SLVSAE4A July 2010 – August 2014 TPS53128
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 PWM Operation
- 7.3.2 Light-Load Condition
- 7.3.3 Drivers
- 7.3.4 PWM Frequency And Adaptive On-Time Control
- 7.3.5 5-Volt Regulator
- 7.3.6 Soft Start
- 7.3.7 Pre-Bias Support
- 7.3.8 Output Discharge Control
- 7.3.9 Over Current Limit
- 7.3.10 Over/Under Voltage Protection
- 7.3.11 UVLO Protection
- 7.3.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8 Application and Implementation
8.1 Application Information
8.2 Typical Application
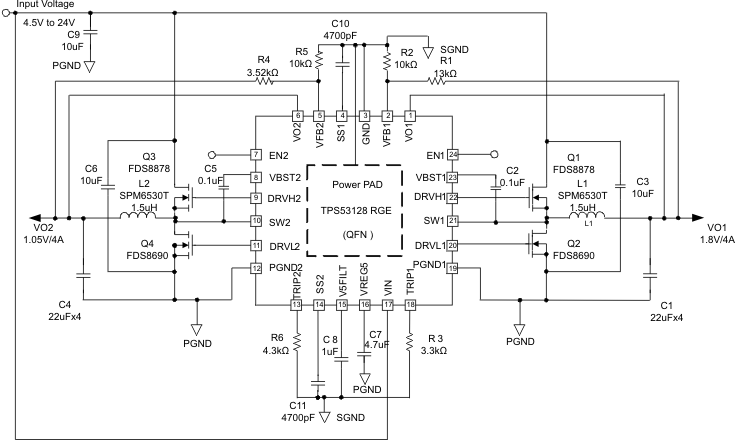 Figure 10. QFN
Figure 10. QFN
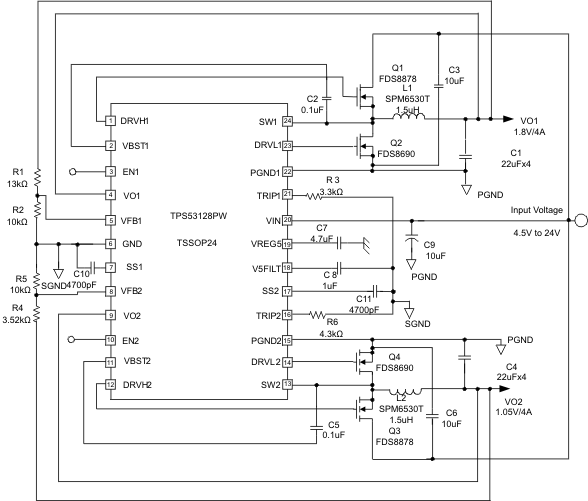 Figure 11. TSSOP
Figure 11. TSSOP
8.2.1 Design Requirements
8.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- Choose inductor.
- Choose output capacitor.
- Choose input capacitor.
- Choose bootstrap capacitor.
- Choose VREG5 and V5FILT capacitor.
- Choose output voltage divider resistors.
- Choose register setting for over current limit.
- Choose soft start capacitor.
The inductance value is selected to provide approximately 30% peak to peak ripple current at maximum load. Larger ripple current increases output ripple voltage, improve S/N ratio and contribute to stable operation.
Equation 4 can be used to calculate L1.
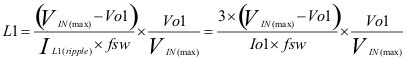
The inductors current ratings needs to support both the RMS (thermal) current and the Peak (saturation) current. The RMS and peak inductor current can be estimated as follows.
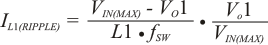
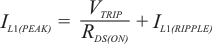
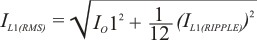
Note: The calculation above shall serve as a general reference. To further improve transient response, the output inductance could be reduced further. This needs to be considered along with the selection of the output capacitor.
The capacitor value and ESR determines the amount of output voltage ripple and load transient response. it is recommended to use a ceramic output capacitor.
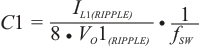
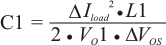
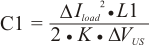
Where
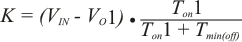
Select the capacitance value greater than the largest value calculated from Equation 8, Equation 9 and Equation 10. The capacitance for C1 should be greater than 66 μF.
Where
ΔVOS = The allowable amount of overshoot voltage in load transition
ΔVUS = The allowable amount of undershoot voltage in load transition
Tmin(off) = Minimum off time
The TPS53128 requires an input decoupling capacitor and a bulk capacitor is needed depending on the application. A minimum 10-μF high-quality ceramic capacitor is recommended for the input capacitor. The capacitor voltage rating needs to be greater than the maximum input voltage.
The TPS53128 requires a bootstrap capacitor from SW to VBST to provide the floating supply for the high-side drivers. A minimum 0.1-μF high-quality ceramic capacitor is recommended. The voltage rating should be greater than 10 V.
