SLUSD62 December 2017 TPS40345
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.2 Inductor Selection (L1)
- 8.2.2.3 Output Capacitor Selection (C12)
- 8.2.2.4 Peak Current Rating of Inductor
- 8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor Selection (C8)
- 8.2.2.6 MOSFET Switch Selection (Q1 and Q2)
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor (C6)
- 8.2.2.8 VDD Bypass Capacitor (C7)
- 8.2.2.9 BP Bypass Capacitor (C5)
- 8.2.2.10 Short-Circuit Protection (R11)
- 8.2.2.11 Feedback Divider (R4, R5)
- 8.2.2.12 Compensation: (C2, C3, C4, R3, R6)
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRC|10
Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VDD | –0.3 | 22 | V |
| SW | –3 | 27 | V |
| SW (< 100 ns pulse width, 10 µJ) | –5 | V | |
| BOOT | –0.3 | 30 | V |
| HDRV | –5 | 30 | V |
| BOOT-SW, HDRV-SW (differential from BOOT or HDRV to SW) | –0.3 | 7 | V |
| COMP, PGOOD, FB, BP, LDRV, EN/SS | –0.3 | 7 | V |
| Operating junction temperature, TJ | –40 | 145 | °C |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –55 | 150 | °C |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device at these or any other condition beyond those included under Recommended Operating Conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods of time may affect device reliability.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1500 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input voltage, VDD | 3 | 20 | V | ||
| Operating junction temperature, TJ | –20 | 125 | °C | ||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TPS40345 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DRC (VSON) | |||
| 10 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 44.3 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 56.1 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 19.2 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.7 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 19.4 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 5.5 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
TJ = –20°C to 125°C, VVDD = 12 V, all parameters at zero power dissipation (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOLTAGE REFERENCE | |||||||
