SLVSAX2B September 2011 – June 2020 TPS61170-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.7 Typical Characteristics
L = TOKO A915_Y-100M, D1 = ONsemi MBR0540T1, unless otherwise notedTable 1. Table of Graphs
| FIGURE | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | VIN = 5V; VOUT = 12 V, 18 V, 24 V, 30 V | Figure 17 | |
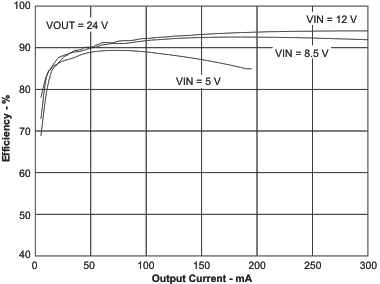
| Efficiency | VIN = 5 V, 8.5 V, 12 V; VOUT = 24 V | Figure 1 | |
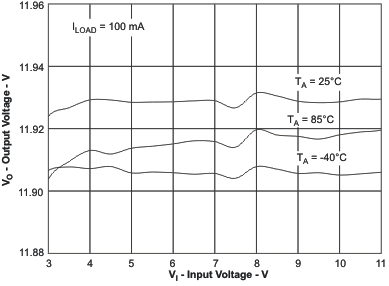
| Output voltage accuracy | ILOAD= 100 mA | Figure 2 | |
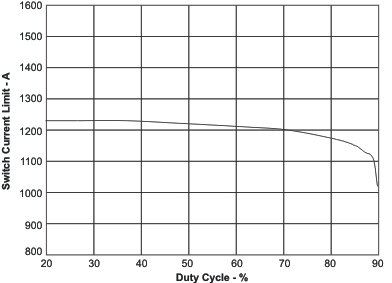
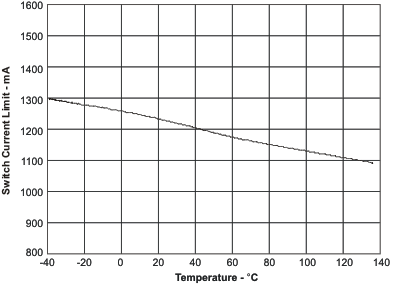
| Switch current limit | TA = 25°C | Figure 3 | |
| Switch current limit | Figure 4 | ||
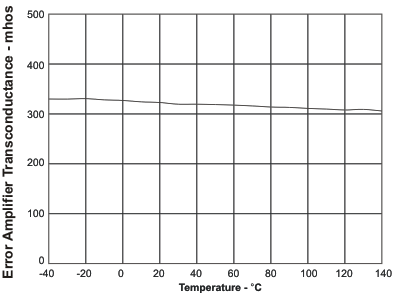
| Error amplifier transconductance | Figure 5 | ||
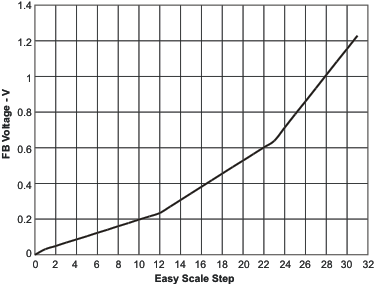
| EasyScale step | Figure 6 | ||
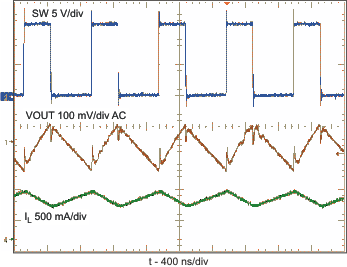
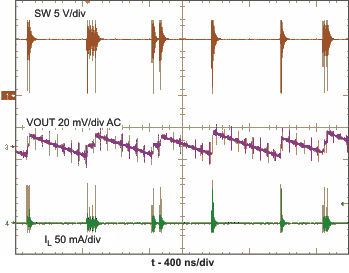
| PWM switching operation | VIN = 5 V; VOUT = 12 V; ILOAD= 250 mA | Figure 7 | |
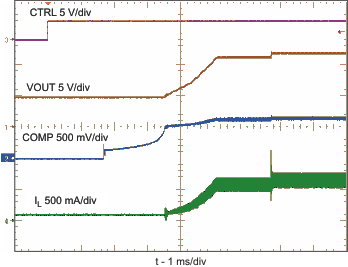
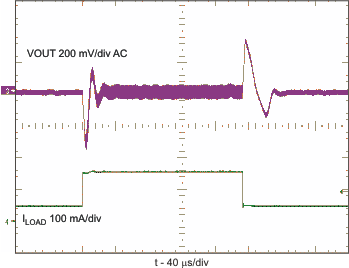
| Load transient response | VIN = 5 V; VOUT = 12 V; ILOAD= 50 mA to 150 mA | Figure 8 | |
| Start-up | VIN = 5 V; VOUT = 12 V; ILOAD= 250 mA | Figure 9 | |
| Skip-cycle switching | VIN = 9 V ; VOUT = 12 V, ILOAD= 100 μA | Figure 10 | |