JAJSR90 September 2023 LMQ644A2-Q1
PRODMIX
- 1
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Input Voltage Range (VIN)
- 8.3.2 Enable EN Pin and Use as VIN UVLO
- 8.3.3 Output Voltage Selection and Soft Start
- 8.3.4 SYNC Allows Clock Synchronization and Mode Selection
- 8.3.5 Clock Locking
- 8.3.6 Adjustable Switching Frequency
- 8.3.7 Power-Good Output Voltage Monitoring
- 8.3.8 Internal LDO, VCC UVLO, and BIAS Input
- 8.3.9 Bootstrap Voltage and VCBOOT-UVLO (CB1 and CB2 Pin)
- 8.3.10 CONFIG Device Configuration Pin
- 8.3.11 Spread Spectrum
- 8.3.12 Soft Start and Recovery From Dropout
- 8.3.13 Overcurrent and Short-Circuit Protection
- 8.3.14 Hiccup
- 8.3.15 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Choosing the Switching Frequency
- 9.2.2.2 Setting the Output Voltage
- 9.2.2.3 Inductor Selection
- 9.2.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.5 Input Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.6 BOOT Capacitor
- 9.2.2.7 VCC
- 9.2.2.8 CFF and RFF Selection
- 9.2.2.9 SYNCHRONIZATION AND MODE
- 9.2.2.10 External UVLO
- 9.2.2.11 Typical Thermal Performance
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 9.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 9.4 Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.4.3.6 Recovery from Dropout
In some applications, input voltage can drop below the desired output voltage then recover to a higher value suddenly. With most regulators, the sudden increase in input voltage results in output voltage rising at a rate limited only by current limit until regulation is achieved. As input voltage reaches the desired output voltage, there is overshoot due to wind up in the control loop. This overshoot can be large in applications that have small output capacitors and light loads. Also, large inrush currents can cause large fluctuations on the input line after the regulator starts regulating the output voltage. This typically requires less current than during this initial inrush.
The LMQ644xx greatly reduces inrush current and overshoot. This is done by engaging the soft-start circuit whenever the input voltage suddenly rises, after dipping low enough to cause the output voltage to droop. To prevent this feature from accidentally engaging, output voltage must fall more than 1% to engage this feature. Also, this feature engages only if operating in dropout or current limit, preventing interference with normal transient response but allowing several percent overshoot while engaging. If output voltage is very close to its desired level, overshoot is reduced by inductor current not having time to rise to a high level before regulation starts.
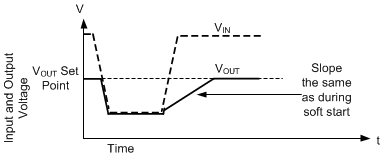 Figure 8-21 When Output Voltage Falls, It Recovers Slowly Preventing Overshoot and Large Inrush Currents
Figure 8-21 When Output Voltage Falls, It Recovers Slowly Preventing Overshoot and Large Inrush Currents