SWRU548C February 2019 – September 2021 CC3235MODAS , CC3235MODASF , CC3235MODS , CC3235MODSF
- 1Introduction
-
2Hardware
- 2.1 Block Diagram
- 2.2
Hardware Features
- 2.2.1 Key Benefits
- 2.2.2 XDS110-Based Onboard Debug Probe
- 2.2.3 Debug Probe Connection: Isolation Jumper Block
- 2.2.4 Application (or "Backchannel") UART
- 2.2.5 JTAG Headers
- 2.2.6 Using the XDS110 Debug Probe with a Different Target
- 2.2.7 Power Connections
- 2.2.8 Reset Pullup Jumper
- 2.2.9 Clocking
- 2.2.10 I2C Connection
- 2.2.11 Sense on Power (SOP)
- 2.2.12 Push-Buttons and LED Indicators
- 2.3 Electrical Characteristics
- 2.4 Antenna Characteristics
- 2.5 BoosterPack Plug-in Module Pinout
- 3Layout Guidelines
- 4Operational Setup and Testing
- 5Development Environment Requirements
- 6Additional Resources
- 7Assembly Drawing and Schematics
2.5 BoosterPack Plug-in Module Pinout
The LaunchPad development kit adheres to the 40-pin LaunchPad development kit pinout standard. This standard was created to aid compatibility between LaunchPad development kits and BoosterPack plug-in modules across the TI ecosystem.
While most BoosterPack plug-in modules are compliant with the standard, some are not. The LAUNCHCC3235MOD LaunchPad development kit is compatible with all 40-pin BoosterPack plug-in modules that are compliant with the standard. If the reseller or owner of the BoosterPack plug-in module does not explicitly indicate compatibility with the LAUNCHCC3235MOD LaunchPad development kit, compare the schematic of the candidate BoosterPack plug-in module with the LaunchPad development kit to ensure compatibility. Keep in mind that sometimes conflicts can be resolved by changing the CC3235MODSF12MOB device pin function configuration in software.
 Figure 2-14 BoosterPack Checker
Tool
Figure 2-14 BoosterPack Checker
ToolTo check the compatibility of a BoosterPack plug-in module with the LaunchPad development kit of your choice, use the BoosterPack Checker Tool. This allows you to select any LaunchPad development kit that TI offers and determine its compatibility with any number of BoosterPack plug-in modules that we offer. You can also add your own BoosterPack plug-in module to check its compatibility as you prototype that next design.
Figure 2-15 shows the 40-pin pinout of the LAUNCHCC3235MOD LaunchPad development kit.
Note that software's configuration of the pin functions plays a role in compatibility. The LaunchPad development kit side of the dashed line shows only the applicable function for conforming to the standard. However, each pin has other functionality that can be configured by the software. See the CC3235MODx device data sheet for more details on individual pin functions.
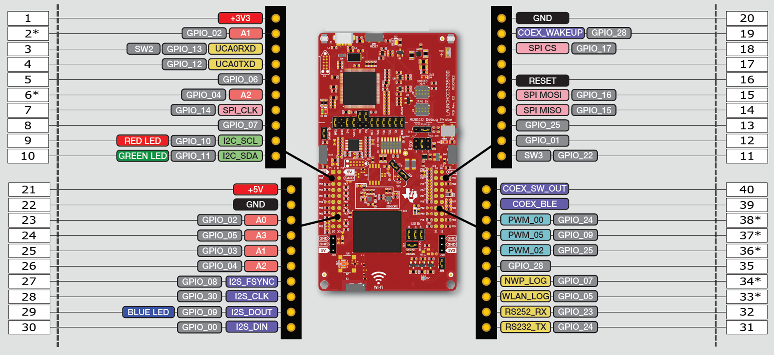 Figure 2-15 LAUNCHCC3235MOD BoosterPack
Header Pin Assignments
Figure 2-15 LAUNCHCC3235MOD BoosterPack
Header Pin AssignmentsRESET output is an open-drain-type output and can only drive the pin low. The pullup ensures that the line is pulled back high when the button is released. No external BoosterPack can drive this pin low.
All the signals are referred to by the pin number in the SDK; Figure 2-15 shows the default mappings. Some of the pins are repeated across the connector. For instance, pin 62 is available on P1 and P4, but only P1 is connected by default. The signal on P4 is marked with an asterisk (*) to signify that it is not connected by default. The signal can be routed to the pin by using a 0-Ω resistor in the path. For the exact resistor placement, see the CC3235MODSF SimpleLinkTM Wi-Fi® Wireless MCU LaunchPad Board Design Files.