SBOS629B April 2018 – May 2025 OPA858
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Device Comparison Table
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.6 Typical Characteristics
at VS+ = 2.5 V, VS– = –2.5 V, VIN+ = 0 V, RF = 453 Ω, gain = 7 V/V, RL = 200 Ω, output load referenced to midsupply, and TA = 25°C (unless otherwise noted)

| VOUT = 100 mVPP; see Figure 7-1 and Figure 7-2 for circuit configuration |

| VOUT = 100 mVPP |

| VOUT = 100 mVPP; see Figure 7-3 for circuit configuration |

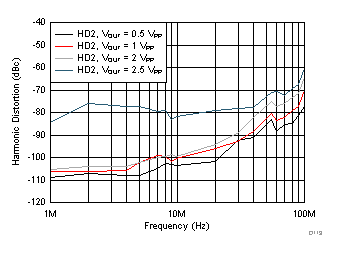
| VOUT = 2 VPP |

| Small-signal response |

| VOUT = 2 VPP |

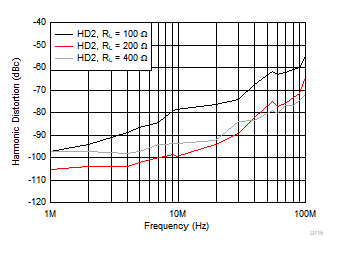
| VOUT = 2 VPP |
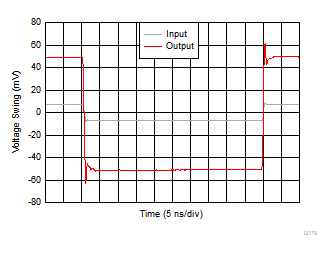
| Average rise-and-fall time (10%–90%) = 450 ps |
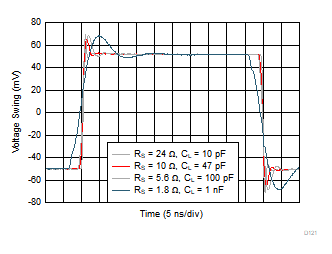
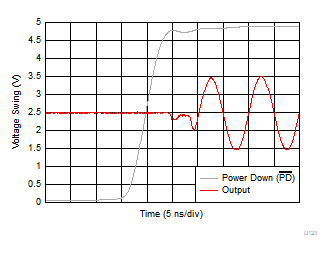
| VS+ = 5 V, VS– = ground |

| Small-signal response |
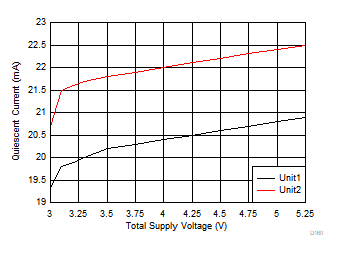
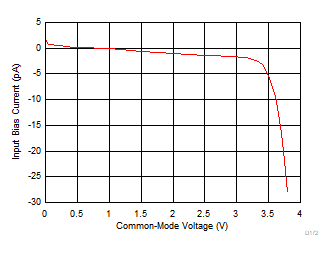
| 2 typical units |
| 30 units tested |
| µ = 1 µV/°C | σ = 2.2 µV/°C | 28 units tested |
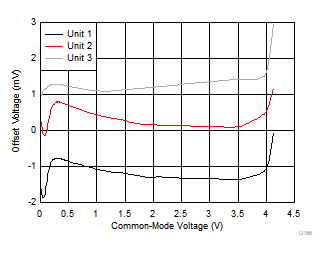
| VS = 5 V | 3 typical units |
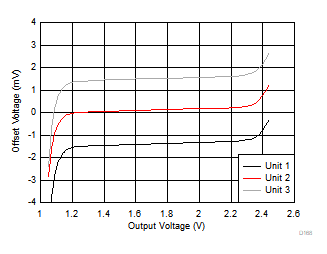
| VS = 3.3 V | 3 typical units |

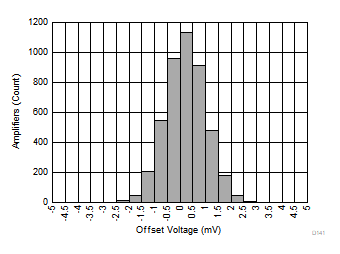
| µ = –0.28 mV | σ = 0.8 mV | 4555 units tested |

| VOUT = 100 mVPP | ||
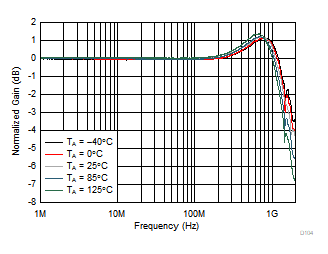
| VOUT = 100 mVPP |

| VOUT = 2 VPP |
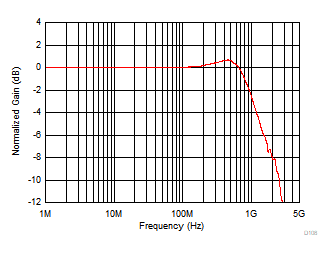
| VS = 3.3 V | VOUT = 1 VPP |

| Small-signal response |
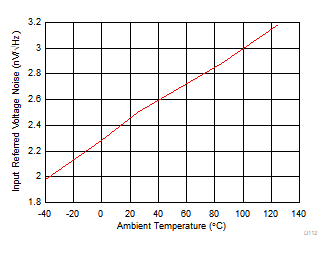
| Frequency = 10 MHz |
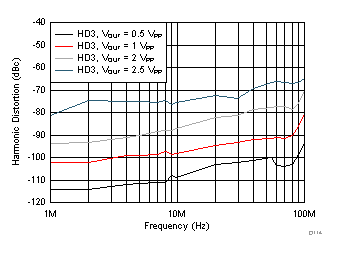

| VOUT = 2 VPP |

| VOUT = 2 VPP |

| Average rise-and-fall time (10%–90%) = 750 ps |

| 2 × output overdrive |

| VS+ = 5 V, VS– = ground |
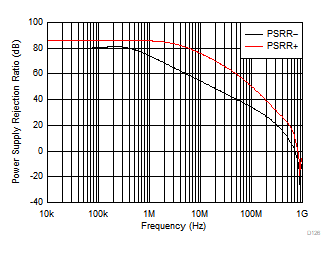
| Small-signal response |
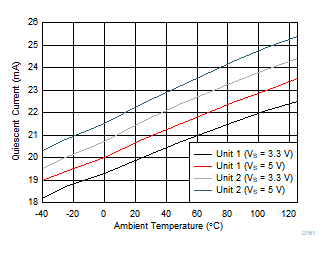
| 2 typical units |
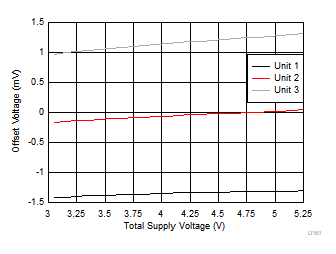
| 3 typical units |

| VS = 3.3 V | 3 typical units |
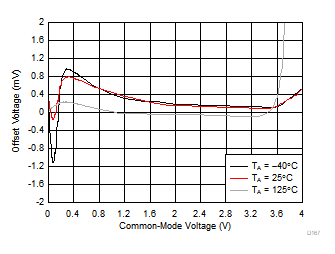

| VS = 5 V | 3 typical units |

| 3 typical units |

| µ = 20.35 mA | σ = 0.2 mA | 4555 units tested |

| µ = –0.1 pA | σ = 0.39 pA | 4555 units tested |