SLVAES1A June 2020 – May 2022 DRV8300
- Trademarks
- 1Motor Considerations and Why Brushless DC Motors?
- 2Motor Driver Architecture
- 3Texas Instruments' Brushless-DC Motor Drivers
- 4Conclusion
- 5Revision History
2.2 Three Use Cases: Speed, Torque, or Position:
Motor Drivers are typically used for three applications that are well suited for specific motor driver architectures. As discussed in Section 2.1, the power, voltage, and current determine whether a gate driver or integrated FET driver architecture is best. The next consideration is whether or not to integrate control depending on one of the three following use cases and their typical applications:
- Speed: the motor should
maintain a variable or consistent speed
- Appliance fans, vacuum cleaners, laptop cooling fans, blowers, ceiling fans
- Torque: the motor should
be used to apply a force
- Power tools, electric bikes, automated doors and gates, power seats, smart locks
- Position (servo control): the motor should move to a certain
position, be able to hold the position and move back and forth
- IP Network Camera, drone gimbal, collaborative robots, HVAC damper
Figure 2-2 highlights the relationship between the three use cases and their corresponding architectures.
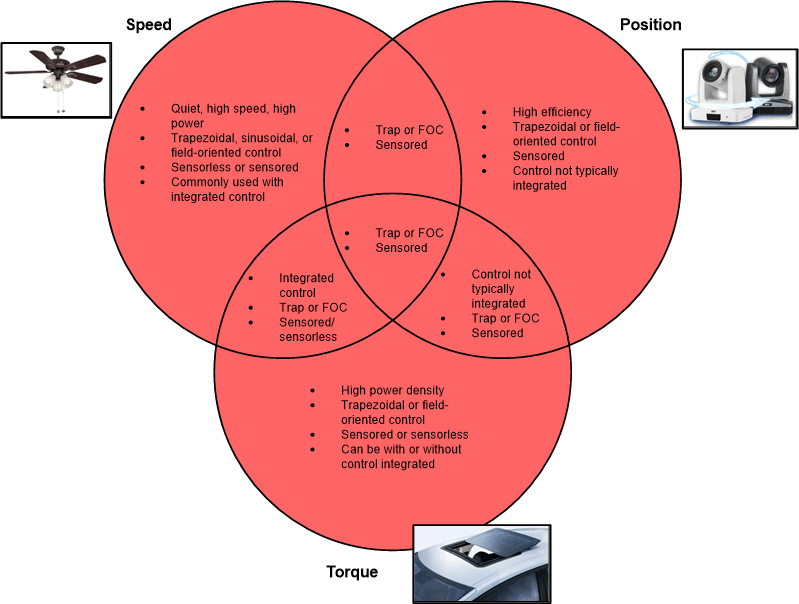 Figure 2-2 Comparison of Three Use
Cases
Figure 2-2 Comparison of Three Use
Cases