SBOU079D july 2009 – july 2023 INA220 , INA220-Q1
3.6 INA220 Jumper Settings
Figure 3-4 shows the default jumpers configuration for the INA220EVM. In general, the jumper settings of the USB DIG Platform will not need to be changed, but you may want to change some of the jumpers on the INA220_Test_Board to match your specific configuration. For instance, you may wish to set a specific I2C address.
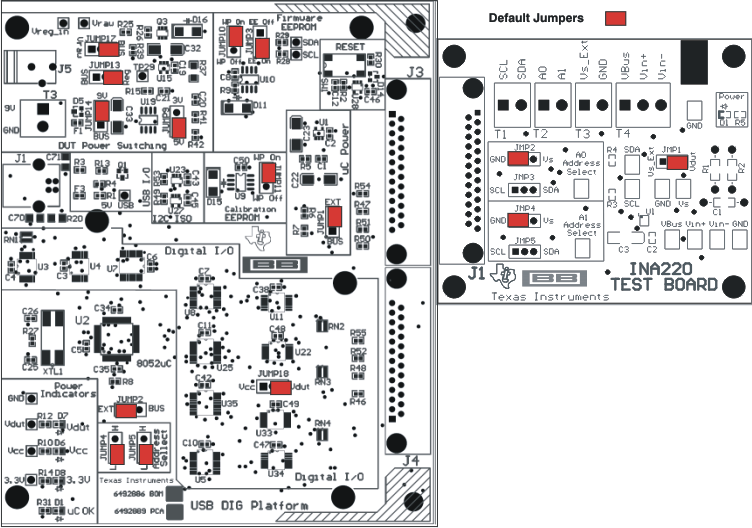 Figure 3-4 INA220EVM Default Jumper Settings
Figure 3-4 INA220EVM Default Jumper SettingsTable 3-1 explains the function of the jumpers on the INA220_Test_Board.
JUMPER | DEFAULT | PURPOSE |
|---|---|---|
| JMP1 | VDUT | This jumper determines the source for the INA220 power supply. In the Vdut position, the USB DIG board supplies the power to the INA220. In the Vs_Ext position, an external supply connected to the INA220 T3 terminal supplies power. |
| JMP2, JMP3 | JMP2 (GND) | A0 address input selection. This jumper determines which signal is connected to the A0 pin of the INA220. |
| JMP4, JMP5 | JMP4 (GND) | A1 address input selection. This jumper determines which signal is connected to the A1 pin of the INA220. |
Table 3-2 summarizes the function of the USB DIG platform jumpers. For most applications, the default jumper position will be used. Table 3-3 and Table 3-4 describe the options for the power-supply configuration. For example, the logic power supply can be changed from the default of 5 V to 3 V. A separate document (SBOU058) details the operation and design of the USB DIG platform.
| JUMPER | DEFAULT | PURPOSE |
|---|---|---|
| JUMP1 | EXT | This jumper selects external power or bus power. External power is applied on J5 (on USB DIG board) or T3 (9 VDC). Bus power is 5 V from the USB. External power is typically used because the USB power is noisy. |
| JUMP2 | EXT | Same as JUMP1. |
| JUMP3 | EE ON | This jumper determines where the TUSB3210 will load the USB DIG Platform firmware upon power-up or reset. The EE Off position is used for development for development or firmware updates. |
| JUMP4, JUMP5 | L, L | This jumper sets the address for the USB board. Only change from the default setting if using multiple boards. |
| JUMP9 | 5 V | This jumper selects the voltage of the device under test supply (VDUT = 5 V or 3 V). This jumper is typically the only jumper that is changed for most applications. |
| JUMP10 | WP ON | This jumper write-protects the firmware EEPROM. |
| JUMP11 | WP ON | This jumper write-protects the calibration EEPROM. |
| JUMP13 | Reg | This jumper uses the regulator output to generate the VDUT supply. The USB can be used as the VDUT supply. |
| JUMP14 | 9 V | This jumper uses the external power (9 V as apposed to the bus) |
| JUMP17 | BUS | While in the BUS position, VDUT operation is normal. While in the VRAW position, the VDUT supply is connected to an external source. This flexibility allows for any value of VDUT between 3 V and 5 V. CAUTION: When JUMP17 is in the VRAW position, adjusting the VDUT voltage beyond the 3 V to 5 V range will damage the EVM. |
| JUMP18 | VDUT | This jumper connects the pullup on the GPIO to the VDUT supply or the VCC supply. |
MODE | JUMPER | COMMENT |
|---|---|---|
| External Power—5V (default jumper settings) | JUMP17 = BUS (not used) JUMP13 = REG JUMP14 = 9 V JUMP1 = EXT JUMP2 = EXT JUMP6 = 5 V JUMP7 = REF | In this mode, all power is supplied to the EVM by J5 (on USB DIG board) or T3. The external supply must be between 5.8 V and 10.4 V for proper operation. All digital I/Os are regulated to 5 V using U19 (REG101). |
| External Power—3V (typical jumper settings) | JUMP17 = BUS (not used) JUMP13 = REG JUMP14 = 9 V JUMP1 = EXT JUMP2 = EXT JUMP6 = 3 V JUMP7 = REF | In this mode, all power is supplied to the EVM by J5 (on USB DIG board) or T3. The external supply must be between 5.8 V and 10.4 V for proper operation. All digital I/Os are regulated to 3 V using U19 (REG101). |
| External Power—Variable Supply | JUMP17 = Vraw JUMP13 = BUS JUMP14 = 9 V (not used) JUMP1 = EXT JUMP2 = EXT JUMP6 = 5 V (not used) JUMP7 = REG (ratiometric mode) | In this mode, all the digital I/Os are referenced to the supply that is attached to either J5 (on USB DIG board) or T3. CAUTION: The supply is directly applied to devices with 5.5 V absolute maximum ratings. This mode of operation is useful when a device supply other than 3.0 V or 5.0 V is required.It is absolutely critical that the supply voltage does not exceed 5.5 V in this mode. |
MODE | JUMPER | COMMENT |
|---|---|---|
| Bus Power—5V | JUMP17 = BUS JUMP13 = BUS JUMP14 = 9 V (not used) JUMP1 = BUS JUMP2 = BUS JUMP6 = 5 V (not used) JUMP7 = REG (ratiometric mode, 5-V supply) | In this mode, the USB bus completely powers the EVM. The USB bus is regulated by the controller (computer) to be 5 V. This mode relies upon external regulation. This mode is recommended only when an external 9-V supply is not available. If an external 9-V supply is available, use either External Power—5V mode or External Power—3V mode. |
| Bus Power—3V | JUMP17 = BUS (not used) JUMP13 = REG JUMP14 = BUS JUMP1 = BUS JUMP2 = BUS JUMP6 = 3 V JUMP7 = REG (ratiometric mode, 5-V supply) | In this mode, the USB bus completely powers the EVM. The regulator (U19, REG101) generates a 3-V supply for all digital I/O. |