SBASAP4 April 2025 ADC3664-EP , ADC3664-SEP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics - Power Consumption
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics - DC Specifications
- 5.7 Electrical Characteristics - AC Specifications
- 5.8 Timing Requirements
- 5.9 Typical Characteristics
- 6 Parameter Measurement Information
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application Information Disclaimer
- 9 Register Maps
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Revision History
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RSB|40
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
7.3.4.5 Decimation Filter
The ADC3664-xEP supports complex decimation by 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32 with a pass-band bandwidth of approximately 80% and a stopband rejection of at least 85dB. Table 7-2 gives an overview of the pass-band bandwidth of the different decimation settings with respect to ADC sampling rate FS. In real decimation mode, the output bandwidth is half of the complex bandwidth.
| REAL/COMPLEX DECIMATION | DECIMATION SETTING N | OUTPUT RATE | OUTPUT BANDWIDTH | OUTPUT RATE (FS = 125MSPS) | OUTPUT BANDWIDTH (FS = 125MSPS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complex | 2 | FS / 2 complex | 0.8 × FS / 2 | 62.5MSPS complex | 50MHz |
| 4 | FS / 4 complex | 0.8 × FS / 4 | 31.25MSPS complex | 25MHz | |
| 8 | FS / 8 complex | 0.8 × FS / 8 | 15.625MSPS complex | 12.5MHz | |
| 16 | FS / 16 complex | 0.8 × FS / 16 | 7.8125MSPS complex | 6.25MHz | |
| 32 | FS / 32 complex | 0.8 × FS / 32 | 3.90625MSPS complex | 3.125MHz | |
| Real | 2 | FS / 2 real | 0.4 × FS / 2 | 62.5MSPS | 25MHz |
| 4 | FS / 4 real | 0.4 × FS / 4 | 31.25MSPS | 12.5MHz | |
| 8 | FS / 8 real | 0.4 × FS / 8 | 15.625MSPS | 6.25MHz | |
| 16 | FS / 16 real | 0.4 × FS / 16 | 7.8125MSPS | 3.125MHz | |
| 32 | FS / 32 real | 0.4 × FS / 32 | 3.90625MSPS | 1.5625MHz |
The decimation filter responses normalized tot he ADC sampling clock frequency are illustrated in Figure 7-21 to Figure 7-30. They are interpreted as follows:
Each figure contains the filter pass-band, transition band(s) and alias or stop-band(s) as shown in Figure 7-20. The x-axis shows the offset frequency (after the NCO frequency shift) normalized to the ADC sampling rate FS.
For example, in the divide-by-4 complex setup, the output data rate is FS / 4 complex with a Nyquist zone of FS / 8 or 0.125 × FS. The transition band (colored in blue) is centered around 0.125 × FS and the alias transition band is centered at 0.375 × FS. The stop-bands (colored in red), which alias on top of the pass-band, are centered at 0.25 × FS and 0.5 × FS. The stop-band attenuation is greater than 85dB.
 Figure 7-20 Interpretation of the Decimation Filter Plots
Figure 7-20 Interpretation of the Decimation Filter Plots Figure 7-21 Decimation by 2 complex frequency response
Figure 7-21 Decimation by 2 complex frequency response Figure 7-23 Decimation by 4 complex frequency response
Figure 7-23 Decimation by 4 complex frequency response Figure 7-25 Decimation by 8 complex frequency response
Figure 7-25 Decimation by 8 complex frequency response Figure 7-27 Decimation by 16 complex frequency response
Figure 7-27 Decimation by 16 complex frequency response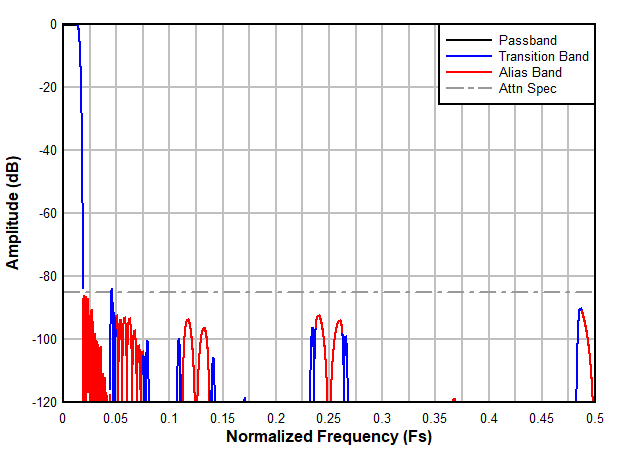 Figure 7-29 Decimation by 32 complex frequency response
Figure 7-29 Decimation by 32 complex frequency response Figure 7-22 Decimation by 2 complex passband ripple response
Figure 7-22 Decimation by 2 complex passband ripple response Figure 7-24 Decimation by 4 complex passband ripple response
Figure 7-24 Decimation by 4 complex passband ripple response Figure 7-26 Decimation by 8 complex passband ripple response
Figure 7-26 Decimation by 8 complex passband ripple response Figure 7-28 Decimation by 16 complex passband ripple response
Figure 7-28 Decimation by 16 complex passband ripple response Figure 7-30 Decimation by 32 complex passband ripple response
Figure 7-30 Decimation by 32 complex passband ripple response