TIDT278 April 2022
3.2 Input Voltage Ripple
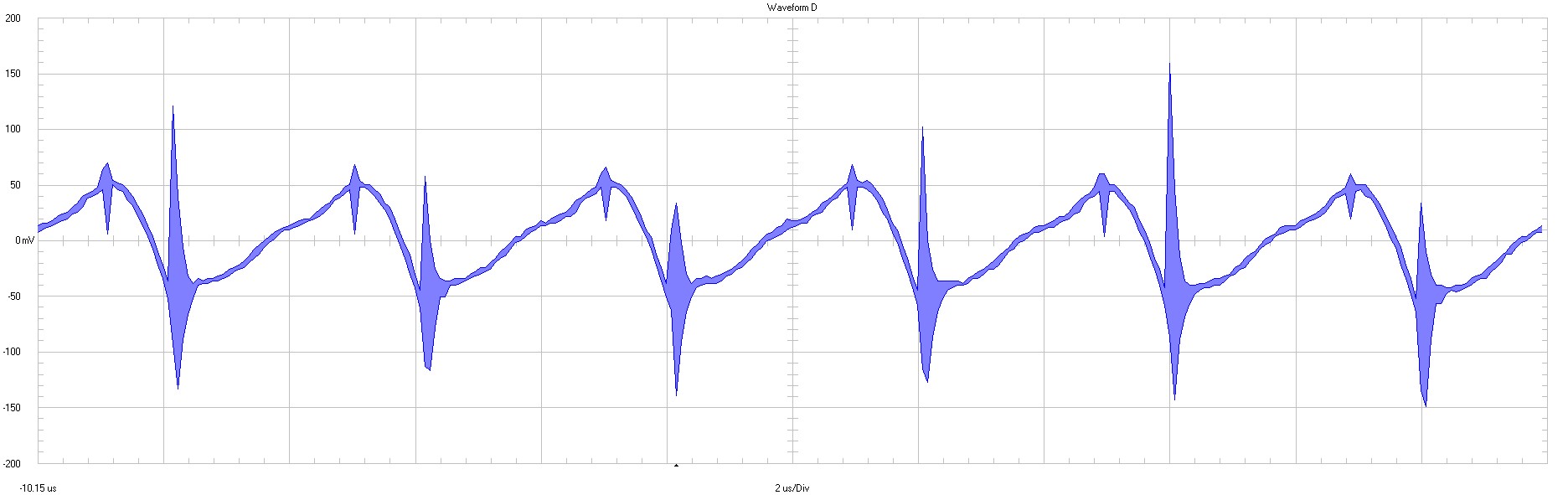
|
Power stage in 50 mV / div 2 µs / div 20 MHz bandwidth |
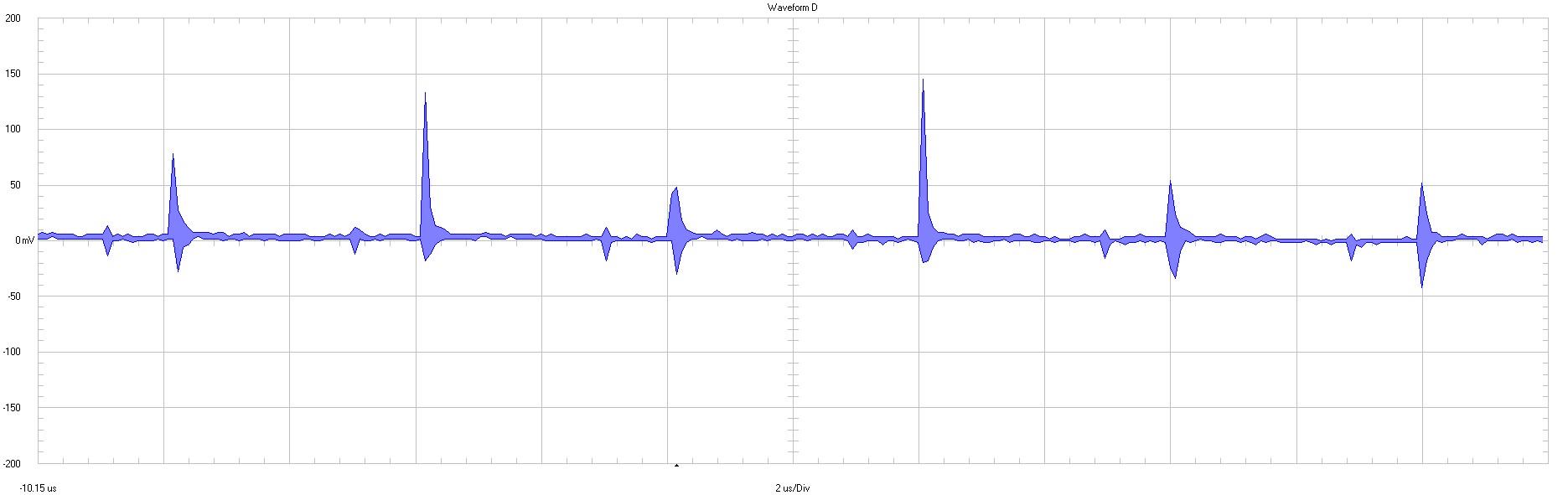
|
between D9 and L1 50 mV / div 2 µs / div 20 MHz bandwidth |
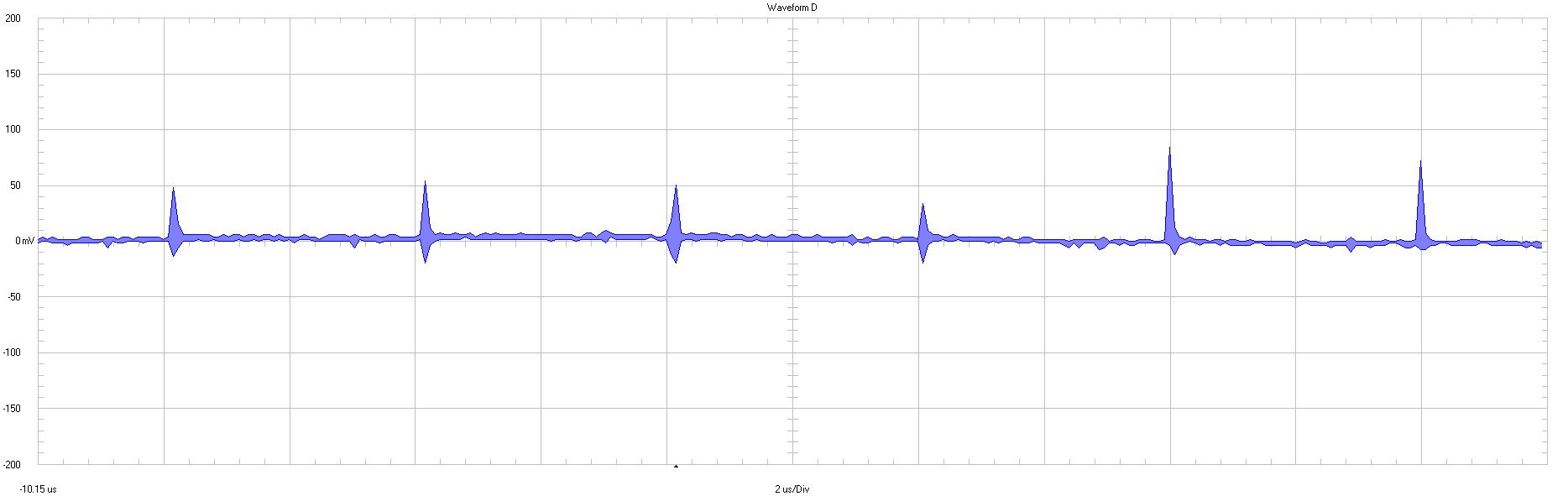
|
Jmp1 50 mV / div 2 µs / div 20 MHz bandwidth |
