SLUSB76B February 2013 – May 2015
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Input Voltage Protection
- 8.3.2 Battery Protection
- 8.3.3 DEFAULT Mode
- 8.3.4 USB Friendly Power Up
- 8.3.5 Input Current Limiting at Power Up
- 8.3.6 Factory Mode
- 8.3.7 Spread Spectrum Mode
- 8.3.8 PWM Controller in Charge Mode
- 8.3.9 Battery Charging Process
- 8.3.10 Thermal Regulation and Protection
- 8.3.11 Charge Status Output, STAT Pin
- 8.3.12 Control Bits in Charge Mode
- 8.3.13 Control Pins in Charge Mode
- 8.3.14 Boost Mode Operation
- 8.3.15 High Impedance (Hi-Z) Mode
- 8.3.16 Serial Interface Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Register Maps
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings(1)(2)
over operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage (with respect to PGND(3)) | VBUS; VPMID ≥ VBUS – 0.3 V | –2 | 20 | V | |
| Input voltage (with respect to PGND(3)) | SCL, SDA, OTG, SLRST, CSIN, CSOUT, CD | –0.3 | 7 | V | |
| Output voltage (with respect to PGND(3)) | PMID, STAT | –0.3 | 20 | V | |
| VREF | -0.3 | 7 | V | ||
| SW, BOOT | –0.7 | 20 | V | ||
| Voltage difference between CSIN and CSOUT inputs (V(CSIN) – V(CSOUT)) | ±7 | V | |||
| Voltage difference between BOOT and SW inputs (V(BOOT) – V(SW)) | –0.3 | 7 | V | ||
| Voltage difference between VBUS and PMID inputs (V(VBUS) – V(PMID)) | –7 | 0.7 | V | ||
| Voltage difference between PMID and SW inputs (V(PMID) – V(SW)) | –0.7 | 20 | V | ||
| Output sink | STAT | 10 | 10 | mA | |
| Output current (average) | SW | 1.55(2) | A | ||
| TA | Operating free-air temperature range | –30 | 85 | °C | |
| Tstg | Storage temperature range | –45 | 150 | °C | |
| TJ | Junction temperature | –40 | 125 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. All voltage values are with respect to the network ground terminal unless otherwise noted.
(2) Duty cycle for output current should be less than 50% for 10-year lifetime when output current is above 1.5 A.
(3) All voltages are with respect to PGND if not specified. Currents are positive into, negative out of the specified terminal, if not specified. For thermal limitations and considerations of packages, see Thermal Information.
7.2 ESD Ratings
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001, all pins(1) | 0 | 2000 | V |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101, all pins(2) | 0 | 500 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VBUS | Supply voltage, bq24157S | 4 | 6(1) | V | |
| TJ | Operating junction temperature range | –40 | 125 | °C | |
(1) The inherent switching noise voltage spikes should not exceed the absolute maximum rating on either the BOOST or SW pins. A tight layout minimizes switching noise.