The TPS53128 requires both the VREG5 regulator and V5FILT input are bypassed. A minimum 4.7-μF high-quality ceramic capacitor must be connected between the VREG5 and GND for proper operation. A minimum 1-μF high-quality ceramic capacitor must be connected between the V5FILT and GND for proper operation. Both of these capacitors’ voltage ratings should be greater than 10 V.
The output voltage is set with a resistor divider from the output voltage node to the VFBx pin. It is recommended to use 1% tolerance or better resisters. Select R2 between 10 kΩ and 100 kΩ and use Equation 12 or Equation 13 to calculate R1.
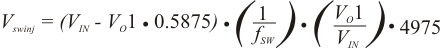
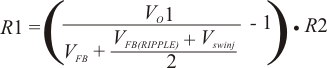
Where
VFB(RIPPLE) = Ripple voltage at VFB
Vswinj = Ripple voltage at error comparator
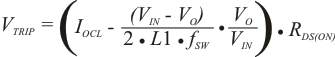
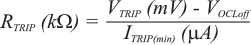
Where
RDS(ON) = Low side FET on-resistance
ITRIP(min) = TRIP pin source current (8.5 μA)
VOCL0ff = Minimum over current limit offset voltage (–20 mV)
IOCL = Over current limit
Soft start time equation is as follows.
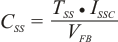
8.2.3 Application Curves
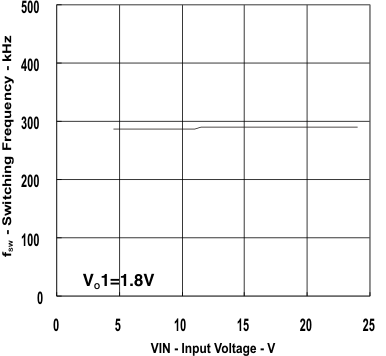
