SBAS925A August 2018 – November 2018 ADS1119
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RTE|16
Orderable Information
8.5.1.5 Data Transfer Protocol
Figure 34 shows the format of the data transfer. The master initiates all transactions with the ADS1119 by generating a START (S) condition. A high-to-low transition on the SDA line while SCL is high defines a START condition. The bus is considered to be busy after the START condition.
Following the START condition, the master sends the 7-bit slave address corresponding to the address of the ADS1119 that the master wants to communicate with. The master then sends an eighth bit that is a data direction bit (R/W). An R/W bit of 0 indicates a write operation, and an R/W bit of 1 indicates a read operation. After the R/W bit, the master generates a ninth SCLK pulse and releases the SDA line to allow the ADS1119 to acknowledge (ACK) the reception of the slave address by pulling SDA low. In case the device does not recognize the slave address, the ADS1119 holds SDA high to indicate a not acknowledge (NACK) signal.
Next follows the data transmission. If the transaction is a read (R/W = 1), the ADS1119 outputs data on SDA. If the transaction is a write (R/W = 0), the host outputs data on SDA. Data are transferred byte-wise, most significant bit (MSB) first. The number of bytes that can be transmitted per transfer is unrestricted. Each byte must be acknowledged (via the ACK bit) by the receiver. If the transaction is a read, the master issues the ACK. If the transaction is a write, the ADS1119 issues the ACK.
The master terminates all transactions by generating a STOP (P) condition. A low-to-high transition on the SDA line while SCL is high defines a STOP condition. The bus is considered free again tBUF (bus-free time) after the STOP condition.
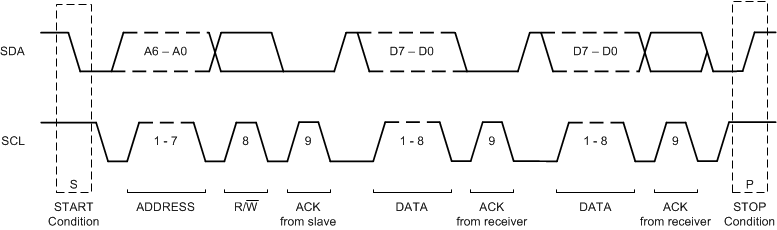 Figure 34. I2C Data Transfer Format
Figure 34. I2C Data Transfer Format