SLYY211 October 2021 TMS320F2800132 , TMS320F2800133 , TMS320F2800135 , TMS320F2800137 , TMS320F2800152-Q1 , TMS320F2800153-Q1 , TMS320F2800154-Q1 , TMS320F2800155 , TMS320F2800155-Q1 , TMS320F2800156-Q1 , TMS320F2800157 , TMS320F2800157-Q1 , TMS320F280021 , TMS320F280021-Q1 , TMS320F280023 , TMS320F280023-Q1 , TMS320F280023C , TMS320F280025 , TMS320F280025-Q1 , TMS320F280025C , TMS320F280025C-Q1 , TMS320F280033 , TMS320F280034 , TMS320F280034-Q1 , TMS320F280036-Q1 , TMS320F280036C-Q1 , TMS320F280037 , TMS320F280037-Q1 , TMS320F280037C , TMS320F280037C-Q1 , TMS320F280038-Q1 , TMS320F280038C-Q1 , TMS320F280039 , TMS320F280039-Q1 , TMS320F280039C , TMS320F280039C-Q1 , TMS320F280040-Q1 , TMS320F280040C-Q1 , TMS320F280041 , TMS320F280041-Q1 , TMS320F280041C , TMS320F280041C-Q1 , TMS320F280045 , TMS320F280048-Q1 , TMS320F280048C-Q1 , TMS320F280049 , TMS320F280049-Q1 , TMS320F280049C , TMS320F280049C-Q1 , TMS320F28075 , TMS320F28075-Q1 , TMS320F28076 , TMS320F28374D , TMS320F28374S , TMS320F28375D , TMS320F28375S , TMS320F28375S-Q1 , TMS320F28376D , TMS320F28376S , TMS320F28377D , TMS320F28377D-EP , TMS320F28377D-Q1 , TMS320F28377S , TMS320F28377S-Q1 , TMS320F28378D , TMS320F28378S , TMS320F28379D , TMS320F28379D-Q1 , TMS320F28379S
- 1 Message from the editors
- 2 System Design
- 3 Controllers
- 4 ADC
- 5 Comparator
- 6 Processing
- 7 Encoders
- 8 Pulse width modulation (PWM)
- 9 DAC
- 10Mathematical models
- 11Important Notice
3.3 Nonlinear PID
A nonlinear proportional integral derivative (Nonlinear PID) controller utilizes a power function to implement the control law. The NLPID is an adaptation of the linear PID in which a non-linear law based on a power function is placed in series with each path.
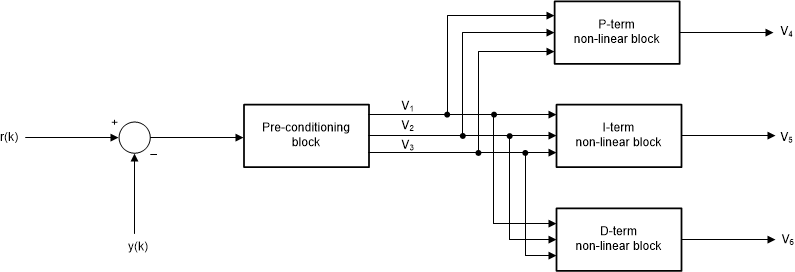 Figure 3-4 Nonlinear PID input
architecture.
Figure 3-4 Nonlinear PID input
architecture.Tuning parameter
Each nonlinear block shapes the servo error according to a power function law in which the normalized input (the servo error) is raised to the power of an adjustable tuning parameter, . The tuning parameter determines the degree and direction of the gain shape.
| Parameter | Value | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| < 1 | Smaller gain as error is large, not sensitive to small error. | |
| > 1 | Higher gain when error is large, higher gain when error is small and by that more sensitive to small changes. | |
| -1 < < 0 | Solves integral windup problem by reducing the integral action when error is large. | |
| > 1 | Makes the differential gain small when the error is small which results in less sensitivity to noise. |
To prevent undesired results, the solution is to define an input range covering the origin over which the gain is held constant. The gain in this region is chosen to ensure that linear and nonlinear curves intersect precisely at their boundaries, resulting in a smooth, glitch-free transition from one region to the other.
Equations
Nonlinear control law
Proportional error expression
Integral error expression
Derivative error expression
Reconstructed nonlinear control law
Where
x = input
y = output
= tuning parameter
= logarithmic decrement
K = controller gain
Figure 3-6 shows the linear and nonlinear regions for a tuning parameter less than one. Notice that the linear gain is independent of the input x, so it does not need to be computed each time the controller runs. The linear gain is fixed for each path and needs to only be recomputed when either of the nonlinear parameters in that path is adjusted.
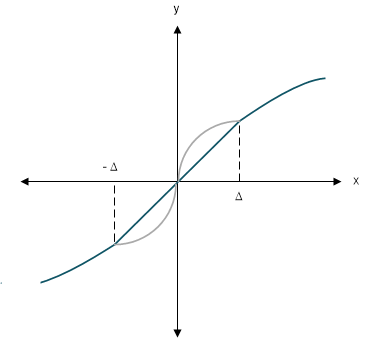 Figure 3-6 Nonlinear PID linearized
region.
Figure 3-6 Nonlinear PID linearized
region.