JAJSCD5A August 2016 – August 2016 MSP430F6459-HIREL
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1デバイスの概要
- 2改訂履歴
- 3Device Comparison
- 4Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Active Mode Supply Current Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 5.5 Low-Power Mode Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 5.6 Low-Power Mode With LCD Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 5.7 Schmitt-Trigger Inputs - General-Purpose I/O
- 5.8 Leakage Current - General-Purpose I/O
- 5.9 Outputs - General-Purpose I/O (Full Drive Strength)
- 5.10 Outputs - General-Purpose I/O (Reduced Drive Strength)
- 5.11 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for PZ Package
- 5.12 Typical Characteristics - Outputs, Reduced Drive Strength (PxDS.y = 0)
- 5.13 Typical Characteristics - Outputs, Full Drive Strength (PxDS.y = 1)
- 5.14 Timing and Switching Characteristics
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 CPU
- 6.3 Instruction Set
- 6.4 Operating Modes
- 6.5 Interrupt Vector Addresses
- 6.6 Memory Organization
- 6.7 Bootloader (BSL)
- 6.8 JTAG Operation
- 6.9 Flash Memory
- 6.10 Memory Integrity Detection (MID)
- 6.11 RAM
- 6.12 Backup RAM
- 6.13
Peripherals
- 6.13.1 Digital I/O
- 6.13.2 Port Mapping Controller
- 6.13.3 Oscillator and System Clock
- 6.13.4 Power-Management Module (PMM)
- 6.13.5 Hardware Multiplier (MPY)
- 6.13.6 Real-Time Clock (RTC_B)
- 6.13.7 Watchdog Timer (WDT_A)
- 6.13.8 System Module (SYS)
- 6.13.9 DMA Controller
- 6.13.10 Universal Serial Communication Interface (USCI)
- 6.13.11 Timer TA0
- 6.13.12 Timer TA1
- 6.13.13 Timer TA2
- 6.13.14 Timer TB0
- 6.13.15 Comparator_B
- 6.13.16 ADC12_A
- 6.13.17 DAC12_A
- 6.13.18 CRC16
- 6.13.19 Voltage Reference (REF) Module
- 6.13.20 LCD_B
- 6.13.21 LDO and PU Port
- 6.13.22 Embedded Emulation Module (EEM) (L Version)
- 6.13.23 Peripheral File Map
- 6.14
Input/Output Schematics
- 6.14.1 Port P1, P1.0 to P1.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.2 Port P2, P2.0 to P2.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.3 Port P3, P3.0 to P3.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.4 Port P4, P4.0 to P4.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.5 Port P5, P5.0 and P5.1, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.6 Port P5, P5.2 to P5.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.7 Port P6, P6.0 to P6.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.8 Port P7, P7.2, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.9 Port P7, P7.3, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.10 Port P7, P7.4 to P7.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.11 Port P8, P8.0 to P8.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.12 Port P9, P9.0 to P9.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.14.13 Port PU.0, PU.1 Ports
- 6.14.14 Port J, PJ.0 JTAG Pin TDO, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger or Output
- 6.14.15 Port J, PJ.1 to PJ.3 JTAG Pins TMS, TCK, TDI/TCLK, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger or Output
- 6.15 Device Descriptors
- 7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 9メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
8 デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
8.1 使い始めと次の手順
この MSP430™ファミリのデバイス、および開発に役立つツールやライブラリの詳細については、「Getting Started」ページを参照してください。
8.2 Device Nomenclature
To designate the stages in the product development cycle, TI assigns prefixes to the part numbers of all MSP430 MCU devices and support tools. Each MSP430 MCU commercial family member has one of three prefixes: MSP, PMS, or XMS (for example, MSP430F5438A). TI recommends two of three possible prefix designators for its support tools: MSP and MSPX. These prefixes represent evolutionary stages of product development from engineering prototypes (with XMS for devices and MSPX for tools) through fully qualified production devices and tools (with MSP for devices and MSP for tools).
Device development evolutionary flow:
XMS – Experimental device that is not necessarily representative of the electrical specifications for the final device
PMS – Final silicon die that conforms to the electrical specifications for the device but has not completed quality and reliability verification
MSP – Fully qualified production device
Support tool development evolutionary flow:
MSPX – Development-support product that has not yet completed TI's internal qualification testing.
