SLUSBS8B December 2013 – November 2019 BQ40Z50
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics: Supply Current
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics: Power Supply Control
- 7.7 Electrical Characteristics: AFE Power-On Reset
- 7.8 Electrical Characteristics: AFE Watchdog Reset and Wake Timer
- 7.9 Electrical Characteristics: Current Wake Comparator
- 7.10 Electrical Characteristics: VC1, VC2, VC3, VC4, BAT, PACK
- 7.11 Electrical Characteristics: SMBD, SMBC
- 7.12 Electrical Characteristics: PRES, BTP_INT, DISP
- 7.13 Electrical Characteristics: LEDCNTLA, LEDCNTLB, LEDCNTLC
- 7.14 Electrical Characteristics: Coulomb Counter
- 7.15 Electrical Characteristics: CC Digital Filter
- 7.16 Electrical Characteristics: ADC
- 7.17 Electrical Characteristics: ADC Digital Filter
- 7.18 Electrical Characteristics: CHG, DSG FET Drive
- 7.19 Electrical Characteristics: PCHG FET Drive
- 7.20 Electrical Characteristics: FUSE Drive
- 7.21 Electrical Characteristics: Internal Temperature Sensor
- 7.22 Electrical Characteristics: TS1, TS2, TS3, TS4
- 7.23 Electrical Characteristics: PTC, PTCEN
- 7.24 Electrical Characteristics: Internal 1.8-V LDO
- 7.25 Electrical Characteristics: High-Frequency Oscillator
- 7.26 Electrical Characteristics: Low-Frequency Oscillator
- 7.27 Electrical Characteristics: Voltage Reference 1
- 7.28 Electrical Characteristics: Voltage Reference 2
- 7.29 Electrical Characteristics: Instruction Flash
- 7.30 Electrical Characteristics: Data Flash
- 7.31 Electrical Characteristics: OCD, SCC, SCD1, SCD2 Current Protection Thresholds
- 7.32 Timing Requirements: OCD, SCC, SCD1, SCD2 Current Protection Timing
- 7.33 Timing Requirements: SMBus
- 7.34 Timing Requirements: SMBus XL
- 7.35 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Primary (1st Level) Safety Features
- 8.3.2 Secondary (2nd Level) Safety Features
- 8.3.3 Charge Control Features
- 8.3.4 Gas Gauging
- 8.3.5 Configuration
- 8.3.6 Battery Parameter Measurements
- 8.3.7 Battery Trip Point (BTP)
- 8.3.8 Lifetime Data Logging Features
- 8.3.9 Authentication
- 8.3.10 LED Display
- 8.3.11 Voltage
- 8.3.12 Current
- 8.3.13 Temperature
- 8.3.14 Communications
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Applications and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RSM|32
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RSM|32
発注情報
9.2.2.3.3 PACK and FET Control
The PACK and VCC inputs provide power to the BQ40Z50 from the charger. The PACK input also provides a method to measure and detect the presence of a charger. The PACK input uses a 100-Ω resistor; whereas, the VCC input uses a diode to guard against input transients and prevents mis-operation of the date driver during short-circuit events.
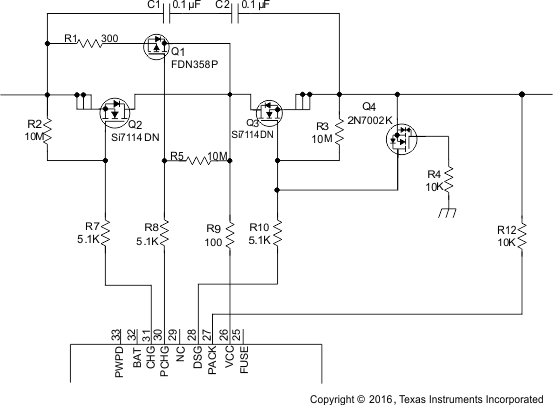 Figure 33. BQ40Z50 PACK and FET Control
Figure 33. BQ40Z50 PACK and FET Control The N-channel charge and discharge FETs are controlled with 5.1-kΩ series gate resistors, which provide a switching time constant of a few microseconds. The 10-MΩ resistors ensure that the FETs are off in the event of an open connection to the FET drivers. Q4 is provided to protect the discharge FET (Q3) in the event of a reverse-connected charger. Without Q4, Q3 can be driven into its linear region and suffer severe damage if the PACK+ input becomes slightly negative.
Q4 turns on in that case to protect Q3 by shorting its gate to source. To use the simple ground gate circuit, the FET must have a low gate turn-on threshold. If it is desired to use a more standard device, such as the 2N7002 as the reference schematic, the gate should be biased up to 3.3 V with a high-value resistor. The BQ40Z50 device has the capability to provide a current-limited charging path typically used for low battery voltage or low temperature charging. The BQ40Z50 device uses an external P-channel, pre-charge FET controlled by PCHG.