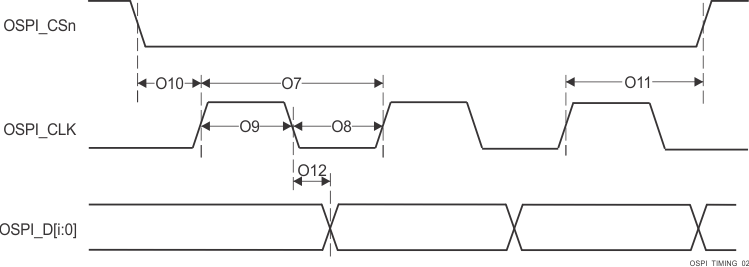 Figure 6-97 OSPI0 Switching Characteristics – PHY SDR Data
Training
Figure 6-97 OSPI0 Switching Characteristics – PHY SDR Data
Training