SLLU149E June 2011 – February 2016 TUSB7320 , TUSB7340
- TUSB73x0 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 1 Typical System Implementation
- 2 Power
- 3 Device Reset
- 4 General High Speed Layout Guidelines
- 5 USB Connection
- 6 Package and Breakout
- 7 PCI Express Connection
- 8 Wake from S3
- 9 Device Input Clock
- 10JTAG Interface
- 11Differential Pair ESD Protection
- 12SuperSpeed Redriver
- 13SMI Pin Implementation
- 14Schematics
- Revision History
4.4 Avoiding Crosstalk
Crosstalk is defined as interference from one trace to another by either or both inductive and capacitive coupling. Best ways to avoid crosstalk are:
- Provide stable reference planes for all high speed signals (as noted in previous sections).
- Use the 3W rule (3 times the width of trace for separation) where applicable on all signals, but absolutely use on clock signals.
- Use ground traces/guards around either “victim” or “aggressor” signals prone to crosstalk.
- When constrained and space limited on areas of the PCB to route parallel buses, series and/or end termination resistors can be used to route traces closer than what is normally recommended. However, calculations and simulations must be done to validate the use of series or end termination resistors to eliminate crosstalk.
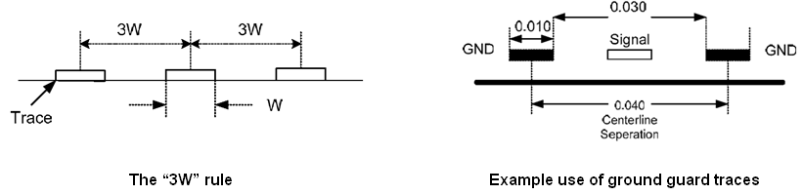 Figure 4-6 Ways to Avoid Crosstalk
Figure 4-6 Ways to Avoid Crosstalk