SLUU297B December 2007 – January 2022 TPS40195
6.3 Loop Analysis (TP7, TP8, TP10)
The TPS40195EVM contains a 1.30-kΩ series resistor in the feedback loop to allow for matched impedance signal injection into the feedback for loop response analysis.
- Set up the EVM as described in Section 5.2 and Figure 5-1.
- Connect a input signal amplitude measurement probe (Channel A) to TP7 as shown in Figure 6-2.
- Connect a output signal amplitude measurement probe (Channel B) to TP8 as shown in Figure 6-2.
- Connect the ground lead of Channel A and Channel B to TP10 as shown in Figure 6-2.
- Inject 30-mV or less signal across R11 (TP7 and TP8) through an isolation transformer.
- Sweep frequency from 100 Hz to 1 MHz with 10 Hz or lower post filter.
- Control loop gain can be measured by 20 × Log (ChannelB/ChannelA).
- Control loop phase is measured by the phase difference between Channel A and Channel B.
- Disconnect Isolation transformer from TP7 and TP8 before making other measurements (signal injection into feedback may interfere with accuracy of other measurements).
- See Section 6.6 for equipment shutdown.
See Section 7.5 for typical bode plots and transient performance of this EVM.
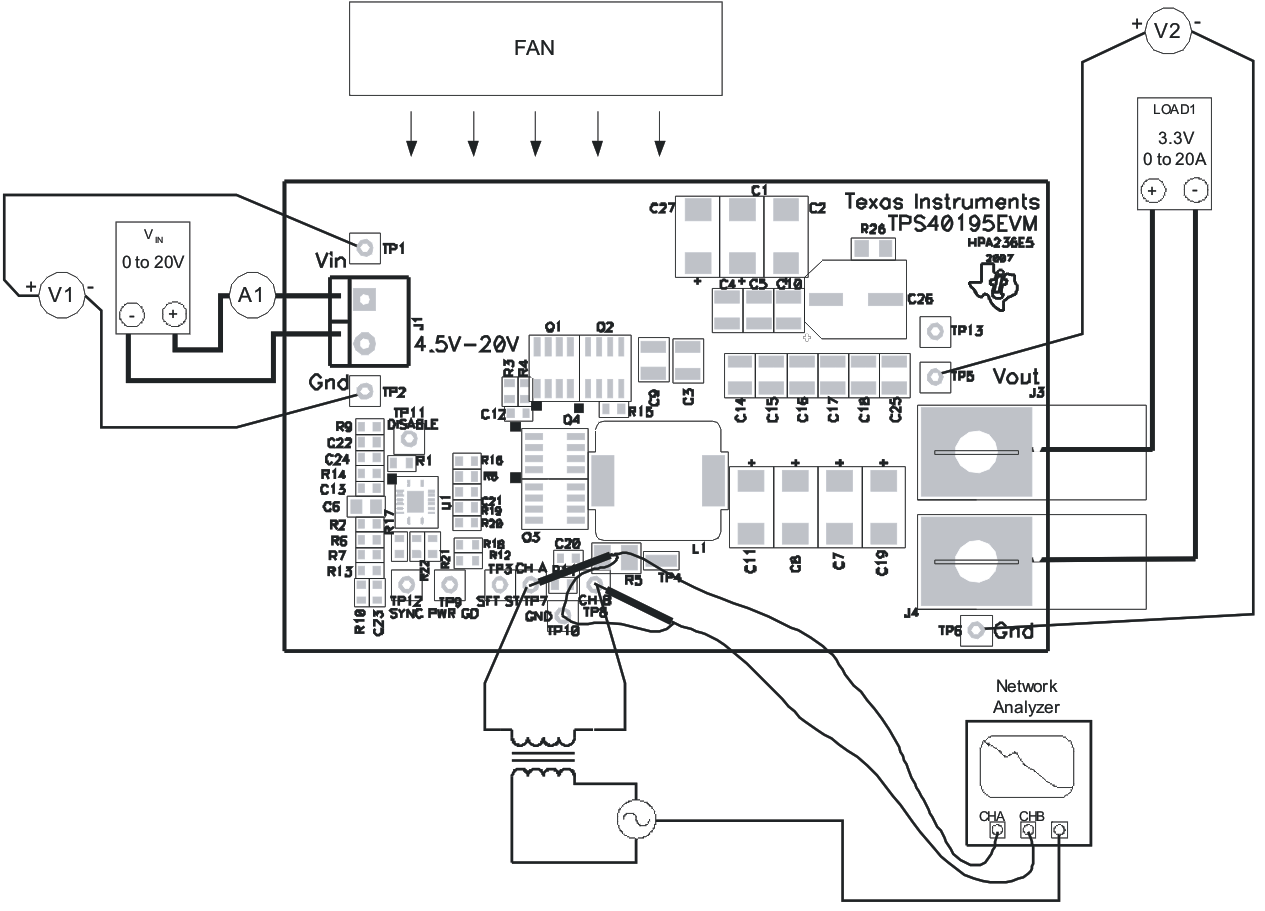 Figure 6-2 Control Loop Measurement Setup
Figure 6-2 Control Loop Measurement Setup