SLAAED3A October 2023 – May 2024 TAA5212 , TAA5242 , TAC5111 , TAC5112 , TAC5142 , TAC5211 , TAC5212 , TAC5242
3.1 Differential AC Coupled Power Tune Mode
When balancing power and performance are needed, the following example provides the register setting for a differential AC-Coupled input with 1.8 V AVDD in power tune mode. Register PWR_TUNE_CFG0 in B0_P0_R78 (0x4E) provides the configuration to place the device into power compensation mode.
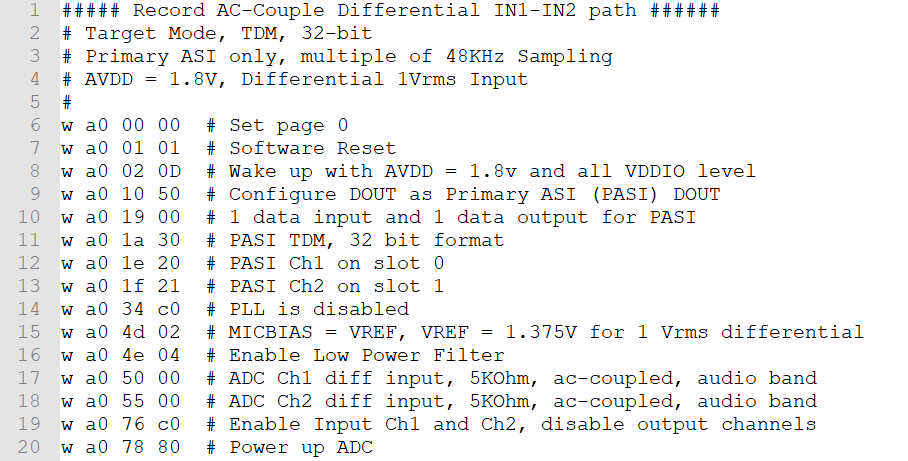 Figure 3-1 Power Tune Mode Differential AC-Coupled Register Setting
Figure 3-1 Power Tune Mode Differential AC-Coupled Register Setting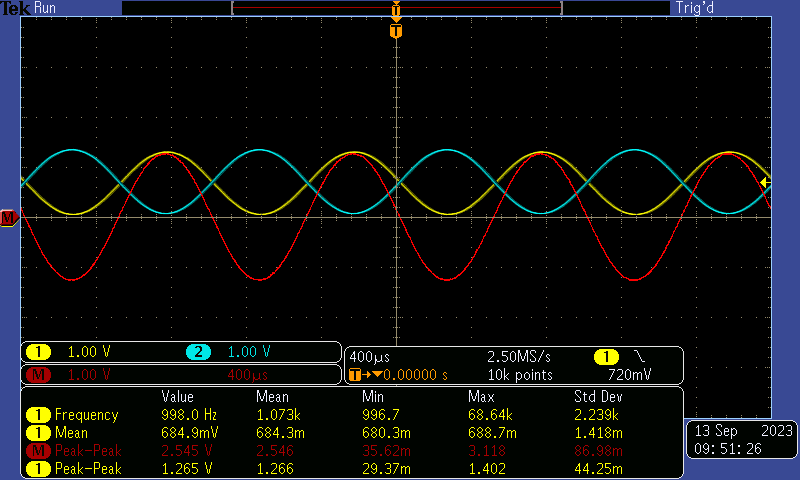 Figure 3-2 Power Tune Differential AC-Coupled Input at
-1dBrG (0dBrG = 1Vrms)
Figure 3-2 Power Tune Differential AC-Coupled Input at
-1dBrG (0dBrG = 1Vrms)A frequency plot of the Dynamic Range with -60dBrG input and SNR with input AC signal shorted to ground are provided here.
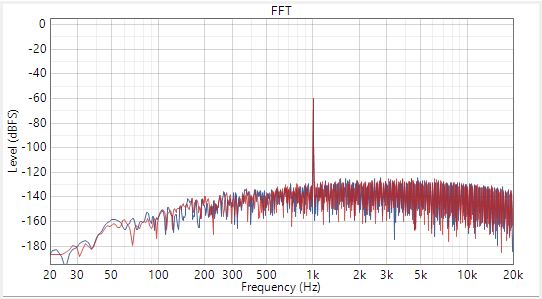 Figure 3-3 Power Tune Mode Differential AC-Coupled
Dynamic Range at -60dBrG
Figure 3-3 Power Tune Mode Differential AC-Coupled
Dynamic Range at -60dBrG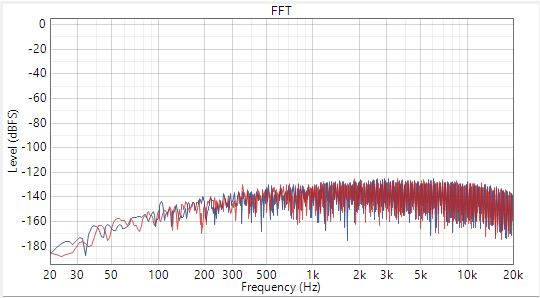 Figure 3-4 Power Tune Mode Differential AC-Coupled SNR
Figure 3-4 Power Tune Mode Differential AC-Coupled SNR