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | bq24157S | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| YFF (20 PINS) | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 85 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 25 | |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 55 | |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 4 | |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 50 | |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | N/A | |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
Circuit of Figure 28, VBUS = 5 V, HZ_MODE = 0, OPA_MODE = 0 (CD = 0), TJ = –40°C to 125°C, TJ = 25°C for typical values (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUT CURRENTS | |||||||
| I(VBUS) | VBUS supply current control | VBUS > VBUS(min), PWM switching | 10 | mA | |||
| VBUS > VBUS(min), PWM not switching | 5 | ||||||
| 0°C < TJ < 85°C, CD = 1 or HZ_MODE = 1 | 15 | 23 | μA | ||||
| Ilgk | Leakage current from battery to VBUS pin | 0°C < TJ < 85°C, V(CSOUT) = 4.2 V, high impedance mode, VBUS = 0 V | 5 | μA | |||
| Battery discharge current in high impedance mode, (CSIN, CSOUT, SW pins) | 0°C < TJ < 85°C, V(CSOUT) = 4.2 V, high impedance mode, V = 0 V, SCL, SDA, OTG = 0 V or 1.8 V | 23 | μA | ||||
| VOLTAGE REGULATION | |||||||
| V(OREG) | Output regulation voltage programable range | Operating in voltage regulation, programmable | 3.5 | 4.44 | V | ||
| Voltage regulation accuracy | TA = 25°C | –0.5% | 0.5% | ||||
| TA = -40°C to 125°C | –1% | 1% | |||||
| CURRENT REGULATION (FAST CHARGE) | |||||||
| IO(CHARGE) | Output charge current programmable range | V(LOWV) ≤ V(CSOUT) < V(OREG), VBUS > V(SLP), R(SNS) = 68 mΩ, LOW_CHG = 0, Programmable |
550 | 1250 | mA | ||
| Low charge current (default after POR in 15 min mode) | VLOWV ≤ VCSOUT < VOREG, VBUS > VSLP, RSNS= 68 mΩ, LOW_CHG = 1, OTG = High |
325 | 350 | mA | |||
| VLOWV ≤ VCSOUT < VOREG, VBUS > VSLP, RSNS= 68 mΩ, LOW_CHG = 0, OTG = High |
550 | 569 | |||||
| Regulation accuracy of the voltage across R(SNS) (for charge current regulation)
V(IREG) = IO(CHARGE) × R(SNS) |
37.4 mV ≤ V(IREG)< 44.2 mV | –3.5% | 3.5% | ||||
| 44.2 mV ≤ V(IREG) | –3% | 3% | |||||
| WEAK BATTERY DETECTION | |||||||
| V(LOWV) | Weak battery voltage threshold programmable range2(2) | Adjustable using I2C control | 3.4 | 3.7 | V | ||
| Weak battery voltage accuracy | –5% | 5% | |||||
| Hysteresis for V(LOWV) | Battery voltage falling | 100 | mV | ||||
| Deglitch time for weak battery threshold | Rising voltage, 2-mV overdrive, tRISE = 100 ns | 30 | ms | ||||
| CD, OTG, AND SLRST PIN LOGIC LEVEL | |||||||
| VIL | Input low threshold level | 0.4 | V | ||||
| VIH | Input high threshold level | 1.3 | V | ||||
| I(bias) | Input bias current | Voltage on control pin is 5 V | 1.0 | µA | |||
| CHARGE TERMINATION DETECTION | |||||||
| I(TERM) | Termination charge current programmable range | V(CSOUT) > V(OREG) – V(RCH), VBUS > V(SLP), R(SNS) = 68 mΩ, programmable |
50 | 400 | mA | ||
| Deglitch time for charge termination | Both rising and falling, 2-mV overdrive, tRISE, tFALL = 100 ns |
30 | ms | ||||
