SPRS657F February 2010 – January 2017 AM1705
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
-
3Device Comparison
- 3.1 Device Characteristics
- 3.2 Device Compatibility
- 3.3 ARM Subsystem
- 3.4 Memory Map Summary
- 3.5 Pin Assignments
- 3.6
Terminal Functions
- 3.6.1 Device Reset and JTAG
- 3.6.2 High-Frequency Oscillator and PLL
- 3.6.3 External Memory Interface A (ASYNC)
- 3.6.4 External Memory Interface B (SDRAM only)
- 3.6.5 Serial Peripheral Interface Modules (SPI0, SPI1)
- 3.6.6 Enhanced Capture/Auxiliary PWM Modules (eCAP0, eCAP1, eCAP2)
- 3.6.7 Enhanced Pulse Width Modulators (eHRPWM0, eHRPWM1, eHRPWM2)
- 3.6.8 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder Pulse Module (eQEP)
- 3.6.9 Boot
- 3.6.10 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitters (UART0, UART1, UART2)
- 3.6.11 Inter-Integrated Circuit Modules(I2C0, I2C1)
- 3.6.12 Timers
- 3.6.13 Multichannel Audio Serial Ports (McASP0, McASP1)
- 3.6.14 Universal Serial Bus Modules (USB0)
- 3.6.15 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 3.6.16 Multimedia Card/Secure Digital (MMC/SD)
- 3.6.17 Reserved and No Connect
- 3.6.18 Supply and Ground
- 3.6.19 Unused USB0 (USB2.0) Pin Configurations
- 4Device Configuration
-
5Device Operating Conditions
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings Over Operating Junction Temperature Range (Unless Otherwise Noted)
- 5.2 Handling Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Notes on Recommended Power-On Hours (POH)
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Ranges of Supply Voltage and Operating Junction Temperature (Unless Otherwise Noted)
-
6Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications
- 6.1 Parameter Information
- 6.2 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 6.3 Power Supplies
- 6.4 Reset
- 6.5 Crystal Oscillator or External Clock Input
- 6.6 Clock PLLs
- 6.7 Interrupts
- 6.8 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 6.9 EDMA
- 6.10 External Memory Interface A (EMIFA)
- 6.11 External Memory Interface B (EMIFB)
- 6.12 Memory Protection Units
- 6.13 MMC / SD / SDIO (MMCSD)
- 6.14 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)
- 6.15 Management Data Input/Output (MDIO)
- 6.16 Multichannel Audio Serial Ports (McASP0, McASP1)
- 6.17 Serial Peripheral Interface Ports (SPI0, SPI1)
- 6.18 Enhanced Capture (eCAP) Peripheral
- 6.19 Enhanced Quadrature Encoder (eQEP) Peripheral
- 6.20 Enhanced High-Resolution Pulse-Width Modulator (eHRPWM)
- 6.21 Timers
- 6.22 Inter-Integrated Circuit Serial Ports (I2C0, I2C1)
- 6.23 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 6.24 USB0 OTG (USB2.0 OTG)
- 6.25 Power and Sleep Controller (PSC)
- 6.26 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem (PRUSS)
- 6.27 Emulation Logic
- 6.28 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- 7Device and Documentation Support
- 8Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- PTP|176
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- PTP|176
Orderable Information
7 Device and Documentation Support
TI offers an extensive line of development tools. Tools and software to evaluate the performance of the device, generate code, and develop solutions are listed below.
7.1 Device Nomenclature
To designate the stages in the product development cycle, TI assigns prefixes to the part numbers of all microprocessors (MPUs) and support tools. Each device has one of three prefixes: X, P, or null (no prefix) (for example, AM1705). Texas Instruments recommends two of three possible prefix designators for its support tools: TMDX and TMDS. These prefixes represent evolutionary stages of product development from engineering prototypes (TMDX) through fully qualified production devices and tools (TMDS).
Device development evolutionary flow:
-
X Experimental device that is not necessarily representative of the final device's electrical specifications and may not use production assembly flow.
-
P Prototype device that is not necessarily the final silicon die and may not necessarily meet final electrical specifications.
-
nullProduction version of the silicon die that is fully qualified.
Support tool development evolutionary flow:
-
TMDX Development-support product that has not yet completed Texas Instruments internal qualification testing.
-
TMDS Fully-qualified development-support product.
