SNOA993A June 2018 – July 2021 LDC2112 , LDC2114 , LDC3114 , LDC3114-Q1
5.3 Button Actuation Time
The minimum button actuation time is the hysteresis value divided by the baseline increment. Figure 5-4 shows the output codes and OUTx assertion for the same stimuli with different baseline increment settings. Larger values of baseline increment can effectively “turn-off” a button before the actual stimuli has been removed.
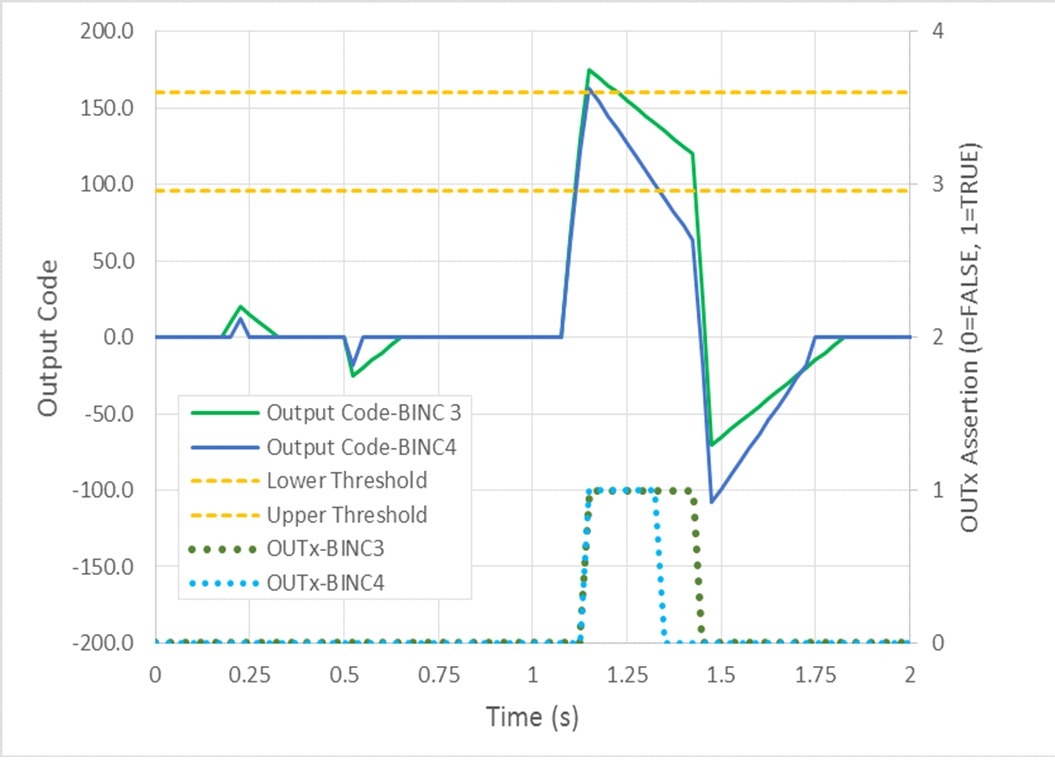 Figure 5-4 Effect of Baseline Increment
on Minimum Actuation time
Figure 5-4 Effect of Baseline Increment
on Minimum Actuation time