SBAS653B April 2014 – October 2020 ADS4245-EP
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics:
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: General
- 6.7 Digital Characteristics
- 6.8 Timing Characteristics: LVDS And CMOS Modes
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics:
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics: General
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics: Contour
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Serial Register Map
- 7.6 Description Of Serial Registers
- 8 Application Information Disclaimer
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- RGC|64
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- RGC|64
Orderable Information
8.2.1.3 Application Curves
In addition, the drive circuit may have to be designed to provide a low insertion loss over the desired frequency range and matched impedance to the source. Furthermore, the ADC input impedance must be considered. Figure 8-11 and Figure 8-12 show the impedance (ZIN = RIN || CIN) looking into the ADC input terminals.
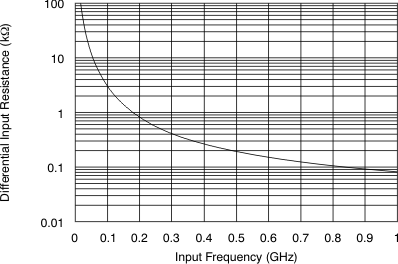 Figure 8-11 ADC Analog Input Resistance (RIN) Across Frequency
Figure 8-11 ADC Analog Input Resistance (RIN) Across Frequency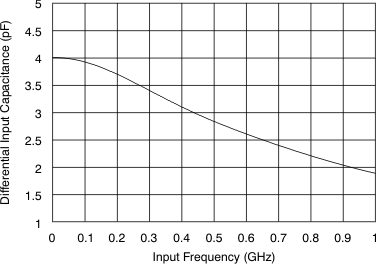 Figure 8-12 ADC Analog Input Capacitance (CIN) Across Frequency
Figure 8-12 ADC Analog Input Capacitance (CIN) Across Frequency