MSP – Fully-qualified development-support product
XMS and PMS devices and MSPX development-support tools are shipped against the following disclaimer:
"Developmental product is intended for internal evaluation purposes."
MSP devices and MSP development-support tools have been characterized fully, and the quality and reliability of the device have been demonstrated fully. TI's standard warranty applies.
Predictions show that prototype devices (XMS and PMS) have a greater failure rate than the standard production devices. TI recommends that these devices not be used in any production system because their expected end-use failure rate still is undefined. Only qualified production devices are to be used.
TI device nomenclature also includes a suffix with the device family name. This suffix indicates the package type (for example, PZP) and temperature range (for example, T). Figure 8-1 provides a legend for reading the complete device name for any family member.
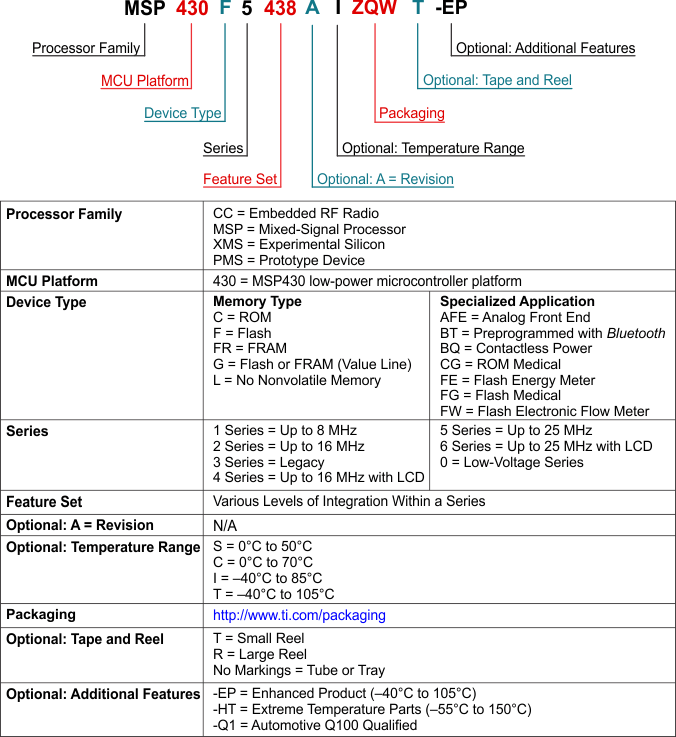 Figure 8-1 Device Nomenclature
Figure 8-1 Device Nomenclature
8.3 ツールとソフトウェア
すべての MSP430™マイクロコントローラは、広範なソフトウェアおよびハードウェア開発ツールによりサポートされています。ツールはTIおよびさまざまなサードパーティーから入手できます。www.ti.com/msp430toolsで、すべてのツールを参照できます。
8.3.1 ハードウェアの特長
利用可能な特長の詳細については、『MSP430用Code Composer Studio ユーザー・ガイド』(SLAU157)を参照してください。
| MSP430アーキテクチャ | 4線式JTAG | 2線式JTAG | ブレーク・ポイント (N) |
範囲ブレーク・ポイント | クロック制御 | 状態シーケンサ | トレース・バッファ | LPMx.5デバッグ・サポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSP430Xv2 | ○ | ○ | 8 | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
8.3.2 推奨ハードウェア・オプション
8.3.2.1 ターゲット・ソケット基板
ターゲット・ソケット基板により、JTAGを使用してデバイスを簡単にプログラムおよびデバッグできます。これらの基板には、プロトタイプ作成用のヘッダー・ピン出力も用意されています。ターゲット・ソケット基板は個別にも、JTAGプログラマおよびデバッガが含まれているキットとしても注文できます。互換性のあるターゲット基板と、対応しているパッケージを、次の表に示します。
| パッケージ | ターゲット基板とプログラマのバンドル | ターゲット基板のみ |
|---|---|---|
| 100ピンLQFP (PZ) | MSP-FET430U100USB | MSP-TS430PZ100USB |
8.3.2.2 検証用基板
一部のMSP430デバイス用に、検証用基板と評価キットが利用可能です。これらのキットには、完全なシステムの評価とプロトタイプ作成を行うため、追加のハードウェア・コンポーネントと接続が用意されています。詳細については、www.ti.com/msp430toolsを参照してください。
8.3.2.3 デバッグおよびプログラミングのツール
ハードウェアのプログラミングおよびデバッグ用のツールは、TIおよびサードパーティーの供給元から入手できます。利用可能なツールすべてのリストは、www.ti.com/msp430toolsで参照できます。
8.3.2.4 量産プログラマ
量産プログラマは、複数のデバイスを同時にプログラムし、ファームウェアをデバイスへ短時間でロードできます。
| 型番 | PCポート | 特長 | プロバイダ |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSP-GANG | シリアルおよびUSB | 8つまでのデバイスを同時にプログラムできます。PCからも使用でき、スタンドアロンのパッケージとしても使用できます。 | テキサス・インスツルメンツ |
