SLVUAX8B November 2016 – August 2021 TPS54824
- Trademarks
- 1Introduction
-
2Test Setup and Results
- 2.1 Input/Output Connections
- 2.2 Efficiency
- 2.3 Output Voltage Load Regulation
- 2.4 Output Voltage Line Regulation
- 2.5 Load Transients
- 2.6 Loop Characteristics
- 2.7 Output Voltage Ripple
- 2.8 Input Voltage Ripple
- 2.9 Powering Up
- 2.10 Powering Down
- 2.11 Start-Up Into Pre-Bias
- 2.12 Hiccup Mode Current Limit
- 3Board Layout
- 4Schematic and Bill of Materials
- 5Revision History
2.12 Hiccup Mode Current Limit
Figure 2-17, Figure 2-18, and Figure 2-19 show the TPS54824EVM-779 hiccup mode current limit feature. When an overcurrent event occurs, the TPS54824EVM-779 shuts down and restarts. Figure 2-17 shows the restart sequence in an overcurrent condition. Figure 2-18 shows the TPS54824EVM-779 entering hiccup mode and Figure 2-19 shows the TPS54824EVM-779 exiting hiccup mode.
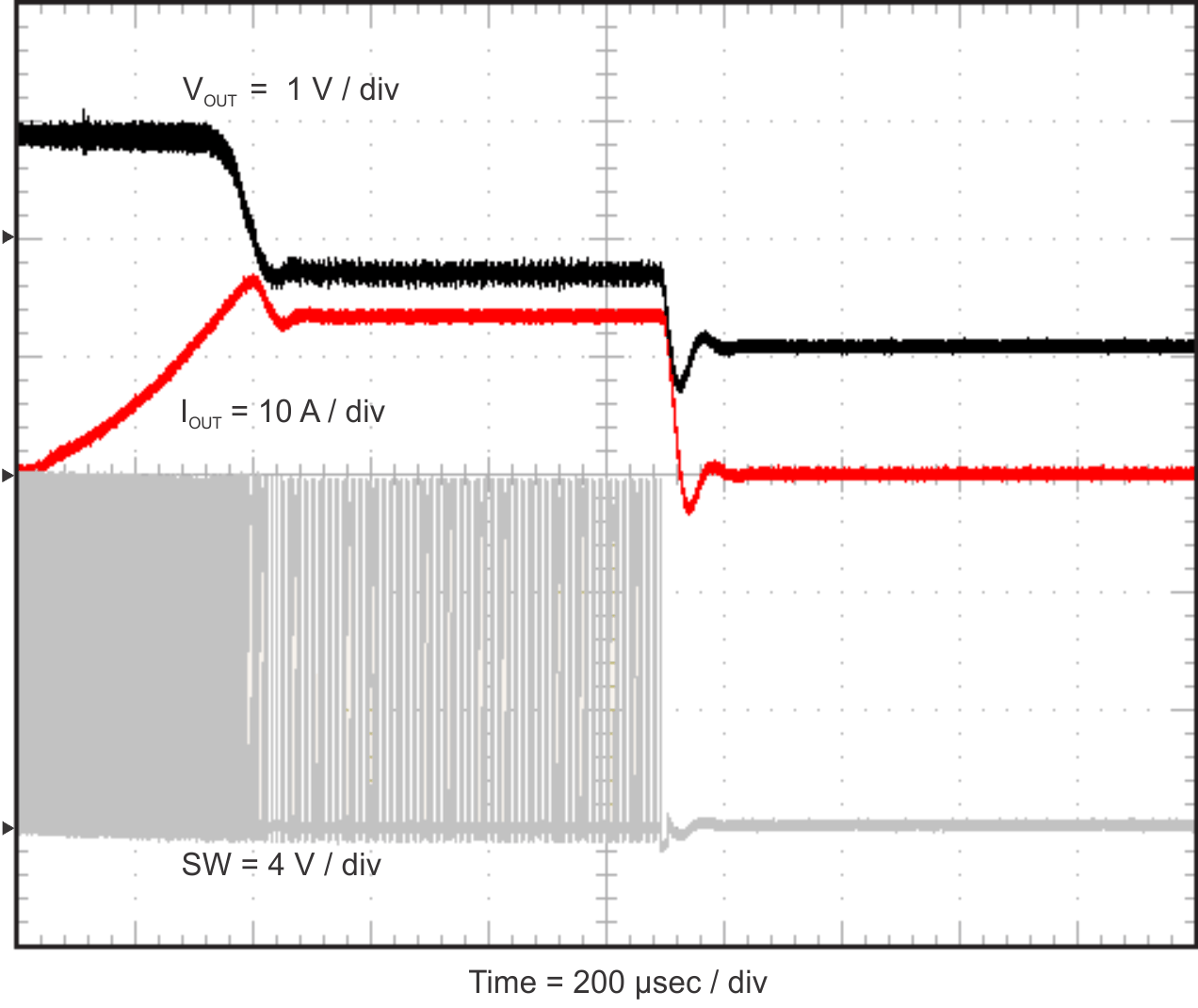 Figure 2-17 TPS54824EVM-779 Hiccup Mode
Current Limit
Figure 2-17 TPS54824EVM-779 Hiccup Mode
Current Limit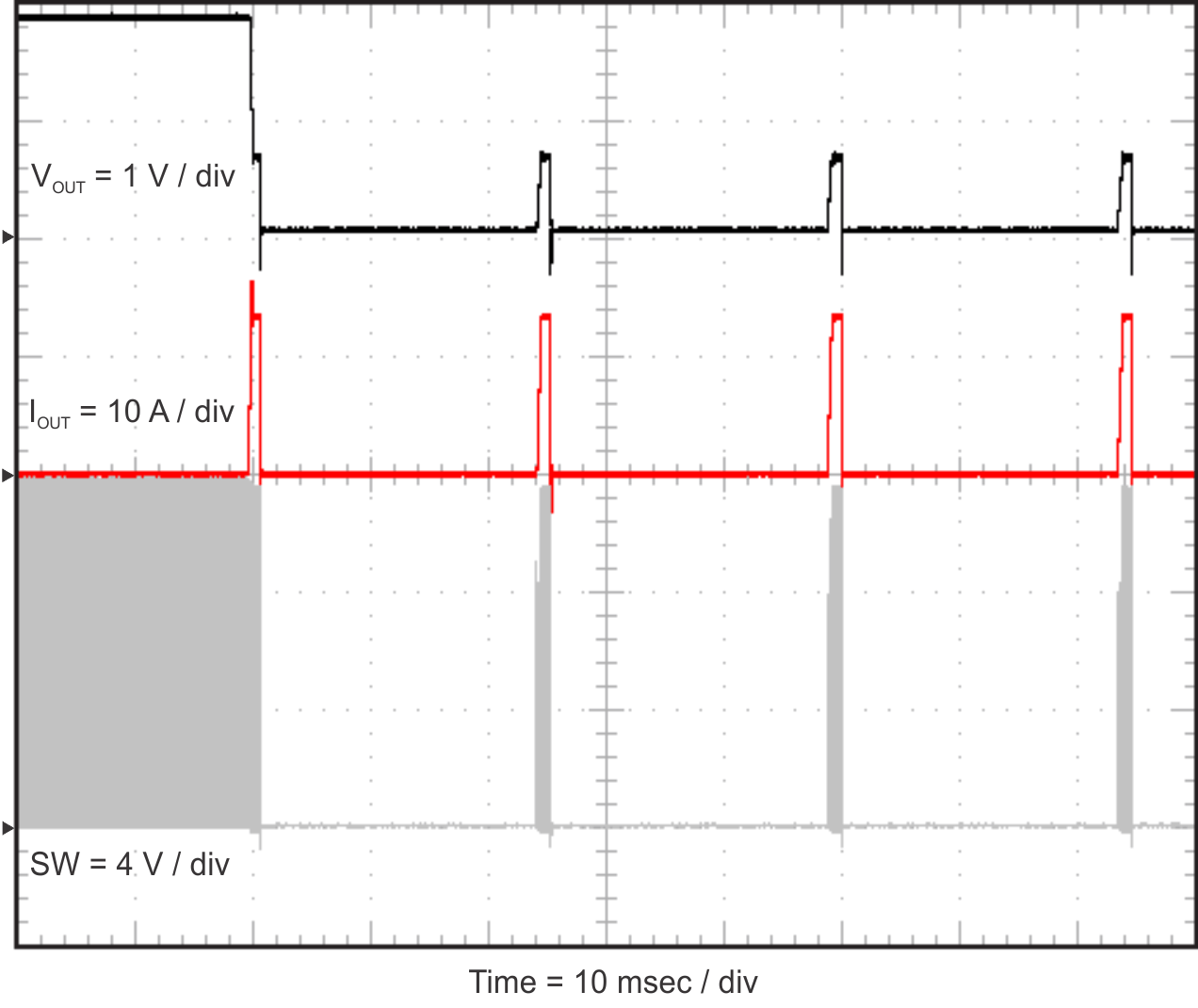 Figure 2-18 TPS54824EVM-779 Hiccup Mode
Start
Figure 2-18 TPS54824EVM-779 Hiccup Mode
Start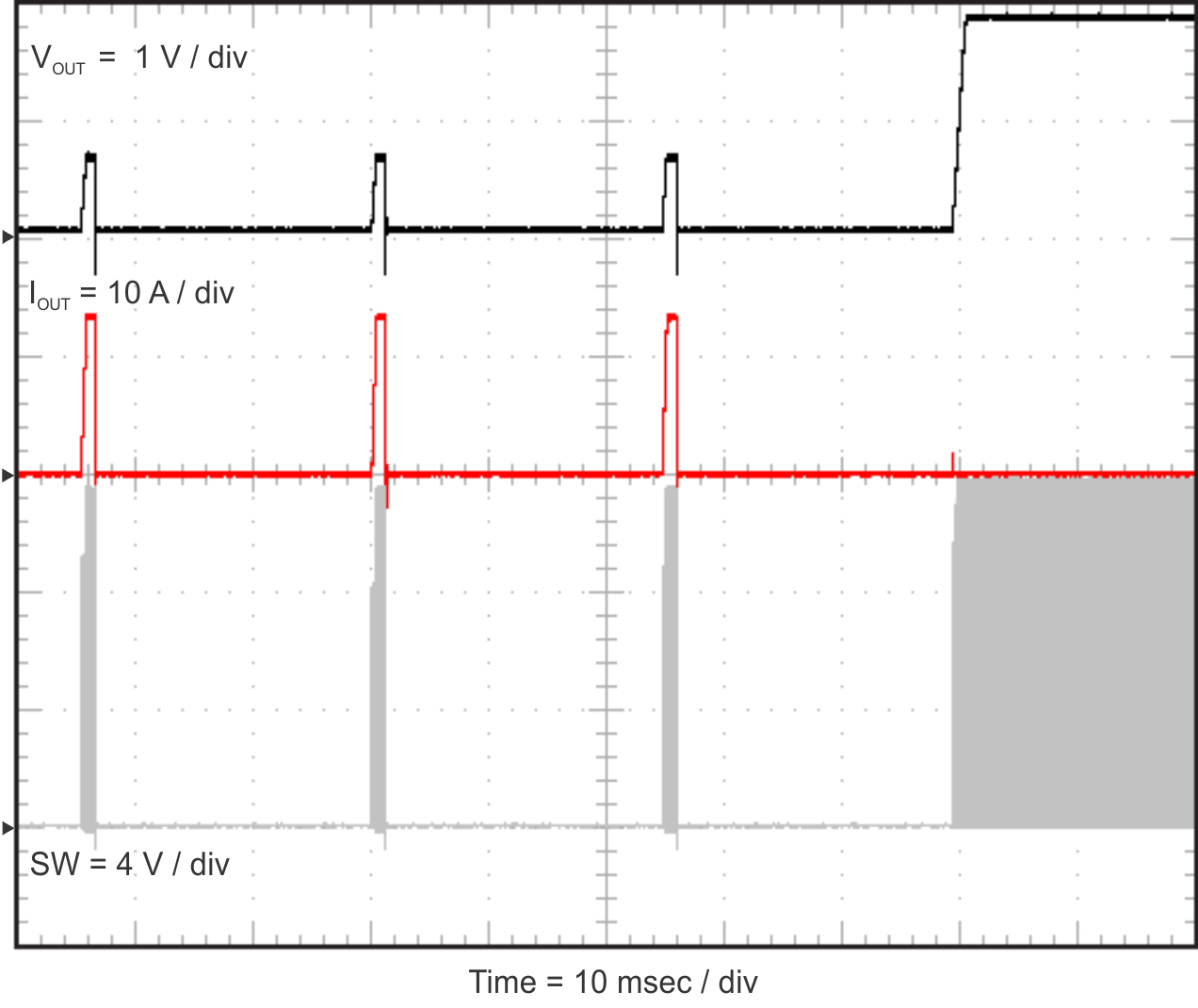 Figure 2-19 TPS54824EVM-779 Hiccup Mode
Stop
Figure 2-19 TPS54824EVM-779 Hiccup Mode
Stop