SLVAES1A June 2020 – May 2022 DRV8300
- Trademarks
- 1Motor Considerations and Why Brushless DC Motors?
- 2Motor Driver Architecture
- 3Texas Instruments' Brushless-DC Motor Drivers
- 4Conclusion
- 5Revision History
2.3.2 Sinusoidal
Sinusoidal commutation is another commutation method that drives current through all three phases at a time and the current waveforms in all three motor windings vary smoothly and sinusoidally for 180 electrical degrees (Figure 2-4). A sinusoidal magnetic flux from the stator attracts the rotor permanent magnets to smoothly spin the rotor. Motors with sinusoidal BEMF generate very low torque ripple because the motor current is also sinusoidal and the delivered torque is constant. This means that the motor is acoustically quiet with good power efficiency. However, in sinusoidal commutation, switching losses are high as the commutation occurs throughout 180 electrical degrees with no window for High-Z.
In sensored controls, commutation signals (varying PWM duty cycle waveforms for each phase) are generated based on rotor position to drive the MOSFETS and generate smooth sinusoidal modulation of stator currents. In sensorless controls, a commutation look-up table is implemented. Based on BEMF estimation, commutation signals drive the MOSFETS to generate smooth sinusoidal modulation of stator currents.
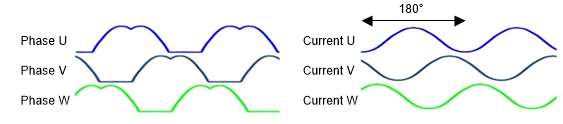 Figure 2-4 Sinusoidal Control
(180°)
Figure 2-4 Sinusoidal Control
(180°)