| Regulation accuracy for termination current across R(SNS)
V(IREG_TERM) = IO(TERM) × R(SNS) |
3.4 mV ≤ V(IREG_TERM) ≤ 6.8 mV | –15% | 15% | ||||
| 6.8 mV < V(IREG_TERM) ≤ 17 mV | –10% | 10% | |||||
| 17 mV < V(IREG_TERM) ≤ 27.2 mV | –5.5% | 5.5% | |||||
| BAD ADAPTOR DETECTION | |||||||
| VIN(min) | Input voltage lower limit | Bad adaptor detection | 3.6 | 3.8 | 4.0 | V | |
| Deglitch time for VBUS rising above VIN(min) | Rising voltage, 2-mV overdrive, tRISE = 100 ns | 30 | ms | ||||
| Hysteresis for VIN(min) | Input voltage rising | 100 | 200 | mV | |||
| ISHORT | Current source to GND | During bad adaptor detection | 20 | 30 | 40 | mA | |
| tINT | Detection Interval | Input power source detection | 2 | s | |||
| INPUT BASED DYNAMIC POWER MANAGEMENT | |||||||
| VIN_DPM | Input Voltage DPM threshold programmable range | 4.2 | 4.76 | V | |||
| VIN DPM threshold accuracy | –3% | 1% | |||||
| INPUT CURRENT LIMITING | |||||||
| IIN_LIMIT | Input current limiting threshold | IIN = 100 mA | TJ = 0°C to 125°C | 88 | 93 | 98 | mA |
| TJ = –40°C to 125°C | 86 | 93 | 98 | ||||
| IIN = 500 mA | TJ = 0°C to 125°C | 450 | 475 | 500 | mA | ||
| TJ = –40°C to 125°C | 440 | 475 | 500 | ||||
| VREF BIAS REGULATOR | |||||||
| VREF | Internal bias regulator voltage | VBUS > VIN(min) or V(CSOUT) > VBUS(min), I(VREF) = 1 mA, C(VREF) = 1 μF |
2 | 6.5 | V | ||
| VREF output short current limit | 30 | mA | |||||
| BATTERY RECHARGE THRESHOLD | |||||||
| V(RCH) | Recharge threshold voltage | Below V(OREG) | 100 | 120 | 150 | mV | |
| Deglitch time | V(SCOUT) decreasing below threshold, tFALL = 100 ns, 10-mV overdrive |
130 | ms | ||||
| STAT OUTPUTS | |||||||
| VOL(STAT) | Low-level output saturation voltage, STAT pin | IO = 10 mA, sink current | 0.55 | V | |||
| High-level leakage current for STAT | Voltage on STAT pin is 5 V | 1 | μA | ||||
| I2C BUS LOGIC LEVELS AND TIMING CHARACTERISTICS | |||||||
| VOL | Output low threshold level | IO = 10 mA, sink current | 0.4 | V | |||
| VIL | Input low threshold level | V(pullup) = 1.8 V, SDA and SCL | 0.4 | V | |||
| VIH | Input high threshold level | V(pullup) = 1.8 V, SDA and SCL | 1.2 | V | |||
| I(BIAS) | Input bias current | V(pullup) = 1.8 V, SDA and SCL | 1 | μA | |||
| f(SCL) | SCL clock frequency | 3.4 | MHz | ||||
| BATTERY DETECTION | |||||||
| I(DETECT) | Battery detection current before charge done (sink current) (1) | Begins after termination detected, V(CSOUT) ≤ V(OREG) |
–0.5 | mA | |||
| tDETECT | Battery detection time | 262 | ms | ||||
| SLEEP COMPARATOR | |||||||
| V(SLP) | Sleep-mode entry threshold, VBUS – VCSOUT |
2.3 V ≤ V(CSOUT) ≤ V(OREG), VBUS falling | 0 | 40 | 100 | mV | |
| V(SLP_EXIT) | Sleep-mode exit hysteresis | 2.3 V ≤ V(CSOUT) ≤ V(OREG) | 140 | 200 | 260 | mV | |
| Deglitch time for VBUS rising above V(SLP) + V(SLP_EXIT) | Rising voltage, 2-mV overdrive, tRISE = 100 ns | 30 | ms | ||||
| UNDERVOLTAGE LOCKOUT (UVLO) | |||||||
| UVLO | IC active threshold voltage | VBUS rising – exits UVLO | 3.05 | 3.3 | 3.55 | V | |
| UVLO(HYS) | IC active hysteresis | VBUS falling below UVLO – enters UVLO | 120 | 150 | mV | ||