Figure 3-4 Input Voltage
Ripple
The input filter is attenuating the reflected ripple (= conducted emissions).
To attenuate RF spikes further a ferrite bead (600 Ω at 100 MHz) could be added to the input.
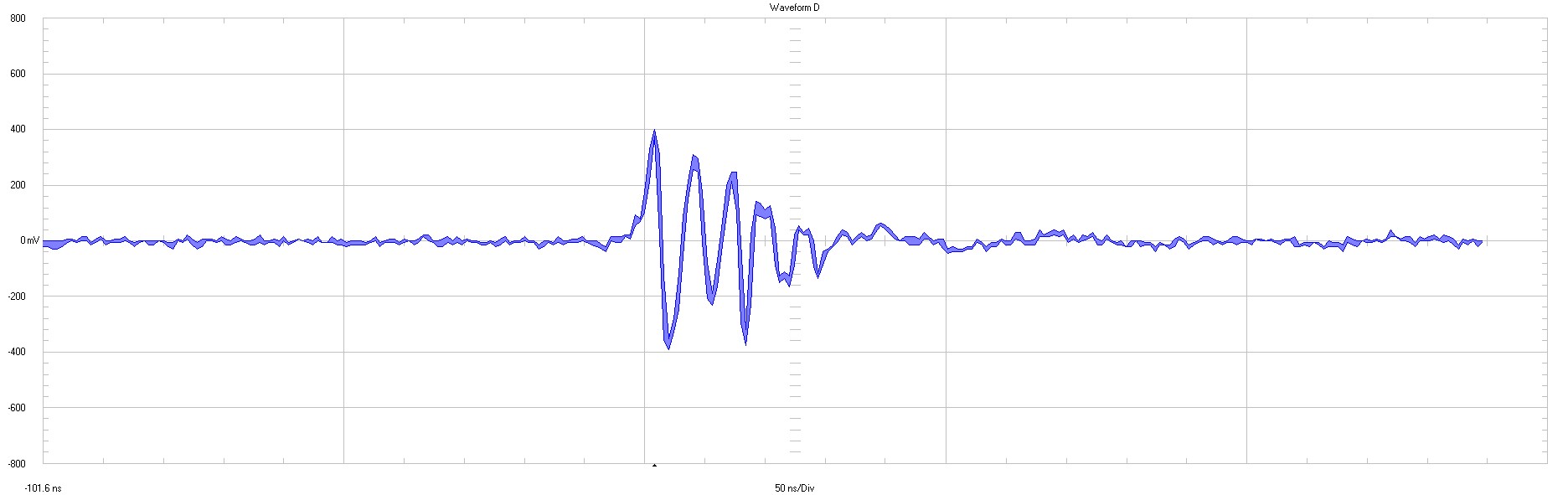
|
Jmp1 200 mV / div 50 ns / major div full bandwidth |
Figure 3-5 Input Ripple (Jmp1 Zoomed and
Full Bandwidth)