SCAS886E August 2009 – December 2015 CDCLVP1212
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics: LVCMOS Input
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics: Differential Input
- 7.7 Electrical Characteristics: LVPECL Output, At VCC = 2.375 V to 2.625 V
- 7.8 Electrical Characteristics: LVPECL Output, at VCC = 3.0 V to 3.6 V
- 7.9 Pin Characteristics
- 7.10 Timing Requirements
- 7.11 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RHA|40
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- RHA|40
発注情報
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted) (1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage range(2) | –0.5 | 4.6 | V |
| VIN | Input voltage range (3) | –0.5 | VCC + 0.5 | V |
| VOUT | Output voltage range (3) | –0.5 | VCC + 0.5 | V |
| IIN | Input current | 20 | mA | |
| IOUT | Output current | 50 | mA | |
| TA | Specified free-air temperature range (no airflow) | –40 | 85 | °C |
| Tstg | Storage temperature range | –65 | 150 | °C |
| TJ | Maximum junction temperature | 125 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All supply voltages must be supplied simultaneously.
(3) The input and output negative voltage ratings may be exceeded if the input and output clamp-current ratings are observed.
7.2 ESD Ratings
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD)(1) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001, all pins(2) | 2000 | V | |
(1) Electrostatic discharge (ESD) to measure device sensitivity and immunity to damage caused by assembly line electrostatic discharges in to the device.
(2) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage | 2.375 | 2.50/3.30 | 3.60 | V | |
| TA | Ambient temperature | –40 | 85 | °C | ||
| TPCB | PCB temperature (measured at thermal pad) | 105 | °C | |||
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1)(2)(3) | VALUE | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RθJA | Thermal resistance, junction-to-ambient | 0 LFM | 36.1 (5) | °C/W |
| 150 LFM | 30.2 (5) | |||
| 400 LFM | 28.2 (5) | |||
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 23.7 | °C/W | |
| RθJP(4) | Thermal resistance, junction-to-pad | 3.58 | °C/W | |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.5 | °C/W | |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 10.0 | °C/W | |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 3.8 | °C/W | |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the IC Package Thermal Metrics application report (SPRA953).
(2) The package thermal resistance is calculated in accordance with JESD 51 and JEDEC 2S2P (high-K board).
(3) Connected to GND with 16 thermal vias (0.3-mm diameter).
(4) θJP (junction-to-pad) is used for the QFN package, because the primary heat flow is from the junction to the GND pad of the QFN package.
(5) 4 x 4 vias on Pad
7.5 Electrical Characteristics: LVCMOS Input
at VCC = 2.375 V to 3.6 V and TA = –40°C to 85°C and TPCB ≤ 105°C (unless otherwise noted) (1)7.6 Electrical Characteristics: Differential Input
at VCC = 2.375 V to 3.6 V and TA = –40°C to 85°C and TPCB ≤ 105°C (unless otherwise noted)(1)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fIN | Input frequency | Clock input | 2000 | MHz | ||
| VIN, DIFF, PP | Differential input peak-peak voltage | fIN ≤ 1.5 GHz | 0.1 | 1.5 | V | |
| 1.5 GHz ≤ fIN ≤ 2 GHz | 0.2 | 1.5 | V | |||
| VICM | Input common-mode level | 1.0 | VCC – 0.3 | V | ||
| IIH | Input high current | VCC = 3.6 V, VIH = 3.6 V | 40 | μA | ||
| IIL | Input low current | VCC = 3.6 V, VIL = 0 V | –40 | μA | ||
| ΔV/ΔT | Input edge rate | 20% to 80% | 1.5 | V/ns | ||
| ICAP | Input capacitance | 5 | pF |
7.7 Electrical Characteristics: LVPECL Output, At VCC = 2.375 V to 2.625 V
