SLLA621A September 2023 – October 2023 MCF8315A , MCF8316A
1 Introduction
MCF831x is a code-free and sensorless field-oriented control (FOC) motor driver. MCF831x has a highly integrated architecture, incorporating three 1/2-H bridges with 40-V absolute maximum capability and a very low Rds(ON) of 95-mΩ (high-side + low-side) to enable high power drive capability. Current is sensed using an integrated current sensing circuit which eliminates the need for external sense resistors. An adjustable buck regulator and LDO generate the necessary voltage rails for the device and can be used to power external circuits. Due to their high level of integration, MCF831x devices can satisfy customers by driving their motors with only one chip. The EEPROM inside allows for stand-alone operation through power cycles.
Many customers feel that the flexibility of a code-free system is not sufficient, and that they cannot be programmed to achieve various desired functions like a microcontroller unit (MCU) can. However, MCF831x devices have many configuration registers which can be tuned to meet the needs of most customers. As mentioned at the beginning, for example, customers think that a high level of integration could lead to concerns about thermal performance, or they want to implement some specific functions, such as quick startup, fast braking, control speed precisely to achieve system-level requirements. These challenges can be controlled through the SCH, PCB layout, or EEPROM configuration.
The next step is with the thermals and the quick startup challenges, and discuss how to solve and optimize these challenges.
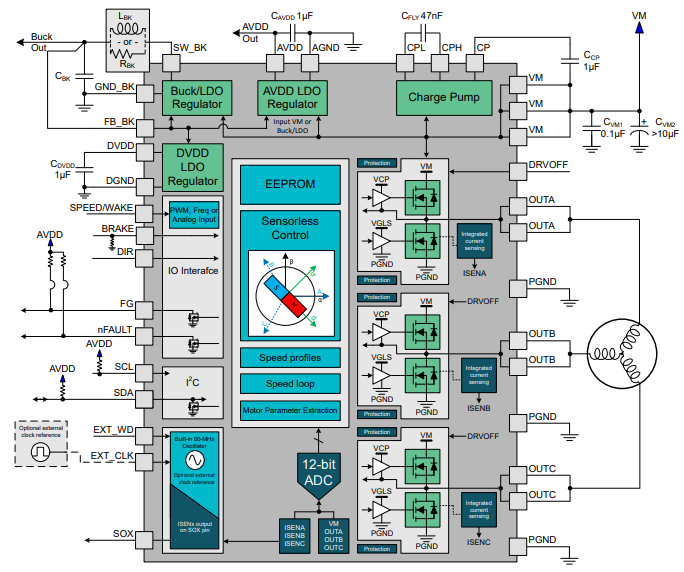 Figure 1-1 MCF831X Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 MCF831X Block Diagram