SLUSBU2A September 2014 – February 2016 TPS92661-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Controlling the Internal LED Bypass Switches
- 7.3.2 Internal Switch Resistance
- 7.3.3 PWM Dimming
- 7.3.4 PWM Clock
- 7.3.5 PWM Synchronization
- 7.3.6 Switch Slew Control
- 7.3.7 Effect of Phase Shifting LED Duty Cycles
- 7.3.8 LED Fault Detection and Protection
- 7.3.9 Glitch-Free Operation
- 7.3.10 Internal Oscillator and Watchdog Timers
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1
Digital Interface Connections
- 7.4.1.1 Address (ADR0, ADR1, and ADR2 Pins)
- 7.4.1.2 Clock (CLK Pin)
- 7.4.1.3 Internal Charge Pump (CPP Pin)
- 7.4.1.4 Enable (EN Pin)
- 7.4.1.5 GND Pin
- 7.4.1.6 Receive (RX Pin)
- 7.4.1.7 Synchronization (SYNC Pin)
- 7.4.1.8 Transmit (TX Pin)
- 7.4.1.9 Primary Power Supply (VIN Pin)
- 7.4.1.10 On-Board 3.3-V Supply (VCC Pin)
- 7.4.2 Internal Pin-to-Pin Resistance
- 7.4.3 UART Physical Layer
- 7.4.4 UART Clock and Baudrate
- 7.4.5 UART Communications Reset
- 7.4.6 UART Device Addressing
- 7.4.7 UART Communications Protocol
- 7.4.8 Transaction Frame Description
- 7.4.9 Frame Initialization Byte
- 7.4.10 Register Address
- 7.4.11 Data Bytes
- 7.4.12 CRC Bytes
- 7.4.13 Registers
- 7.4.1
Digital Interface Connections
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Map
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
パッケージ・オプション
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- PHP|48
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
- PHP|48
発注情報
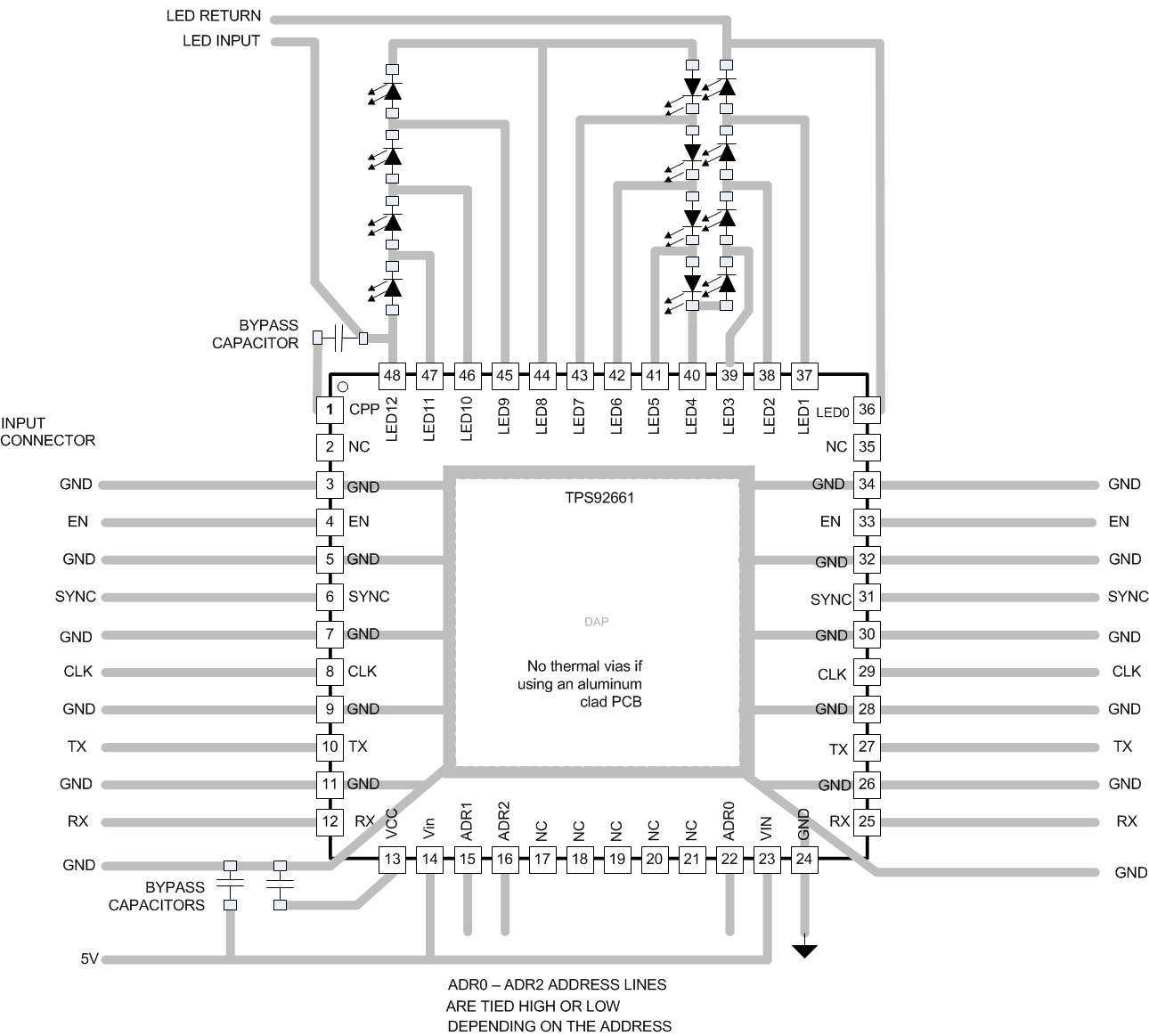
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
The final configuration of the LED matrix varies between applications and balances heat dissipation with light output performance. Layout considerations for passive components are simple; place the VCC and VIN decoupling capacitors close to the device and short the traces to the CPP pin capacitor. The bigger challenge is to develop a careful layout plan that efficiently routes the current source for the LED strings.
The communication connections have been designed for ease of routing on a single-sided, metal core board. Each connection has a parallel connection on the opposite side of the device, allowing multiple devices to use a daisy chain configuration, easing routing requirements.