TA = –40°C to 85°C and TPCB ≤ 105°C (unless otherwise noted) (1)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOH | Output high voltage | TA ≤ 85°C | VCC – 1.26 | VCC – 0.9 | V | |
| TPCB ≤ 105°C | VCC -–1.26 | VCC – 0.83 | ||||
| VOL | Output low voltage | TA ≤ 85°C | VCC – 1.7 | VCC – 1.3 | V | |
| TPCB ≤ 105°C | VCC – 1.7 | VCC – 1.25 | ||||
| VOUT, DIFF, PP | Differential output peak-peak voltage | fIN ≤ 2 GHz | 0.5 | 1.35 | V | |
| fIN = 125 MHz, 312.5 MHz | 1.15 | |||||
| VAC_REF | Input bias voltage(2) | IAC_REF = 2 mA | VCC – 1.6 | VCC – 1.1 | V | |
| tPD | Propagation delay | VIN, DIFF, PP = 0.1 V | 550 | ps | ||
| VIN, DIFF, PP = 0.3 V | 550 | ps | ||||
| tSK,PP | Part-to-part skew | 150 | ps | |||
| tSK,O | Output skew | 25 | ps | |||
| tSK,P | Pulse skew (with 50% duty cycle input) | Crossing-point-to-crossing-point distortion, fOUT = 100 MHz | –50 | 50 | ps | |
| tRJIT | Random additive jitter (with 50% duty cycle input)(7) | fOUT = 100 MHz, VIN,SE = VCC, Vth = 1.25 V, 10 kHz to 20 MHz | 0.11 | ps, RMS | ||
| fOUT = 100 MHz, VIN,SE = 0.9 V, Vth = 1.1 V, 10 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.128 | ps, RMS | ||||
| fOUT = 2 GHz, VIN,DIFF,PP = 0.2 V, VICM = 1 V, 10 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.053 | ps, RMS | ||||
| fOUT = 100 MHz, VIN,DIFF,PP = 0.15 V, VICM = 1 V, 10 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.093 | ps, RMS | ||||
| fOUT = 100 MHz, VIN,DIFF,PP = 1 V, VICM = 1 V, 10 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.092 | ps, RMS | ||||
| fOUT = 122.88 MHz,(3)(6)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 12 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.057 | 0.088 | ps, RMS | |||
| fOUT = 122.88 MHz,(3)(6)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 10 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.057 | 0.088 | ps, RMS | |||
| fOUT = 122.88 MHz,(3)(6)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 1 kHz to 40 MHz |
0.086 | 0.121 | ps, RMS | |||
| fOUT = 156.25 MHz,(6)(4)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 12 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.048 | 0.071 | ps, RMS | |||
| fOUT = 156.25 MHz,(6)(4)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 10 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.048 | 0.071 | ps, RMS | |||
| fOUT = 156.25 MHz,(6)(4)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 1 kHz to 40 MHz |
0.068 | 0.097 | ps, RMS | |||
| fOUT = 312.5 MHz,(6)(5)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 12 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.030 | 0.048 | ps, RMS | |||
| fOUT = 312.5 MHz,(6)(5)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 10 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.030 | 0.048 | ps, RMS | |||
| fOUT = 312.5 MHz,(6)(5)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 1 kHz to 40 MHz |
0.045 | 0.068 | ps, RMS | |||
| tR/tF | Output rise/fall time | 20% to 80% | 200 | ps | ||
| IEE | Supply internal current | Outputs unterminated TA ≤ 85°C |
88 | mA | ||
| Outputs unterminated TPCB ≤ 105°C |
89 | |||||
| ICC | Output and internal supply current | All outputs terminated, 50 Ω to VCC – 2 TA ≤ 85°C |
468 | mA | ||
| All outputs terminated, 50 Ω to VCC – 2 TPCB ≤ 105°C |
516 | |||||
(2) Internally generated bias voltage (VAC_REF) is for 3.3 V operation only. It is recommended to apply externally generated bias voltage for V CC < 3.0 V.
(3) Input source: 122.88-MHz Rohde & Schwarz SMA100A Signal Generator.
(4) Input source: 156.25-MHz Rohde & Schwarz SMA100A Signal Generator.
(5) Input source: 312.5-MHz Rohde & Schwarz SMA100A Signal Generator.
