SBOS831B December 2016 – June 2021 THS4552
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: (VS+) – (VS–) = 5 V
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: (VS+) – (VS–) = 3 V
- 6.7 Typical Characteristics: (VS+) – (VS–) = 5 V
- 6.8 Typical Characteristics: (VS+) – (VS–) = 3 V
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics: 3 V to 5 V Supply Range
-
7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 7.1 Example Characterization Circuits
- 7.2 Output Interface Circuit for DC-Coupled Differential Testing
- 7.3 Output Common-Mode Measurements
- 7.4 Differential Amplifier Noise Measurements
- 7.5 Balanced Split-Supply Versus Single-Supply Characterization
- 7.6 Simulated Characterization Curves
- 7.7 Terminology and Application Assumptions
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1
Application Information
- 9.1.1 Noise Analysis
- 9.1.2 Factors Influencing Harmonic Distortion
- 9.1.3 Driving Capacitive Loads
- 9.1.4 Interfacing to High-Performance Precision ADCs
- 9.1.5 Operating the Power Shutdown Feature
- 9.1.6 Channel-to-Channel Crosstalk
- 9.1.7 Channel-to-Channel Mismatch
- 9.1.8 Designing Attenuators
- 9.1.9 The Effect of Adding a Feedback Capacitor
- 9.2 Typical Applications
- 9.1
Application Information
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTW|24
Orderable Information
9.2.3 ADC3k Driver with a 2nd-Order RLC Interstage Filter Application
The THS4552 is well suited to low-power,
dc-coupled requirements driving low-power pipeline
ADCs (such as the ADC3241 25-MSPS, 14-bit,
dual device). Figure 9-20 shows an example design taking a bipolar input
to a
–1 dBFS swing
at the ADC input of 1.8 VPP. In this
case, a 50 Ω source and input matching is assumed
with a gain of 5 V/V to the output pins with a
2nd-order interstage filter adding a –1 dB
insertion loss. Full-scale voltage at the input of
RT and RG1 is then ±0.2 V.
The 0.95 V output common-mode voltage is provided
by the ADC. The output filter provides a
noise-power bandwidth limit with a low overshoot
step response with no common-mode level shift from
the 0.95 V voltage provided by the ADC.
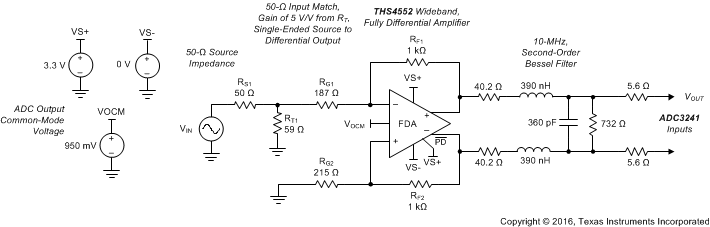 Figure 9-20 ADC3k Driver with a 2nd-Order RLC Interstage
Filter
Figure 9-20 ADC3k Driver with a 2nd-Order RLC Interstage
Filter