| Power up delay | 140 | ms | |||||
| PWM | |||||||
| Voltage from BOOT pin to SW pin | During charge or boost operation | 6.5 | V | ||||
| Internal top reverse blocking MOSFET on-resistance | IIN(LIMIT) = 500 mA, measured from VBUS to PMID | 180 | 250 | mΩ | |||
| Internal top N-channel switching MOSFET on-resistance | Measured from PMID to SW, VBOOT – VSW= 4 V |
120 | 250 | ||||
| Internal bottom N-channel MOSFET on-resistance | Measured from SW to PGND | 110 | 210 | ||||
| f(OSC) | Oscillator frequency | 3.0 | MHz | ||||
| Frequency accuracy | –10% | 10% | |||||
| D(MAX) | Maximum duty cycle | 99.5% | |||||
| D(MIN) | Minimum duty cycle | 0 | |||||
| Synchronous mode to non-synchronous mode transition current threshold(1) | Low-side MOSFET cycle-by-cycle current sensing | 100 | mA | ||||
| CHARGE MODE PROTECTION | |||||||
| VOVP_IN_USB | Input VBUS OVP threshold voltage | VBUS threshold to turn off converter during charge | 6.3 | 6.5 | 6.7 | V | |
| VOVP | Output OVP threshold voltage | V(CSOUT) threshold over V(OREG) to turn off charger during charge | 110 | 117 | 121 | %VOREG | |
| V(OVP) hysteresis | Lower limit for V(CSOUT) falling from above V(OVP) | 11 | |||||
| ILIMIT | Cycle-by-cycle current limit for charge | Charge mode operation | 1.8 | 2.4 | 3.0 | A | |
| VSHORT | Trickle to fast charge threshold | V(CSOUT) rising | 2.0 | 2.1 | 2.2 | V | |
| VSHORT hysteresis | V(CSOUT) falling below VSHORT | 100 | mV | ||||
| ISHORT | Trickle charge charging current | V(CSOUT) ≤ VSHORT) | 20 | 30 | 40 | mA | |
| BOOST MODE OPERATION FOR VBUS (OPA_MODE = 1, HZ_MODE = 0) | |||||||
| VBUS_B | Boost output voltage (to VBUS pin) | 2.5 V < V(CSOUT) < 4.5 V | 5.05 | V | |||
| Boost output voltage accuracy | Including line and load regulation | –3% | 3% | ||||
| IBO | Maximum output current for boost | VBUS_B = 5.05 V, 3.3 V < V(CSOUT) < 4.5 V, TJ= 0°C – 125°C |
350 | mA | |||
| IBLIMIT | Cycle by cycle current limit for boost | VBUS_B = 5.05 V, 2.5 V < V(CSOUT) < 4.5 V | 1.0 | A | |||
| VBUSOVP | Overvoltage protection threshold for boost (VBUS pin) |
Threshold over VBUS to turn off converter during boost | 5.8 | 6.0 | 6.2 | V | |
| VBUSOVP hysteresis | VBUS falling from above VBUSOVP | 162 | mV | ||||
| VBATMAX | Maximum battery voltage for boost (CSOUT pin) |
V(CSOUT) rising edge during boost | 4.75 | 4.9 | 5.05 | V | |
| VBATMAX hysteresis | V(CSOUT) falling from above VBATMAX | 200 | mV | ||||
| VBATMIN | Minimum battery voltage for boost (CSOUT pin) |
During boosting | 2.5 | V | |||
| Before boost starts | 2.9 | 3.05 | V | ||||
| Boost output resistance at high-impedance mode (from VBUS to PGND) | CD = 1 or HZ_MODE = 1 | 217 | kΩ | ||||
| PROTECTION | |||||||
| TSHTDWN) | Thermal trip | 165 | °C | ||||
| Thermal hysteresis | 10 | ||||||
| TCF | Thermal regulation threshold | Charge current begins to reduce | 120 | ||||
(1) Bottom N-channel FET always turns on for approximately 30 ns, and then turns off if current is too low.
(2) While in DEFAULT mode, if a battery that is charged to a voltage higher than this voltage is inserted, the charger enters Hi-Z mode and awaits I2C commands.