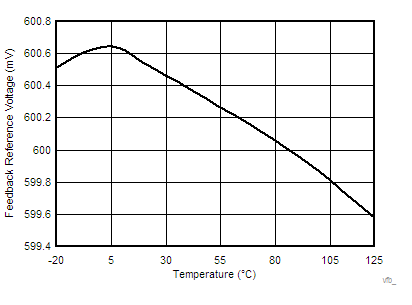
| VFB | FB input voltage | TJ = 25°C, 3 V < VVDD < 20 V | 597 | 600 | 603 | mV | |
| –20°C < TJ < 125°C, 3 V < VVDD < 20 V | 592 | 600 | 608 | ||||
| INPUT SUPPLY | |||||||
| VVDD | Input supply voltage range | 3 | 20 | V | |||
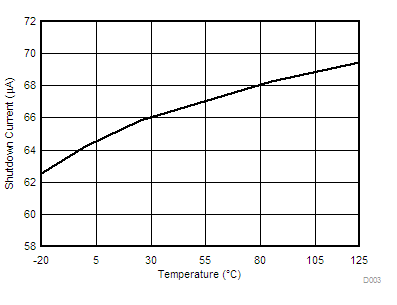
| IDDSD | Shutdown supply current | VEN/SS < 0.2 V | 70 | 100 | µA | ||
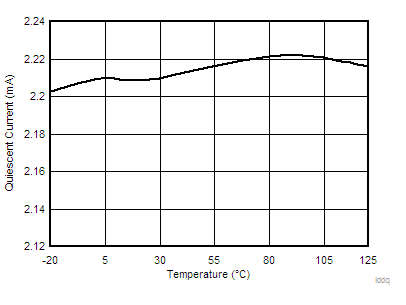
| IDDQ | Quiescent, nonswitching | Let EN/SS float, VFB = 1 V | 2.5 | 3.5 | mA | ||
| ENABLE/SOFT-START | |||||||
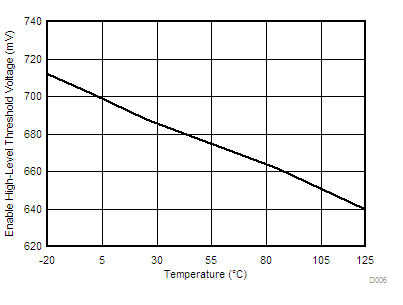
| VIH | High-level input voltage, EN/SS | 0.55 | 0.7 | 1 | V | ||
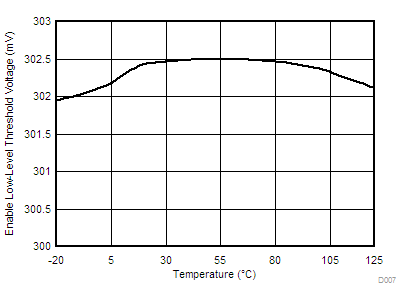
| VIL | Low-level input voltage, EN/SS | 0.27 | 0.3 | 0.33 | V | ||
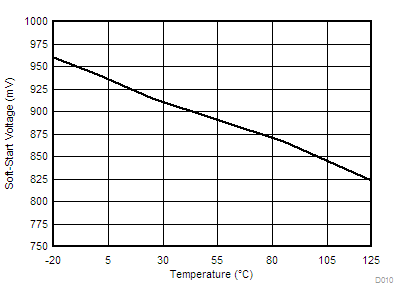
| ISS | Soft-start source current | 8 | 10 | 12 | µA | ||
| VSS | Soft-start voltage level | 0.4 | 0.8 | 1.3 | V | ||
| BP REGULATOR | |||||||
| VBP | Output voltage | IBP = 10 mA | 6.2 | 6.5 | 6.8 | V | |
| VDO | Regulator dropout voltage, VVDD – VBP | IBP = 25 mA, VVDD = 3 V | 70 | 110 | mV | ||
| OSCILLATOR | |||||||
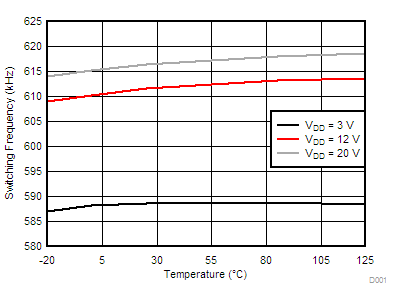
| fSW | PWM frequency | 540 | 600 | 660 | kHz | ||
| VRAMP(1) | Ramp amplitude | VVDD/6.6 | VVDD/6 | VVDD/5.4 | V | ||
| fSWFSS | Frequency spread-spectrum frequency deviation | 12% | fSW | ||||
| fMOD | Modulation frequency | 25 | kHz | ||||
| PWM | |||||||
| DMAX (1) | Maximum duty cycle | VFB = 0 V, 3 V < VVDD < 20 V | 90% | ||||
| tON(min)(1) | Minimum controllable pulse width | 70 | ns | ||||
| tDEAD | Output driver dead time | HDRV off to LDRV on | 5 | 25 | 35 | ns | |
| LDRV off to HDRV on | 5 | 25 | 30 | ||||
| ERROR AMPLIFIER | |||||||
| GBWP (1) | Gain bandwidth product | 10 | 24 | MHz | |||
| AOL (1) | Open loop gain | 60 | dB | ||||
| IIB | Input bias current (current out of FB pin) | VFB = 0.6 V | 75 | nA | |||
| IEAOP | Output source current | VFB = 0 V | 2 | mA | |||
| IEAOM | Output sink current | VFB = 1 V | 2 | ||||
| PGOOD | |||||||
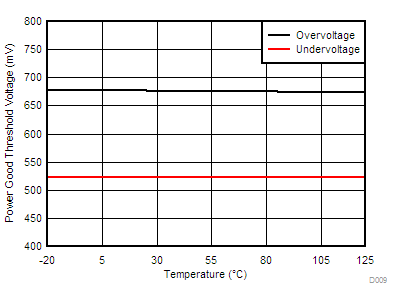