(6) Input source RMS Jitter (tRJIT_IN) and Total RMS Jitter (tRJIT_OUT) measured using Agilent E5052 Phase Noise Analyzer. Buffer device random additive jitter computed as: tRJIT = SQRT[(tRJIT_OUT)2 - (tRJIT_IN)2].
(7) Parameter is specified by characterization. Not tested in production.
7.8 Electrical Characteristics: LVPECL Output, at VCC = 3.0 V to 3.6 V
TA = –40°C to 85°C and TPCB ≤ 105°C (unless otherwise noted) (1)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOH | Output high voltage | TA ≤ 85°C | VCC – 1.26 | VCC – 0.9 | V | |
| TPCB ≤ 105°C | VCC – 1.26 | VCC – 0.85 | ||||
| VOL | Output low voltage | TA ≤ 85°C | VCC – 1.7 | VCC – 1.3 | V | |
| TPCB ≤ 105°C | VCC – 1.7 | VCC – 1.3 | ||||
| VOUT, DIFF, PP | Differential output peak-peak voltage | fIN ≤ 2 GHz | 0.65 | 1.35 | V | |
| VAC_REF | Input bias voltage | IAC_REF = 2 mA | VCC – 1.6 | VCC – 1.1 | V | |
| tPD | Propagation delay | VIN, DIFF, PP = 0.1 V | 550 | ps | ||
| VIN, DIFF, PP = 0.3 V | 550 | ps | ||||
| tSK,PP | Part-to-part skew | 150 | ps | |||
| tSK,O | Output skew | 25 | ps | |||
| tSK,P | Pulse skew (with 50% duty cycle input) | Crossing-point-to-crossing-point distortion, fOUT = 100 MHz | –50 | 50 | ps | |
| tRJIT | Random additive jitter (with 50% duty cycle input)(6) | fOUT = 100 MHz, VIN,SE = VCC, Vth = 1.65 V, 10 kHz to 20 MHz | 0.101 | ps, RMS | ||
| fOUT = 100 MHz, VIN,SE = 0.9 V, Vth = 1.1 V, 10 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.130 | ps, RMS | ||||
| fOUT = 2 GHz, VIN,DIFF,PP = 0.2 V, VICM = 1 V, 10 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.069 | ps, RMS | ||||
| fOUT = 100 MHz, VIN,DIFF,PP = 0.15 V, VICM = 1 V, 10 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.094 | ps, RMS | ||||
| fOUT = 100 MHz, VIN,DIFF,PP = 1 V, VICM = 1 V, 10 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.094 | ps, RMS | ||||
| fOUT = 122.88 MHz,(2)(5)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 12 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.057 | ps, RMS | ||||
| fOUT = 122.88 MHz,(2)(5)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 10 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.057 | ps, RMS | ||||
| fOUT= 122.88 MHz,(2)(5)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 1 kHz to 40 MHz |
0.086 | ps, RMS | ||||
| fOUT = 156.25 MHz,(5)(3)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 12 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.048 | ps, RMS | ||||
| fOUT = 156.25 MHz,(5)(3)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 10 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.048 | ps, RMS | ||||
| fOUT = 156.25 MHz,(5)(3)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 1 kHz to 40 MHz |
0.068 | ps, RMS | ||||
| fOUT = 312.5 MHz,(5)(4)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 12 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.030 | ps, RMS | ||||
| fOUT = 312.5 MHz,(5)(4)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 10 kHz to 20 MHz |
0.030 | ps, RMS | ||||
| fOUT = 312.5 MHz,(5)(4)
Square Wave, VIN-PP = 1 V, 1 kHz to 40 MHz |
0.045 | ps, RMS | ||||
| tR/tF | Output rise/fall time | 20% to 80% | 200 | ps | ||
| IEE | Supply internal current | Outputs unterminated TA ≤ 85°C |
88 | mA | ||
| TPCB ≤ 105°C | 89 | |||||
| ICC | Output and internal supply current | All outputs terminated, 50 Ω to VCC – 2 TA ≤ 85°C |
468 | mA | ||
| All outputs terminated, 50 Ω to VCC – 2 TPCB ≤ 105°C |
516 | |||||
(2) Input source: 122.88-MHz Rohde & Schwarz SMA100A Signal Generator.