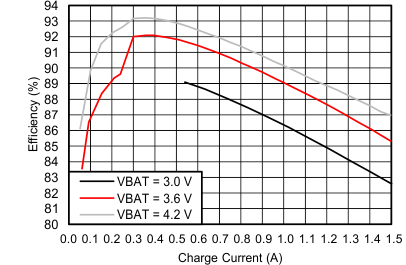
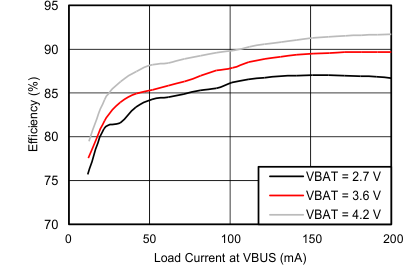
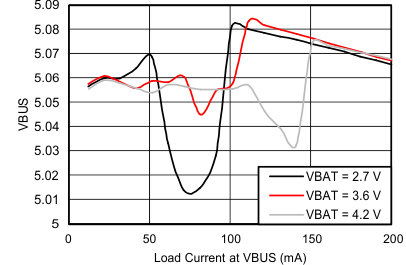
7.6 Typical Performance Characteristics
Using circuit shown in Figure 28, TA = 25°C, unless otherwise specified.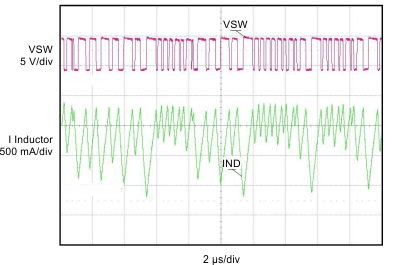
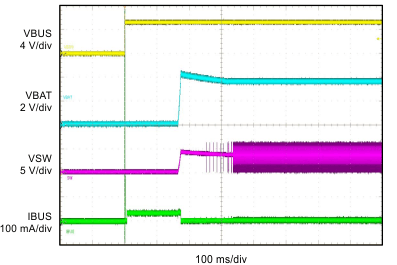
| VBUS = 5 V | VBAT = 3.5 V |
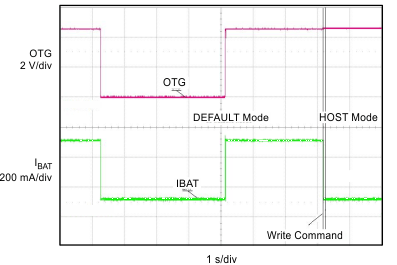
| OTG Control, DEFAULT Mode: VBUS = 5 V, VBAT = 3.1 V, | ||
| IIN_limit = 100 and 500 mA | ||
| I2C Control, HOST Mode: IIN_limit = 100 mA |
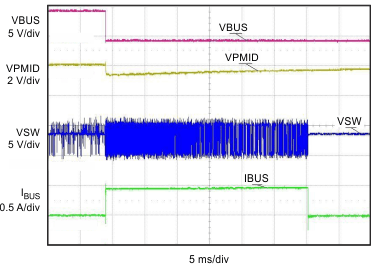
| VBUS = 5.05 V | VBAT = 3.5 V | |
| ILOAD (at VBUS) = 5 to 450 mA | ||
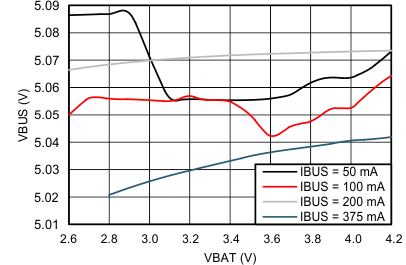
| VBUS = 5.05 V | VBAT = 3.5 V | IBUS = 0 to 217 mA |
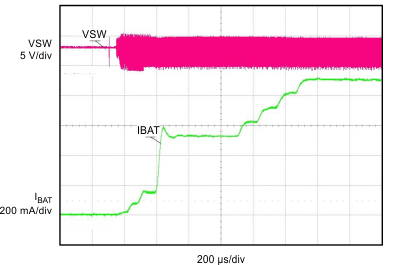
