SPRAC71B February 2019 – October 2023
- 1
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Data Representation
-
3 Calling Conventions
- 3.1 Call and Return
- 3.2 Register Conventions
- 3.3 Argument Passing
- 3.4 Return Values
- 3.5 Structures and Unions Passed and Returned by Reference
- 3.6 Conventions for Compiler Helper Functions
- 3.7 Prolog and Epilog Helper Functions
- 3.8 Scratch Registers for Functions Already Seen
- 3.9 Interrupt Functions
- 4 Data Allocation and Addressing
- 5 Code Allocation and Addressing
- 6 Helper Function API
-
7 Standard C Library API
- 7.1 About Standard C Libraries
- 7.2 Reserved Symbols
- 7.3 <assert.h> Implementation
- 7.4 <complex.h> Implementation
- 7.5 <ctype.h> Implementation
- 7.6 <errno.h> Implementation
- 7.7 <float.h> Implementation
- 7.8 <inttypes.h> Implementation
- 7.9 <iso646.h> Implementation
- 7.10 <limits.h> Implementation
- 7.11 <locale.h> Implementation
- 7.12 <math.h> Implementation
- 7.13 <setjmp.h> Implementation
- 7.14 <signal.h> Implementation
- 7.15 <stdarg.h> Implementation
- 7.16 <stdbool.h> Implementation
- 7.17 <stddef.h> Implementation
- 7.18 <stdint.h> Implementation
- 7.19 <stdio.h> Implementation
- 7.20 <stdlib.h> Implementation
- 7.21 <string.h> Implementation
- 7.22 <tgmath.h> Implementation
- 7.23 <time.h> Implementation
- 7.24 <wchar.h> Implementation
- 7.25 <wctype.h> Implementation
-
8 C++ ABI
- 8.1 Limits (GC++ABI 1.2)
- 8.2 Export Template (GC++ABI 1.4.2)
- 8.3 Data Layout (GC++ABI Chapter 2)
- 8.4 Initialization Guard Variables (GC++ABI 2.8)
- 8.5 Constructor Return Value (GC++ABI 3.1.5)
- 8.6 One-Time Construction API (GC++ABI 3.3.2)
- 8.7 Controlling Object Construction Order (GC++ ABI 3.3.4)
- 8.8 Demangler API (GC++ABI 3.4)
- 8.9 Static Data (GC++ ABI 5.2.2)
- 8.10 Virtual Tables and the Key function (GC++ABI 5.2.3)
- 8.11 Unwind Table Location (GC++ABI 5.3)
-
9 Exception Handling
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 PREL31 Encoding
- 9.3 The Exception Index Table (EXIDX)
- 9.4 The Exception Handling Instruction Table (EXTAB)
- 9.5 Unwinding Instructions
- 9.6 Descriptors
- 9.7 Special Sections
- 9.8 Interaction With Non-C++ Code
- 9.9 Interaction With System Features
- 9.10 Assembly Language Operators in the TI Toolchain
- 10DWARF
- 11ELF Object Files (Processor Supplement)
- 12ELF Program Loading and Linking (Processor Supplement)
- 13Build Attributes
- 14Copy Tables and Variable Initialization
- 15Revision History
13.2 C28x ABI Build Attribute Subsection
Attributes that are specified by this ABI are recorded in the subsection with the vendor string C28x. Toolchains should determine compatibility between relocatable files using solely these attributes; vendor-specific information should not be used other than as permitted by the Tag_Compatibility attribute which is provided for this purpose.
The vendor data in the C28x subsection contains any number of attribute vectors. Attribute vectors begin with a scope tag that specifies whether they apply to the entire file or only to listed sections or symbols. An attribute vector has one of the following three formats:
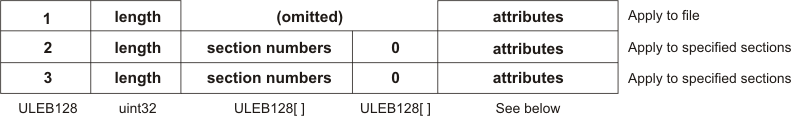
The length field specifies the length in bytes of the entire attribute vector, including the other fields. The symbol and section number fields are sequences of section or symbol indexes, terminated with 0.
Attributes in an attribute vector are represented as a sequence of tag-value pairs. Tags are represented as ULEB128 constants. Values are either ULEB128 constants or NULL-terminated strings.
The effect of omitting a tag in the file scope is identical to including it with a value of 0 or "", depending on the parameter type.
To allow a consumer to skip unrecognized tags, the parameter type is standardized as ULEB128 for even-numbered tags and a NULL-terminated string for odd-numbered tags. Tags 1, 2, 3 (the scope tags) and 32 (Tag_ABI_Compatibility) are exceptions to this convention.
As the ABI evolves, new attributes may be added. To enable older toolchains to robustly process files that may contain attributes they do not comprehend, the ABI adopts the following conventions:
- Tags 0-63 must be comprehended by a consuming tool. A consuming tool may choose to generate an error if an unknown tag in this range is encountered.
- Tags 64-127 convey information a consumer can ignore safely.
- For N >= 128, tag N has the same property as tag N modulo 128.