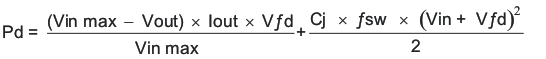JAJS448D March 2010 – October 2018 TPS54260
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Fixed Frequency PWM Control
- 8.3.2 Slope Compensation Output Current
- 8.3.3 Pulse-Skip Eco-Mode
- 8.3.4 Low-Dropout Operation and Bootstrap Voltage (BOOT)
- 8.3.5 Error Amplifier
- 8.3.6 Voltage Reference
- 8.3.7 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 8.3.8 Enable and Adjusting Undervoltage Lockout
- 8.3.9 Slow-Start / Tracking Pin (SS/TR)
- 8.3.10 Overload Recovery Circuit
- 8.3.11 Sequencing
- 8.3.12 Constant Switching Frequency and Timing Resistor (RT/CLK Pin)
- 8.3.13 Overcurrent Protection and Frequency Shift
- 8.3.14 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.3.15 How to Interface to RT/CLK Pin
- 8.3.16 Powergood (PWRGD Pin)
- 8.3.17 Overvoltage Transient Protection
- 8.3.18 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.19 Small Signal Model for Loop Response
- 8.3.20 Simple Small Signal Model for Peak Current Mode Control
- 8.3.21 Small Signal Model for Frequency Compensation
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1
3.3-V Output Application
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.2.1 Custom Design With WEBENCH® Tools
- 9.2.1.2.2 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 9.2.1.2.3 Output Inductor Selection (LO)
- 9.2.1.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 9.2.1.2.5 Catch Diode
- 9.2.1.2.6 Input Capacitor
- 9.2.1.2.7 Slow-Start Capacitor
- 9.2.1.2.8 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.1.2.9 Undervoltage Lock Out Set Point
- 9.2.1.2.10 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 9.2.1.2.11 Compensation
- 9.2.1.2.12 Discontinuous Mode and Eco-Mode Boundary
- 9.2.1.2.13 Power Dissipation Estimate
- 9.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.2 Inverting Power Supply
- 9.2.3 Split-Rail Power Supply
- 9.2.4 12-V to 3.8-V GSM Power Supply
- 9.2.5 24-V to 4.2-V GSM Power Supply
- 9.2.1
3.3-V Output Application
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 13メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
9.2.1.2.5 Catch Diode
The TPS54260 requires an external catch diode between the PH pin and GND. The selected diode must have a reverse voltage rating equal to or greater than Vinmax. The peak current rating of the diode must be greater than the maximum inductor current. The diode should also have a low forward voltage. Schottky diodes are typically a good choice for the catch diode due to their low forward voltage. The lower the forward voltage of the diode, the higher the efficiency of the regulator.
Typically, the higher the voltage and current ratings the diode has, the higher the forward voltage will be. Although the design example has an input voltage up to 13.2 V, a diode with a minimum of 60-V reverse voltage is selected to allow input voltage transients up to the rated voltage of the TPS54260.
For the example design, the B360B-13-F Schottky diode is selected for its lower forward voltage and it comes in a larger package size which has good thermal characteristics over small devices. The typical forward voltage of the B360B-13-F is 0.70 volts.
The diode must also be selected with an appropriate power rating. The diode conducts the output current during the off-time of the internal power switch. The off-time of the internal switch is a function of the maximum input voltage, the output voltage, and the switching frequency. The output current during the off-time is multiplied by the forward voltage of the diode which equals the conduction losses of the diode. At higher switch frequencies, the AC losses of the diode need to be taken into account. The AC losses of the diode are due to the charging and discharging of the junction capacitance and reverse recovery. Equation 37 is used to calculate the total power dissipation, conduction losses plus ac losses, of the diode.
The B360B-13-F has a junction capacitance of 200 pF. Using Equation 37, the selected diode will dissipate 1.32 Watts.
If the power supply spends a significant amount of time at light-load currents or in sleep mode consider using a diode which has a low leakage current and slightly higher forward voltage drop.