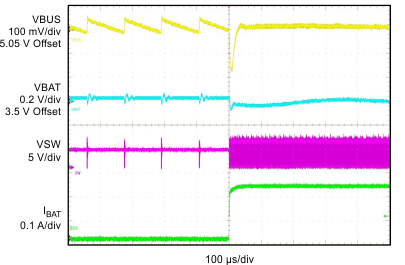
| VIN = 5 V | VBAT = 3.2 V | ICHG = 950 mA |
No Input Current Limit
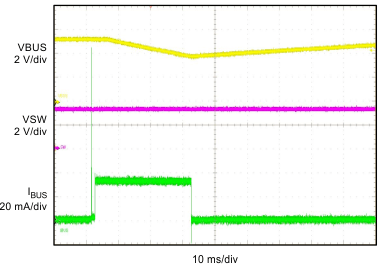
| VBUS = 5 V at 8 mA | VBAT = 3.2 V | IIN_limit = 100 mA |
| ICHG = 550 mA |
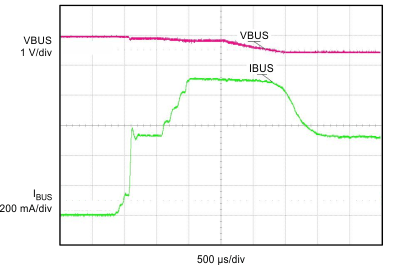
| VBUS = 5 V at 500 mA | VBAT = 3.5 V | ICHG = 1550 mA |
| VIN_DPM = 4.52 V | ||
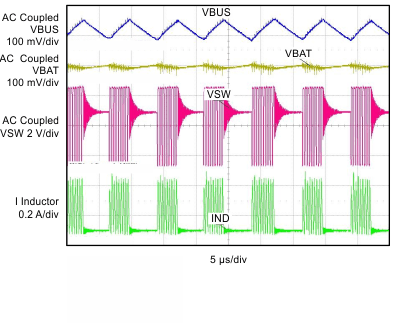
| VBUS = 5.05 V | VBAT = 3.5 V | IBUS = 42 mA |
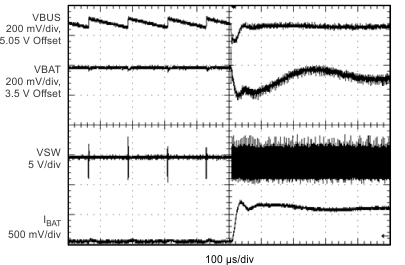
| VBUS = 5.05 V | VBAT = 3.5 V | IBUS = 0 to 360 mA |
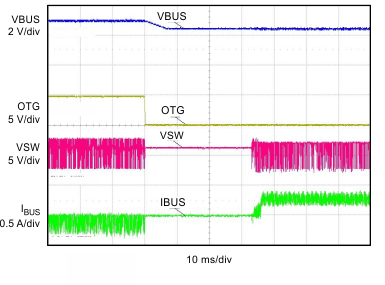
| VBUS = 4.5 V (Charge Mode) | VBUS = 5.1 V (Boost Mode) | |
| VBAT = 3.5 V, IIN_LIM = 500 mA, (HOST Mode) | ||
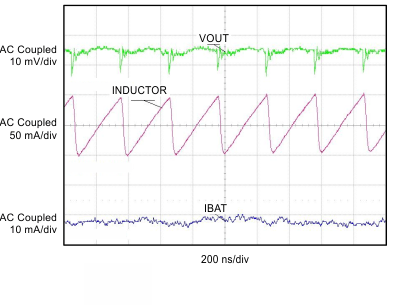
| ICHG = 1.2 A | ||