SBOU157 September 2015
- Voxel Viewer
4.5 Temperature Calibration
The goal of temperature calibration is to derive a set of curve-fitting coefficients used in compensating phase drift due to temperature. Normally temperature calibration only needs to be done once per design. A thermal chamber is required to collect temperature-vs-phase data into a *.csv file format. Then the *.csv file is imported into Voxel Viewer in this step to compute the compensation coefficients. Each row of the *.csv file must contain three numbers separated by comma, with the following meaning:
<Tsensor>, <Tillum>, <Measured Phase>
<Tsensor> is the imaging sensor’s temperature; <Tillum> is the temperature of the illumination driver, both in °C. Typically the data is collected in about 1°C intervals.
Once the *.csv file is imported, click Calibrate, and the computed temperature coefficients will be displayed at the bottom of the window, as is shown in Figure 31.
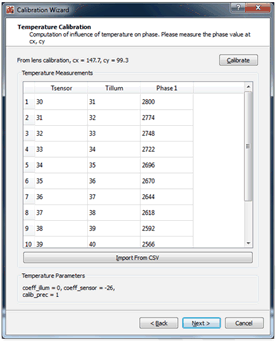 Figure 31. Temperature Calibration Window
Figure 31. Temperature Calibration Window