JAJSGR0F December 2010 – December 2018 TPS51916
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 VDDQ Switch Mode Power Supply Control
- 8.3.2 VREF and REFIN, VDDQ Output Voltage
- 8.3.3 Soft-Start and Powergood
- 8.3.4 Power State Control
- 8.3.5 Discharge Control
- 8.3.6 VTT and VTTREF
- 8.3.7 VDDQ Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
- 8.3.8 VDDQ Out-of-Bound Operation
- 8.3.9 VDDQ Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.10 VTT Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.11 V5IN Undervoltage Lockout Protection
- 8.3.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 D-CAP2™ Mode Operation
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
8.3.9 VDDQ Overcurrent Protection
The VDDQ SMPS has cycle-by-cycle overcurrent limiting protection. The inductor current is monitored during the off-state using the low-side MOSFET RDS(on), and the controller maintains the off-state when the inductor current is larger than the overcurrent trip level. The current monitor circuit inputs are PGND and SW pins so that those should be properly connected to the source and drain terminals of low-side MOSFET. The overcurrent trip level, VOCTRIP, is determined by Equation 1, where RTRIP is the value of the resistor connected between the TRIP pin and GND, and ITRIP is the current sourced from the TRIP pin. ITRIP is 10 μA typically at room temperature, and has 4700ppm/°C temperature coefficient to compensate the temperature dependency of the low-side MOSFET RDS(on).
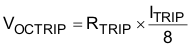
Because the comparison is done during the off-state, VOCTRIP sets the valley level of the inductor current. The load current OCL level, IOCL, can be calculated by considering the inductor ripple current as shown in Equation 2.
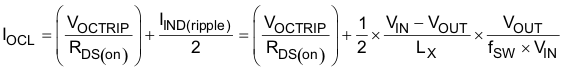
where
- IIND(ripple) is inductor ripple current
In an overcurrent condition, the current to the load exceeds the current to the output capacitor, thus the output voltage tends to fall down. Eventually, it crosses the undervoltage protection threshold and shuts down.