X and P devices and TMDX development-support tools are shipped against the following disclaimer:
"Developmental product is intended for internal evaluation purposes."
Production devices and TMDS development-support tools have been characterized fully, and the quality and reliability of the device have been demonstrated fully. TI's standard warranty applies.
Predictions show that prototype devices (X or P) have a greater failure rate than the standard production devices. Texas Instruments recommends that these devices not be used in any production system because their expected end-use failure rate still is undefined. Only qualified production devices are to be used.
TI device nomenclature also includes a suffix with the device family name. This suffix indicates the package type (for example, ZKB), the temperature range (for example, blank is the default commercial temperature range), and the device speed range, in megahertz (for example, 375). Figure 7-1 provides a legend for reading the complete device name for any AM1705 device.
For orderable part numbers of AM1705 devices in the your package package types, see the Package Option Addendum of this document, ti.com, or contact your TI sales representative.
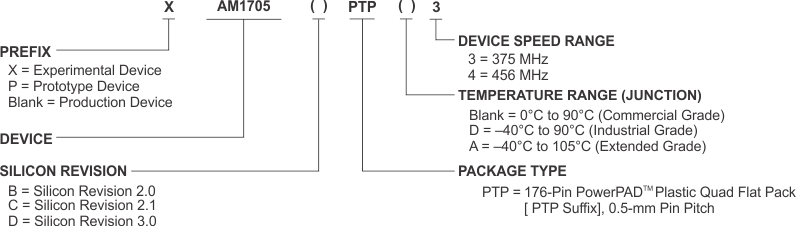 Figure 7-1 Device Nomenclature
Figure 7-1 Device Nomenclature
7.2 Tools and Software
TI offers an extensive line of development tools for the device platform, including tools to evaluate the performance of the processors, generate code, develop algorithm implementations, and fully integrate and debug software and hardware modules. The tool's support documentation is electronically available within the Code Composer Studio™ Integrated Development Environment (IDE).
The following products support development of the device applications:
Software
-
Code Composer Studio™ Integrated Development Environment (IDE): including Editor
-
C/C++/Assembly Code Generation, and Debug plus additional development tools
Development Tools
-
Extended Development System (XDS™) Emulator
For a complete listing of development-support tools for the device, visit the Texas Instruments web site on the Worldwide Web at www.ti.com uniform resource locator (URL). For information on pricing and availability, contact the nearest TI field sales office or authorized distributor.
7.3 Documentation Support
To receive notification of documentation updates, navigate to the device product folder on ti.com. In the upper right corner, click on Alert me to register and receive a weekly digest of any product information that has changed. For change details, review the revision history included in any revised document.
The current documentation that describes the DSP, related peripherals, and other technical collateral is listed below.
User's Guides
7.4 Community Resources
The following links connect to TI community resources. Linked contents are provided "AS IS" by the respective contributors. They do not constitute TI specifications and do not necessarily reflect TI's views; see TI's Terms of Use.
-
TI E2E™ Online Community The TI engineer-to-engineer (E2E) community was created to foster collaboration among engineers. At e2e.ti.com, you can ask questions, share knowledge, explore ideas and help solve problems with fellow engineers.
-
TI Embedded Processors Wiki Established to help developers get started with Embedded Processors from Texas Instruments and to foster innovation and growth of general knowledge about the hardware and software surrounding these devices.
7.5 Trademarks
E2E is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
ETM9, CoreSight are trademarks of ARM Limited.
ARM9 is a trademark of ARM.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
7.6 Electrostatic Discharge Caution

This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Texas Instruments recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper handling and installation procedures can cause damage.
ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation to complete device failure. Precision integrated circuits may be more susceptible to damage because very small parametric changes could cause the device not to meet its published specifications.
7.7 Export Control Notice
Recipient agrees to not knowingly export or re-export, directly or indirectly, any product or technical data (as defined by the U.S., EU, and other Export Administration Regulations) including software, or any controlled product restricted by other applicable national regulations, received from disclosing party under nondisclosure obligations (if any), or any direct product of such technology, to any destination to which such export or re-export is restricted or prohibited by U.S. or other applicable laws, without obtaining prior authorization from U.S. Department of Commerce and other competent Government authorities to the extent required by those laws.
7.8 Glossary
-
TI Glossary This glossary lists and explains terms, acronyms, and definitions.