8.3.3 推奨ソフトウェア・オプション
8.3.3.1 統合開発環境
ソフトウェア開発ツールは、TIまたはサードパーティーから入手できます。オープン・ソースのソリューションも利用可能です。
このデバイスは、 Code Composer Studio™ IDE (CCS)によりサポートされています。
8.3.3.2 MSP430Ware
MSP430Wareは、すべてのMSP430デバイス向けのサンプル・コード、データシート、その他の設計リソースを、1つの便利なパッケージとしてまとめたものです。既存のMSP430用設計リソースの完全なコレクションに加えて、MSP430WareにはMSP430ドライバ・ライブラリという高レベルのAPIも含まれています。このライブラリにより、MSP430ハードウェアを簡単にプログラムできます。MSP430WareはCCSのコンポーネントとして、またはスタンドアロンのパッケージとして入手できます。
8.3.3.3 TI-RTOS
TI-RTOSは、MSP430マイクロコントローラ用の最先端のリアルタイム・オペレーティング・システムです。プリエンプティブな決定論的マルチタスク、ハードウェア抽象化、メモリ管理、およびリアルタイム分析機能があります。TI-RTOSは無償で利用でき、完全なソースコードが付属しています。
8.3.3.4 コマンドライン・プログラマ
MSP430 Flasherは、MSP430マイクロコントローラをFETプログラマまたは eZ430™ 開発ツール経由で、JTAGまたはSpy-Bi-Wire (SBW)通信を使用してプログラムするための、オープン・ソースのシェル・ベース・インターフェイスです。MSP430 Flasherは、IDEを使用せずにバイナリ・ファイル(.txtまたは.hex)をMSP430 Flashへ直接ダウンロードするために使用できます。
8.4 ドキュメントのサポート
ドキュメントの更新についての通知を受け取るには、ti.com (GPN1、GPN2、...)のデバイス製品フォルダを開いてください。右上の隅にある「通知を受け取る」をクリックして登録すると、変更されたすべての製品情報に関するダイジェストを毎週受け取れます。変更の詳細については、修正されたドキュメントに含まれている改訂履歴をご覧ください。
以下のドキュメントでは、MSP430F665x、MSP430F645x、MSP430F565x、MSP430F535xデバイスについて記載されています。これらのドキュメントのコピーは、www.ti.comで入手できます。
-
SLAZ491『MSP430F6459-Hirelデバイス正誤表』このデバイスにおけるすべてのシリコンのリビジョンについて、機能仕様に関する既知の例外が記載されています。
-
SLAU278 『MSP430ハードウェア・ツール・ユーザー・ガイド』 このマニュアルには、TI MSP-FET430フラッシュ・エミュレーション・ツール(FET)のハードウェアについて解説されています。FETは、MSP430 超低消費電力マイクロコントローラ用のプログラム開発ツールです。利用可能なインターフェイスとして、パラレル・ポート・インターフェイスとUSBインターフェイスの両方について解説されています。
-
SLAU319 『MSP430ブートローダ(BSL)によるプログラミング』 MSP430ブートローダ(BSL)を使用すると、プロトタイプ作成フェーズ、最終的な量産、およびサービス中に、MSP430マイクロコントローラの組み込みメモリと通信を行うことができます。必要に応じて、プログラム可能メモリ(フラッシュ・メモリ)とデータ・メモリ(RAM)の両方を変更できます。このブートローダは、一部のデジタル・シグナル・プロセッサ(DSP)に見られる、外部メモリからDSPの内部メモリへプログラム・コード(およびデータ)を自動的にロードする、ブートストラップ・ローダ・プログラムとは異なることに注意してください。
-
SLAU320 『JTAGインターフェイスによるMSP430のプログラミング』 このドキュメントでは、JTAG通信ポートを使用してMSP430のフラッシュ・ベースおよびFRAMベースのマイクロコントローラ・ファミリのメモリ・モジュールを消去、プログラム、検証するために必要な機能について解説しています。さらに、すべてのMSP430 MCUで利用可能なJTAGアクセス・セキュリティ・ヒューズのプログラム方法についても解説しています。このドキュメントには、標準の4線式JTAGインターフェイスと2線式JTAGインターフェイスの両方を使用してMCUにアクセスする方法が解説されています。2線式JTAGインターフェイスはSpy-Bi-Wire (SBW)とも呼ばれます。
-
SLAA322 『MSP430 32kHz水晶発振器』 適切な水晶、正しい負荷電流、および適切な基板レイアウトの選択は、安定した水晶発振器のために重要です。このアプリケーション・レポートでは、水晶発振器の機能について要約し、MSP430の超低消費電力動作用の適切な水晶を選択するためのパラメータについて説明します。また、正しい基板レイアウトについてのヒントや例も紹介しています。このドキュメントには、量産時の安定した発振器の動作を保証するために行うことができる、発振器のテストについての詳細情報も記載されています。
-
