DLPS031C December 2013 – August 2015 DLPC6401
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics (Normal Mode)
- 6.7 System Oscillators Timing Requirements
- 6.8 Test and Reset Timing Requirements
- 6.9 JTAG Interface: I/O Boundary Scan Application Timing Requirements
- 6.10 Port 1 Input Pixel Interface Timing Requirements
- 6.11 Port 2 Input Pixel Interface (FPD-Link Compatible LVDS Input) Timing Requirements
- 6.12 Synchronous Serial Port (SSP) Interface Timing Requirements
- 6.13 Programmable Output Clocks Switching Characteristics
- 6.14 Synchronous Serial Port (SSP) Interface Switching Characteristics
- 6.15 JTAG Interface: I/O Boundary Scan Application Switching Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.4.6 FPD-Link Input LVDS System Power
The DLPC6401 device supports an FPD-Link compatible, LVDS input for an additional method of inputting video or graphics data for display. This interface has some special ASIC power considerations that are separate from the other ASIC 1.2- or 3.3-V power rails. Figure 17 shows a FPD-Link 1.2-V power pin (VDD12_FPD) configuration example.
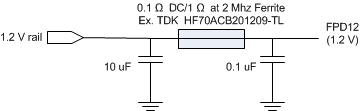 Figure 17. FPD-Link
Figure 17. FPD-Link
In addition, TI recommends to place 0.1-µF low equivalent series resistor (ESR) capacitors to ground as close to the FPD-Link lower pins of the ASIC as possible. FPD-Link 3.3-V power pins (FPD33) should also use external capacitors in the same manner as for VDD12_FPD pins.
When FPD-Link is not used, the user can omit the previously mentioned filtering. However, the corresponding voltages must still be provided to avoid potential long-term reliability issues.