(3) Input source: 156.25-MHz Rohde & Schwarz SMA100A Signal Generator.
(4) Input source: 312.5-MHz Rohde & Schwarz SMA100A Signal Generator.
(5) Input source RMS Jitter (tRJIT_IN) and Total RMS Jitter (tRJIT_OUT) measured using Agilent E5052 Phase Noise Analyzer. Buffer device random additive jitter computed as: tRJIT = SQRT[(tRJIT_OUT)2 - (tRJIT_IN)2].
(6) Parameter is specified by characterization. Not tested in production.
7.9 Pin Characteristics
| PARAMETER | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPULLDOWN | Input pulldown resistor | 150 | kΩ | ||
7.10 Timing Requirements
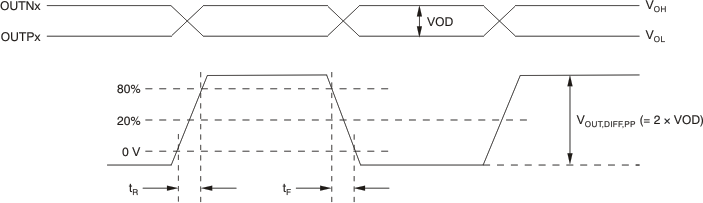 Figure 1. Output Voltage and Rise/Fall Time
Figure 1. Output Voltage and Rise/Fall Time
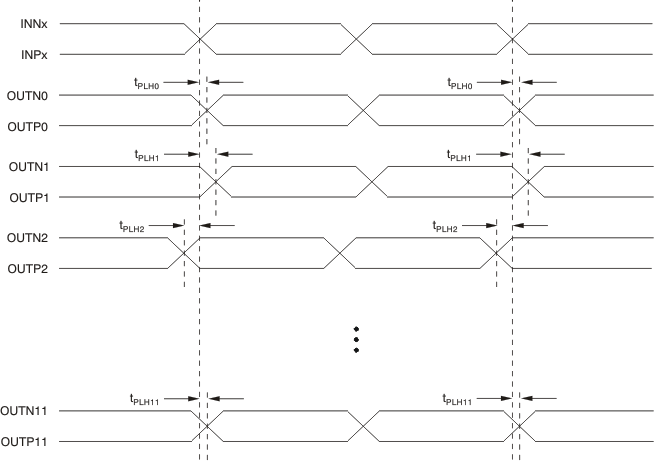
1. Output skew is calculated as the greater of the following: As the difference between the fastest and the slowest tPLHn (n = 0, 1, 2....11), or as the difference between the fastest and the slowest tPHLn (n = 0, 1, 2....11).
2. Part-to-part skew is calculated as the greater of the following: As the difference between the fastest and the slowest tPLHn (n = 0, 1, 2....11) across multiple devices, or the difference between the fastest and the slowest tPHLn (n = 0, 1, 2....11) across multiple devices.
Figure 2. Output and Part-To-Part Skew
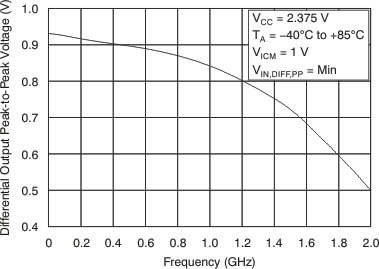
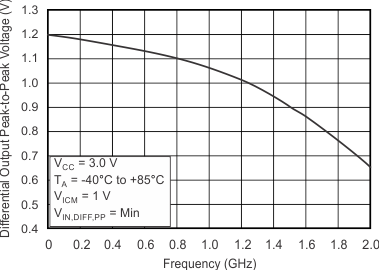
7.11 Typical Characteristics
at TA = –40°C to 85°C (unless otherwise noted)