SLOA089 『基板のレイアウト技法』 オペアンプの回路はアナログ回路で、デジタル回路とは大きく異なります。特別なレイアウト技法を使用して、基板上で専用のセクションに分離する必要があります。プリント基板の影響は高速なアナログ回路でより明白になりますが、この章に示す一般的な誤りは、オーディオ回路の性能にも影響を及ぼします。この章の目的は、設計者が犯す最も一般的な過ちのいくつかについて解説し、それらがどのように性能の劣化を引き起こすかについて説明し、問題を回避するための簡単な修正方法を提示することです。
-
SLAA530 『MSP430 システム・レベルESDの考慮事項』 シリコン・テクノロジがますます低電圧化し、コスト効率に優れ非常に消費電力の低いコンポーネントを設計する必要性が高まっていくにつれ、システム・レベルESDの要求はますます高くなりつつあります。このアプリケーション・レポートでは、基板設計者とOEMが堅牢なシステム・レベルのデザインを理解し設計できるよう、3種類の異なるESDトピックについて扱います。
8.5 ドキュメントの更新通知を受け取る方法
ドキュメントの更新についての通知を受け取るには、ti.comのデバイス製品フォルダを開いてください。右上の隅にある「通知を受け取る」をクリックして登録すると、変更されたすべての製品情報に関するダイジェストを毎週受け取れます。変更の詳細については、修正されたドキュメントに含まれている改訂履歴をご覧ください。
8.6 Community Resources
The following links connect to TI community resources. Linked contents are provided "AS IS" by the respective contributors. They do not constitute TI specifications and do not necessarily reflect TI's views; see TI's Terms of Use.
TI E2E™ Community
TI's Engineer-to-Engineer (E2E) Community. Created to foster collaboration among engineers. At e2e.ti.com, you can ask questions, share knowledge, explore ideas, and help solve problems with fellow engineers.
TI Embedded Processors Wiki
Texas Instruments Embedded Processors Wiki. Established to help developers get started with embedded processors from Texas Instruments and to foster innovation and growth of general knowledge about the hardware and software surrounding these devices.
8.7 商標
MSP430, Code Composer Studio, eZ430, E2E are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
8.8 静電気放電に関する注意事項

すべての集積回路は、適切なESD保護方法を用いて、取扱いと保存を行うようにして下さい。
静電気放電はわずかな性能の低下から完全なデバイスの故障に至るまで、様々な損傷を与えます。高精度の集積回路は、損傷に対して敏感であり、極めてわずかなパラメータの変化により、デバイスに規定された仕様に適合しなくなる場合があります。
8.9 Export Control Notice
Recipient agrees to not knowingly export or re-export, directly or indirectly, any product or technical data (as defined by the U.S., EU, and other Export Administration Regulations) including software, or any controlled product restricted by other applicable national regulations, received from disclosing party under nondisclosure obligations (if any), or any direct product of such technology, to any destination to which such export or re-export is restricted or prohibited by U.S. or other applicable laws, without obtaining prior authorization from U.S. Department of Commerce and other competent Government authorities to the extent required by those laws.
8.10 用語集
-
TI 用語集 この用語集には、用語や略語の一覧および定義が記載されています。