SLOA203 August 2016 DRV10983 , UCC28810
1.1 Introduction
Figure 1 shows a basic block diagram for an AC-operated BLDC ceiling fan demonstrated using the TIDA-00652 reference design.
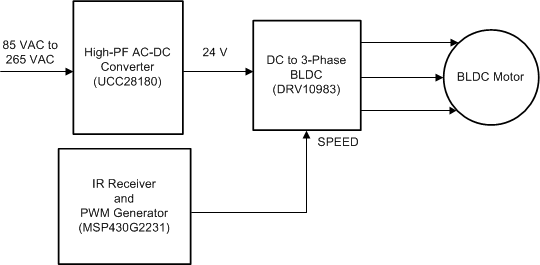 Figure 1. BLDC Ceiling Fan Demonstrated in TIDA-00652
Figure 1. BLDC Ceiling Fan Demonstrated in TIDA-00652 With the addition of a proposed circuit to the existing solution, the speed can be controlled by only toggling the AC mains switch. The proposed solution can completely eliminate the option of a remote to reduce the cost of the microcontroller (MCU), remote, and IR receiver. These devices can be replaced by a low-cost solution based on a ring counter (TI's CD74HC4017 device) and inverter (TI's SN74HCT14 device) which varies the speed by only toggling the AC mains and avoids the cost of a TRIAC component which are used in conventional ceiling fans. This solution can also be used along with the IR remote solution and can be used as additional control in case of the remote is lost.
In addition, using the proposed solution, an arrangement of sequence LEDs can be implemented on the surface of the fan to indicate the speed of the fan. Figure 3 shows this modification of the proposed solution.
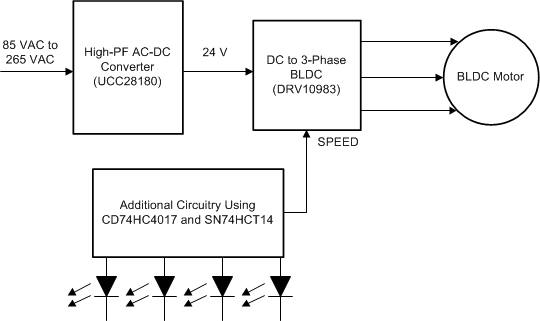 Figure 2. Modified Block Diagram
Figure 2. Modified Block Diagram