SBAA483 February 2021 ADS1120 , ADS112C04 , ADS112U04 , ADS114S06 , ADS114S06B , ADS114S08 , ADS114S08B , ADS1220 , ADS122C04 , ADS122U04 , ADS124S06 , ADS124S08 , ADS125H02 , ADS1260 , ADS1261 , ADS1262 , ADS1263
- Abstract
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
- 2Features Used to Detect Wire Breaks in RTD Systems
- 3Wire-Break Detection Methods for Different RTD Configurations
- 4Settling Time Considerations for RTD Wire-Break Detection
- 5Summary
- A How Integrated PGA Rail Detection Helps Identify Wire Breaks
- B Pseudo-Code for RTD Wire-Break Detection
3.2.2 Wire-Break Detection in a Two-IDAC, 3-Wire RTD System
Many of the same techniques employed in the previous sections can help identify wire breaks in a two-IDAC, 3-wire RTD system, though there are some corner cases that require special attention. These cases are described in Section 3.2.2.1 (low-side RREF) and Section 3.2.2.2 (high-side RREF).
Regardless if a low-side or high-side RREF is being used, a break in lead 3 automatically eliminates the IDAC path to ground and results in a VREF monitor fault. Figure 3-6 shows how this break occurs in a low-side (left) and high-side (right) RREF configuration. This result is true if any other lead is also broken in addition to lead 3.
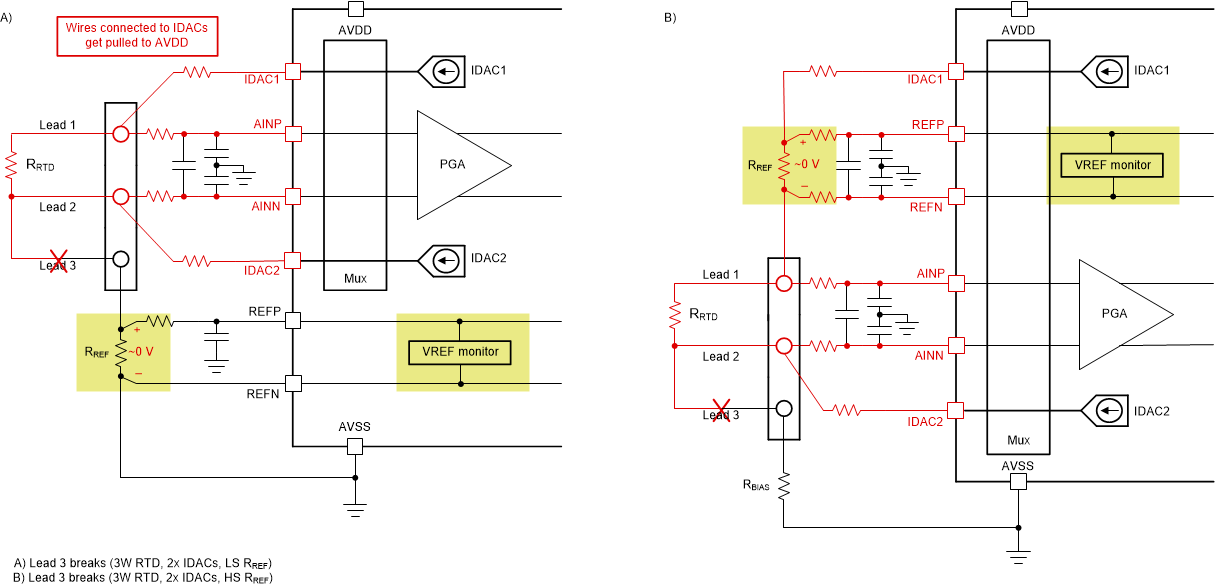 Figure 3-6 VREF Monitor Fault Detected if
Lead 3 Breaks in a Two-IDAC, 3-Wire RTD System Using a Low-Side (Left) and
High-Side (Right) RREF
Figure 3-6 VREF Monitor Fault Detected if
Lead 3 Breaks in a Two-IDAC, 3-Wire RTD System Using a Low-Side (Left) and
High-Side (Right) RREFSimilarly, if both lead 1 and lead 2 break in either the low-side or high-side RREF configuration, neither IDAC has a path to ground and the result is a VREF monitor fault. Figure 3-7 illustrates how this break occurs in a low-side (left) and high-side (right) RREF configuration.
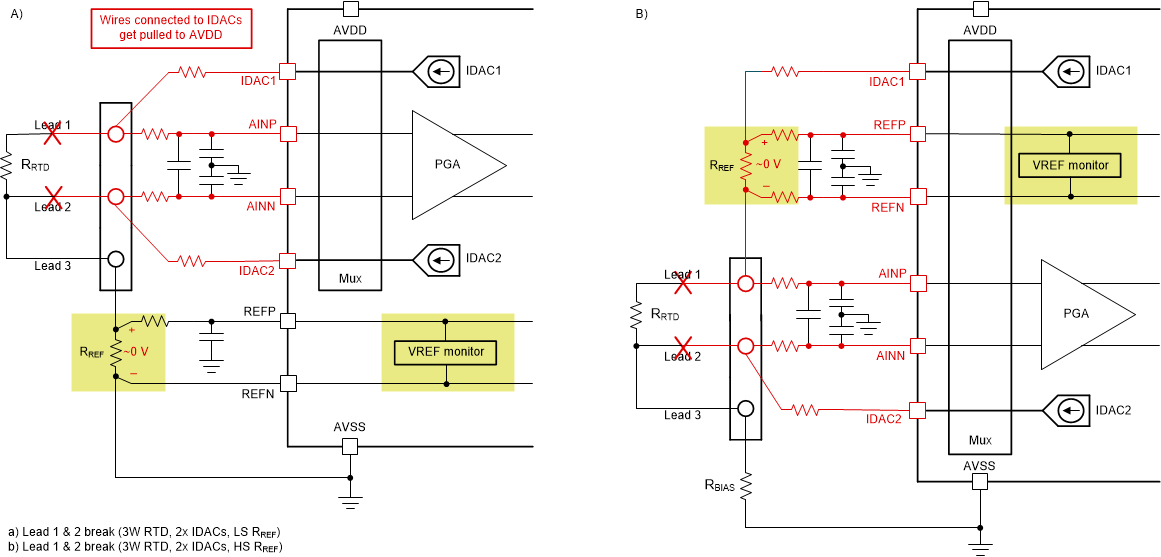 Figure 3-7 VREF Monitor Fault Detected if
Lead 1 and Lead 2 Break in a Two-IDAC, 3-Wire RTD System Using a Low-Side (Left)
and High-Side (Right) RREF
Figure 3-7 VREF Monitor Fault Detected if
Lead 1 and Lead 2 Break in a Two-IDAC, 3-Wire RTD System Using a Low-Side (Left)
and High-Side (Right) RREFThe challenge in a two IDAC, 3-wire RTD system stems from a break in lead 1 or lead 2. In these cases, one IDAC still has a path to ground, making detection less simple. Moreover, the detection schemes differ depending on if a low-side or high-side RREF configuration is used.