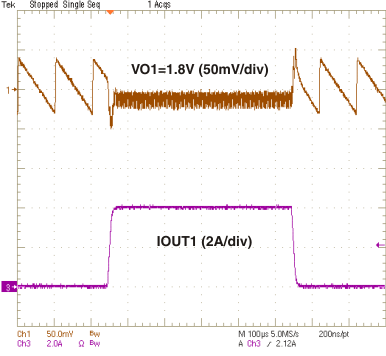
| IO1 = 3 A | VO1 = 1.8 V | |
vs
Input Voltage (Ch1)
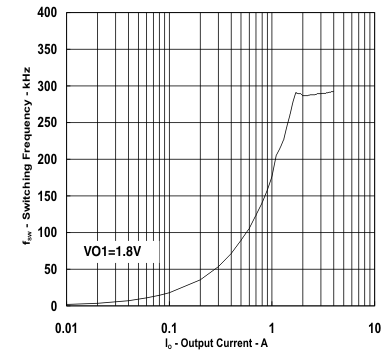
| VO1 = 1.8 V | ||
vs
Output Current (Ch1)
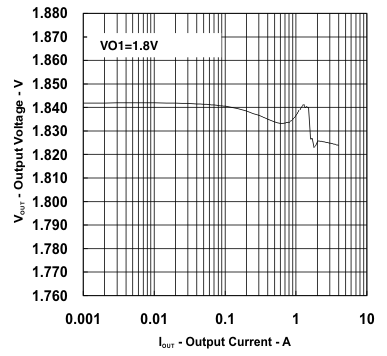
| VIN = 12 V | VO1 = 1.8 V | |
vs
Output Current (Ch1)
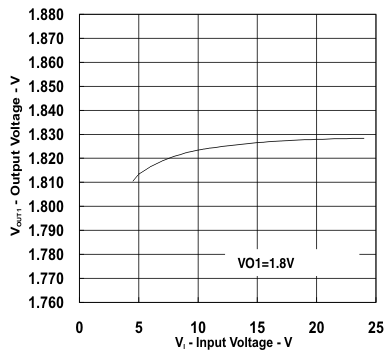
| VIN = 12 V | VO1 = 1.8 V | |
vs
Input Voltage (Ch1)
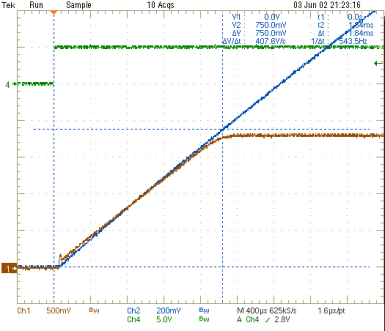
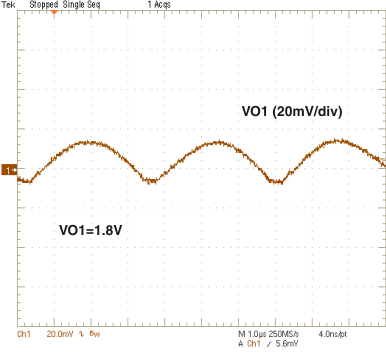
| VO1 = 1.8 V | ||
vs
Output Current (Ch1)
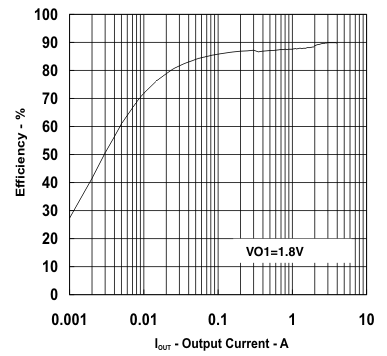
| VO1 = 1.8 V | ||
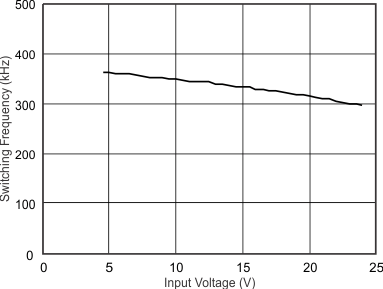
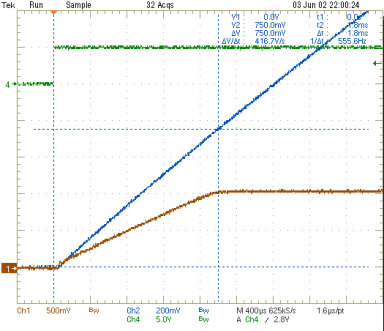
| IO2 = 3 A | VO2 = 1.05 V | |
vs
Input Voltage (Ch2)
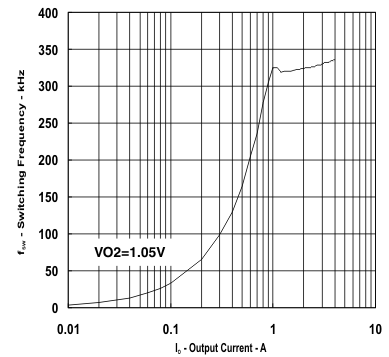
| VO2 = 1.05 V | ||
vs
Output Current (Ch2)
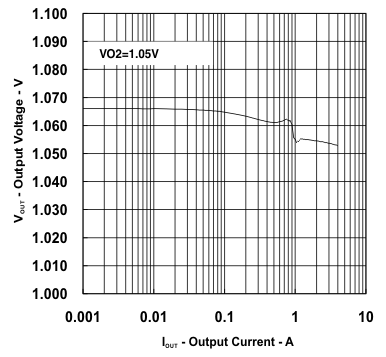
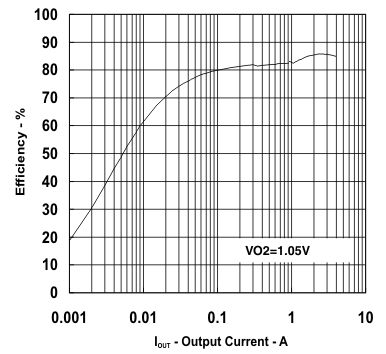
| VIN = 12 V | VO2 = 1.05 V | |
vs
Output Current (Ch2)
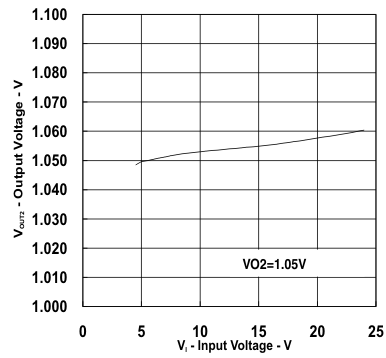
| VIN = 12 V | VO2 = 1.05 V | |
vs
Input Voltage (Ch2)
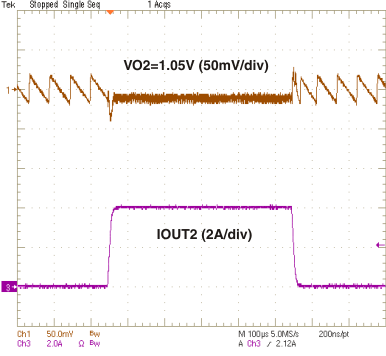
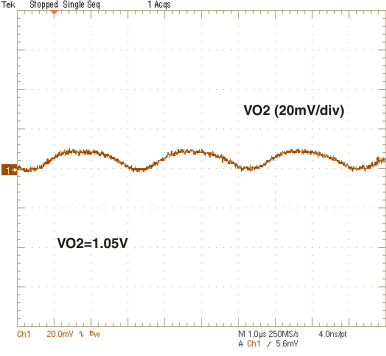
| VO2 = 1.05 V | ||
vs
Output Current (Ch2)
| VO2 = 1.05 V | ||