JAJU858 December 2022
- 概要
- リソース
- 特長
- アプリケーション
- 5
- 1System Description
-
2System Overview
- 2.1 Block Diagram
- 2.2
Design Considerations
- 2.2.1
Isolated AC/DC Power Supply Design
- 2.2.1.1 Input Bulk Capacitance and Minimum Bulk Voltage
- 2.2.1.2 Transformer Turns-Ratio, Primary Inductance, and Primary Peak Current
- 2.2.1.3 Transformer Parameter Calculations: Primary and Secondary RMS Currents
- 2.2.1.4 Main Switching Power MOSFET Selection
- 2.2.1.5 Rectifying Diode Selection
- 2.2.1.6 Output Capacitor Selection
- 2.2.1.7 Capacitance on VDD Pin
- 2.2.1.8 Open-loop Voltage Regulation Versus Pin Resistor Divider, Line Compensation Resistor
- 2.2.1.9 Feedback Elements
- 2.2.1.10 Backup Power Supply
- 2.2.1.11 Supercapacitor Selection
- 2.2.1.12 Supercapacitor Charger Design
- 2.2.2 Control Pilot Signal Interface
- 2.2.3 Relay Drive and Weld Detect
- 2.2.4 Residual Current Detection
- 2.2.1
Isolated AC/DC Power Supply Design
- 2.3 Highlighted Products
- 3Hardware, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design and Documentation Support
- 5About the Author
2.2.2.1 J1772 Duty Cycle
The duty cycle of the pilot signals communicate the limit of current the EVSE is capable of supplying to the vehicle; the vehicle can then use up to that amount of current for the charging circuitry. This current rating is primarily determined by the electromechanical components in the EVSE, such as conductors, relays, contactors, and the service connection.
The relationship between duty cycle and current is defined by two different equations depending on the current range specified; for a 6- to 51-A service, is:
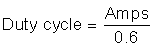
For a higher service in the 51- to 80-A range, is:
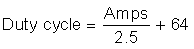
To demonstrate this relationship further, Table 2-2 shows some of the common service ratings.
| AMPS | DUTY CYCLE |
|---|---|
| 5 | 8.3% |
| 15 | 25% |
| 30 | 50% |
| 40 | 66.6% |
| 65 | 90% |
| 80 | 96% |
In this design, the PWM is generated by a timer module on the MSP430™ MCU. The current rating can typically be set as a permanent value in the firmware because the current rating is so tightly coupled to the external hardware.
Advanced EVSEs with a human machine interface (HMI) can enable the current to be derated if the service line is unable to provide enough current with a stable voltage. A significant voltage drop as a result of wire loss is possible in these high-current applications.