SLOA316 November 2021 TAS2764 , TAS2780 , TAS2781
2 Y-Bridge
Traditionally the output stage of Class D amplifier is connected to single power supply, PVDD, which is usually connected to high voltage (2S or 3S battery or an output of boost converter). At low voltage levels of the output signals where headroom needed is much smaller than the available headroom, a lower voltage power supply can be used without degrading the audio performance. Since usually high and low voltages are already available in a system, the Y-Bridge power savings can be achieved without having to change the power architecture of the system. The TI Y-Bridge class D amplifier dynamically shifts between the high voltage (PVDD, for example, 10V-23V) and low voltage (VBAT, for example, 2.7 V - 5 V) rails based on the power needed to deliver the necessary output level. Figure 2-1 shows the functional block diagram of TAS2780.
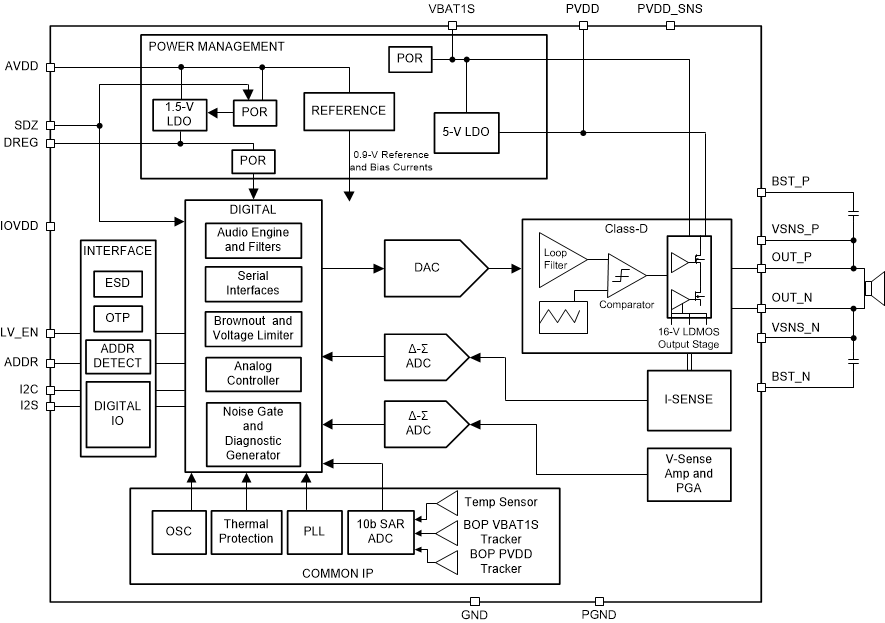 Figure 2-1 Functional Block Diagram
Figure 2-1 Functional Block DiagramThe TAS2780 Class-D output uses a Y-Bridge configuration to improve efficiency during playback. The simplified schematic of Y -Bridge topology is shown in Figure 2-2. As can be seen, both PVDD and VBAT are supplied to the device and connected to Class D output stage. The power supply of output stage is divided into two separate paths, one path connects the output to PVDD and another path connects the output to VBAT. For low and idle level signals, the class D output is connected to the low voltage VBAT rail. This reduces the class-D output swing for small or near Idle signals and thus limits the power consumption of the output stage.
The device can be configured to enable or disable Y-Bridge feature. If Y-bridge mode is disabled, it will only use the selected supply for class-D output. Note clipping can occur if appropriate supply is not selected.
Y-Bridge feature automatically switches between PVDD and VBAT1S. When audio signal increases and crosses a programmed threshold, Class-D output switches over to PVDD supply. When in Y-Bridge mode, if the PVDD falls below a threshold level, the Y-bridge will stop switching between supplies and will remain on the PVDD supply. The threshold for switching between the two supplies is programmable by user.
When voltage levels at OUT_P and OUT_M are switching from 0-V to VBAT1S, the switching losses are much lower when compared to switching between 0-V and PVDD which results in increase in power efficiency.
While switching loses are reduced by using a lower voltage, the conduction losses increases as the VBAT1S path of the output stage usually is designed with higher RDS on to optimize the switching losses. At low output levels, the net power consumption is improved as switching losses are dominant of the two losses.
The TAS2780 can be configured to operate without an external VBAT1S supply, when an internal LDO is used to generate supply voltage at this pin.