SBAS988 November 2023 ADC34RF55
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics - Power Consumption
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics - DC Specifications
- 5.7 Electrical Characteristics - AC Specifications (Dither DISABLED)
- 5.8 Electrical Characteristics - AC Specifications (Dither ENABLED)
- 5.9 Timing Requirements
- 5.10 Typical Characteristics
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Analog Inputs
- 6.3.2 Sampling Clock Input
- 6.3.3 ADC Foreground Calibration
- 6.3.4 SYSREF
- 6.3.5 Decimation Filter
- 6.3.6 JESD204B Interface
- 6.3.7 Test Pattern
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
- 6.6 Register Maps
-
7 Application Information Disclaimer
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2 Typical Application
- 7.3
Initialization Set Up
- 7.3.1
Initial Device Configuration After Power-Up
- 7.3.1.1 STEP 1: RESET
- 7.3.1.2 STEP 2: Device Configuration
- 7.3.1.3 STEP 3: JESD Interface Configuration (1)
- 7.3.1.4 STEP 4: SYSREF Synchronization
- 7.3.1.5 STEP 5: JESD Interface Configuration (2)
- 7.3.1.6 STEP 6: Analog Trim Settings
- 7.3.1.7 STEP 7: Calibration Configuration
- 7.3.1.8 STEP 8: SYSREF Synchronization
- 7.3.1.9 STEP 9: Run Power up Calibration
- 7.3.1.10 Step 10: JESD Interface Synchronization
- 7.3.1.11 Step 11: NCO Configuration
- 7.3.1
Initial Device Configuration After Power-Up
- 7.4 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.5 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RTD|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTD|64
Orderable Information
6.3.7 Test Pattern
The ADC34RF55 provides several different options to output test patterns instead of the actual output data of the ADC to simplify the serial interface and system debug of the JESD204B digital interface link. The output data path is shown in Figure 6-44.
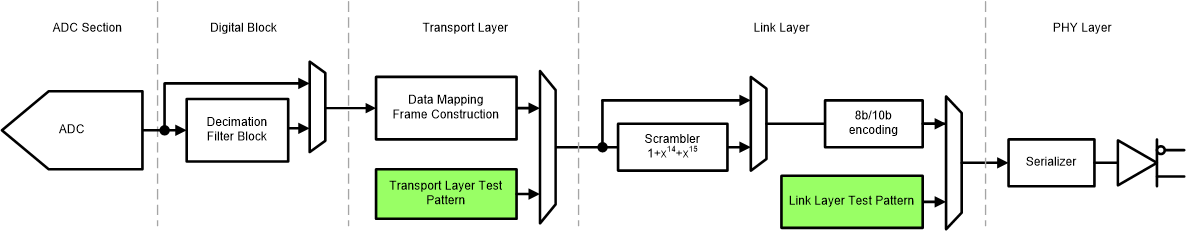 Figure 6-44 Test Pattern Options
Figure 6-44 Test Pattern OptionsThe available test patterns in each block are described in Table 6-41. Both test pattern blocks replace output data from the digital block (and not from the ADC) and are available in decimation or decimation bypass mode.
| TEST PATTERN LOCATION | TYPE | 8b/10b encoded | REGISTER PAGE | REGISTER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRANSPORT LAYER | CUSTOM PATTERN | Yes | JESD 0x05 0x04 | 0x2E, D0 |
| TOGGLE 1010 PATTERN | Yes | 0x2E, D1 | ||
| RAMP PATTERN | Yes | 0x2E, D2 | ||
| LINK LAYER | JESD204B TEST PATTERNS | Depends | 0x2D, D2-D0 | |
| PRBS PATTERN (27.. 231) | No | 0x2F, D6-D4 |
The RAMP pattern provides two different output options. Internally each ADC data bus consists of parallel data streams. The RAMP pattern is generated for each stream and a different starting value can be set for each stream. By default all starting values are 0 and increment =1. For example, DDC bypass mode uses 2 internal data streams per ADC channel. Enabling a RAMP pattern would show a 'slow' ramp which increments once every 2 clock cycles with starting values set to 0 and ramp increment = 1.
On the other hand a RAMP pattern, which increments every clock cycle, can be set using different starting values (e.g. 0/1) for the 2 streams and setting the RAMP increment to 2. Table Table 6-42 shows the register addresses for the different digital streams being used for each operating mode.
| Address (JESD Page) | Bypass Mode LMFS = 8-4-2-2 | Complex Decimation Single Band | Complex Decimation Dual Band |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0xA4/A5/A6 | A0 | A1I0 | A1I0 |
| 0xA8/A9/AA | A1 | A1Q0 | A1Q0 |
| 0xAC/AD/AE | A2I0 | ||
| 0xB0/B1/B2 | A2Q0 | ||
| 0xB4/B5/B6 | B0 | B1I0 | B1I0 |
| 0xB8/B9/BA | B1 | B1Q0 | B2Q0 |
| 0xBC/BD/BE | B2I0 | ||
| 0xC0/C1/C2 | B2Q0 | ||
| 0xC4/C5/C6 | C0 | C1I0 | C1I0 |
| 0xC8/C9/CA | C1 | C1Q0 | C1Q0 |
| 0xCC/CD/CE | C2I0 | ||
| 0xD0/D1/D2 | C2Q0 | ||
| 0xD4/D5/D6 | D0 | D1I0 | D1I0 |
| 0xD8/D9/DA | D1 | D1Q0 | D1Q0 |
| 0xDC/DD/DE | D2I0 | ||
| 0xE0/E1/E2 | D2Q0 |