JAJSHV5B June 2017 – August 2019 ADS1287
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特長
- 2 アプリケーション
- 3 概要
- 4 改訂履歴
- 5 概要(続き)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5
Programming
- 9.5.1 Serial Interface
- 9.5.2
Commands
- 9.5.2.1 WAKEUP: Wake Up Command
- 9.5.2.2 STANDBY: Standby Mode Command
- 9.5.2.3 SYNC: Synchronize ADC Conversions
- 9.5.2.4 RESET: Reset Command
- 9.5.2.5 RDATAC: Read Data Continuous Mode Command
- 9.5.2.6 SDATAC: Stop Read Data Continuous Mode Command
- 9.5.2.7 RDATA: Read Data Command
- 9.5.2.8 RREG: Read Register Data Command
- 9.5.2.9 WREG: Write Register Data Command
- 9.5.2.10 OFSCAL: Offset Calibration Command
- 9.5.2.11 GANCAL: Gain Calibration Command
- 9.6
Register Map
- 9.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 9.6.1.1 ID/CFG: ID, Configuration Register (address = 00h) [reset = x0h]
- 9.6.1.2 CONFIG0: Configuration Register 0 (address = 01h) [reset = 52h]
- 9.6.1.3 CONFIG1: Configuration Register 1 (address = 02h) [reset = 08h]
- 9.6.1.4 High-Pass Filter Corner Frequency (HPFx) Registers (address = 03h, 04h) [reset = 32h, 03h]
- 9.6.1.5 Offset Calibration (OFCx) Registers (address = 05h, 06h, 07h) [reset = 00h, 00h, 00h]
- 9.6.1.6 Full-Scale Calibration (FSCx) Registers (address = 08h, 09h, 0Ah) [reset = 00h, 00h, 40h]
- 9.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13デバイスおよびドキュメントのサポート
- 14メカニカル、パッケージ、および注文情報
パッケージ・オプション
デバイスごとのパッケージ図は、PDF版データシートをご参照ください。
メカニカル・データ(パッケージ|ピン)
- RHF|24
サーマルパッド・メカニカル・データ
発注情報
9.5.2.8 RREG: Read Register Data Command
The RREG command is used to read a single register byte or to read multiple register bytes. The command consists of a two-byte argument followed by the output of register data. The first byte of the command is the register starting address, and the second byte specifies the number of registers to read minus one.
First command byte: 001r rrrr, where rrrrr is the starting address of the first register.
Second command byte: 000n nnnn, where nnnnn is the number of registers to read minus one.
In the read register data example sequence shown in Figure 66, with the 24th falling edge of SCLK, the first register data bit appears on DOUT. Read the first bit of register data on the 25th SCLK rising edge.
See the Timing Requirements table for the specification of the td(CMBT) parameter.
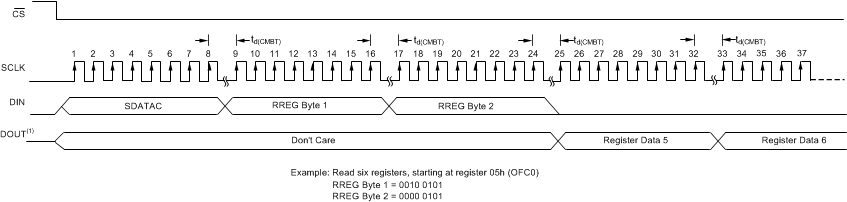
In read-data-continuous mode, the output data shift register is written with new conversion data just before DRDY transitions low. To avoid conflicting data between conversion data and register data, send the SDATAC command before reading register data. The SDATAC command disables loading of conversion data into the output data shift register. Keep CS low between the SDATAC command and the read register command because CS high cancels the SDATAC mode.