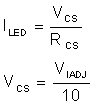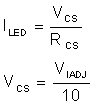TIDUEW9 April 2020
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- Design Images
- 1System Overview
- 2LED Driver Key Parameters
- 3Layout
- 4Related Documentation
1.7 Setting the LED Current and Analog Dimming
Average LED current regulation is set by using a sense resistor in-series with the LEDs. The internal error amplifier regulates the voltage across the sense resistor (VCS) to the IADJ voltage divided by 10. IADJ can be set to any value up to 2.54 V by connecting it to VREF through a resistor divider for static output current settings. IADJ can also be used to change the regulation point if connected to a controlled voltage source or potentiometer to provide analog dimming. The ILED setting is based on the equations in Equation 1.
Equation 1.