| VOV | Feedback upper voltage limit for PGOOD | 655 | 675 | 700 | mV | ||
| VUV | Feedback lower voltage limit for PGOOD | 500 | 525 | 550 | |||
| VPGD-HYST | PGOOD hysteresis voltage at FB | 25 | 40 | ||||
| RPGD | PGOOD pulldown resistance | VFB = 0 V, IFB = 5 mA | 30 | 70 | Ω | ||
| IPGDLK | PGOOD leakage current | 550 mV < VFB < 655 mV, VPGOOD = 5 V |
10 | 20 | µA | ||
| OUTPUT DRIVERS | |||||||
| RHDHI | High-side driver pullup resistance | VBOOT – VSW = 5 V, IHDRV = –100 mA | 0.8 | 1.5 | 2.5 | Ω | |
| RHDLO | High-side driver pulldown resistance | VBOOT – VSW = 5 V, IHDRV = 100 mA | 0.5 | 1 | 2.2 | Ω | |
| RLDHI | Low-side driver pullup resistance | ILDRV = -100 mA | 0.8 | 1.5 | 2.5 | Ω | |
| RLDLO | Low-side driver pulldown resistance | ILDRV = 100 mA | 0.35 | 0.6 | 1.2 | Ω | |
| tHRISE (1) | High-side driver rise time | CLOAD = 5 nF | 15 | ns | |||
| tHFALL(1) | High-side driver fall time | 12 | ns | ||||
| tLRISE(1) | Low-side driver rise time | 15 | ns | ||||
| tLFALL(1) | Low-side driver fall time | 10 | ns | ||||
| OVERCURRENT PROTECTION | |||||||
| tPSSC(min)(1) | Minimum pulse time during short circuit | 250 | ns | ||||
| tBLNKH(1) | Switch leading-edge blanking pulse time | 150 | ns | ||||
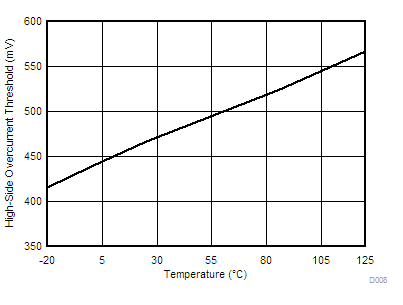
| VOCH | OC threshold for high-side FET | TJ = 25°C | 360 | 450 | 580 | mV | |
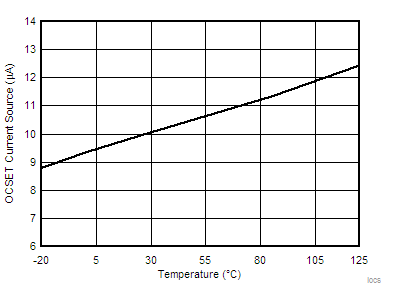
| IOCSET | OCSET current source | TJ = 25°C | 9.5 | 10 | 10.5 | µA | |
| VLD-CLAMP | Maximum clamp voltage at LDRV | 260 | 340 | 400 | mV | ||
| VOCLOS | OC comparator offset voltage for low-side FET | TJ = 25°C | –8 | 8 | mV | ||
| VOCLPRO(1) | Programmable OC range for low-side FET | TJ = 25°C | 12 | 300 | mV | ||
| VTHTC(1) | OC threshold temperature coefficient (both high-side and low-side) | 3000 | ppm | ||||
| tOFF | OC retry cycles on EN/SS pin | 4 | Cycle | ||||
| BOOT DIODE | |||||||
| VDFWD | Bootstrap diode forward voltage | IBOOT = 5 mA | 0.8 | V | |||
| THERMAL SHUTDOWN | |||||||
| TJSD(1) | Junction shutdown temperature | 145 | °C | ||||
| TJSDH(1) | Hysteresis | 20 | °C | ||||
(1) Ensured by design. Not production tested.
6.6 Typical Characteristics