DLPS215A July 2021 – September 2022 DLP301S
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 Storage Conditions
- 6.3 ESD Ratings
- 6.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.5 Thermal Information
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.7 Timing Requirements
- 6.8 Switching Characteristics
- 6.9 System Mounting Interface Loads
- 6.10 Micromirror Array Physical Characteristics
- 6.11 Micromirror Array Optical Characteristics
- 6.12 Window Characteristics
- 6.13 Chipset Component Usage Specification
- 6.14 Software Requirements
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- FQS|99
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
6.7 Timing Requirements
Device electrical characteristics are over Section 6.4 unless otherwise noted.
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPSDR | ||||||
| tr | Rise slew rate(1) | (30% to 80%) × VDD, Figure 6-3 | 1 | 3 | V/ns | |
| tƒ | Fall slew rate(1) | (70% to 20%) × VDD, Figure 6-3 | 1 | 3 | V/ns | |
| tr | Rise slew rate(2) | (20% to 80%) × VDD, Figure 6-4 | 0.25 | V/ns | ||
| tƒ | Fall slew rate(2) | (80% to 20%) × VDD, Figure 6-4 | 0.25 | V/ns | ||
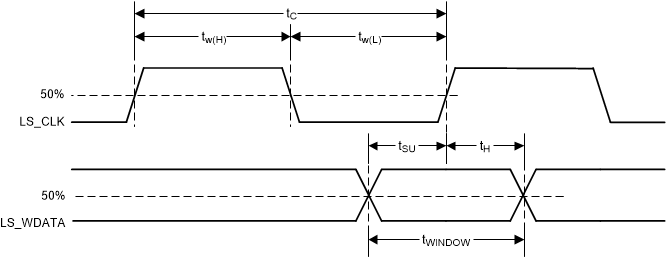
| tc | Cycle time LS_CLK, | Figure 6-2 | 7.7 | 8.3 | ns | |
| tW(H) | Pulse duration LS_CLK high | 50% to 50% reference points, Figure 6-2 | 3.1 | ns | ||
| tW(L) | Pulse duration LS_CLK low | 50% to 50% reference points, Figure 6-2 | 3.1 | ns | ||
| tsu | Setup time | LS_WDATA valid before LS_CLK ↑, Figure 6-2 | 1.5 | ns | ||
| th | Hold time | LS_WDATA valid after LS_CLK ↑, Figure 6-2 | 1.5 | ns | ||
| tWINDOW | Window time(1)(4) | Setup time + Hold time, Figure 6-2 | 3 | ns | ||
| tDERATING | Window time derating(1)(4) | For each 0.25 V/ns reduction in slew rate below 1 V/ns, Figure 6-6 | 0.35 | ns | ||
| SubLVDS | ||||||
| tr | Rise slew rate | 20% to 80% reference points, Figure 6-5 | 0.7 | 1 | V/ns | |
| tƒ | Fall slew rate | 80% to 20% reference points, Figure 6-5 | 0.7 | 1 | V/ns | |
| tc | Cycle time DCLK, | Figure 6-7 | 1.79 | 1.85 | ns | |
| tW(H) | Pulse duration DCLK high | 50% to 50% reference points, Figure 6-7 | 0.79 | ns | ||
| tW(L) | Pulse duration DCLK low | 50% to 50% reference points, Figure 6-7 | 0.79 | ns | ||
| tsu | Setup time | D(0:3)
valid before DCLK ↑ or DCLK ↓, Figure 6-7 |
||||
| th | Hold time | D(0:3)
valid after DCLK ↑ or DCLK ↓, Figure 6-7 |
||||
| tWINDOW | Window time | Setup time + Hold time, Figure 6-7, Figure 6-8 | 0.3 | ns | ||
| tLVDS-ENABLE+REFGEN | Power-up receiver(3) | 2000 | ns | |||
(1) Specification is for LS_CLK and LS_WDATA pins. Refer to LPSDR input rise slew rate and fall slew rate in Figure 6-3.
(2) Specification is for DMD_DEN_ARSTZ pin. Refer to LPSDR input rise and fall slew rate in Figure 6-4.
(3) Specification is for SubLVDS receiver time only and does not take into account commanding and latency after commanding.
(4) Window time derating example: 0.5-V/ns slew rate increases the window time by 0.7 ns, from 3 to 3.7 ns.
Low-speed interface is LPSDR and
adheres to the Section 6.6 and AC/DC Operating Conditions table in JEDEC Standard No. 209B, Low Power
Double Data Rate (LPDDR)JESD209B.
Figure 6-2 LPSDR
Switching Parameters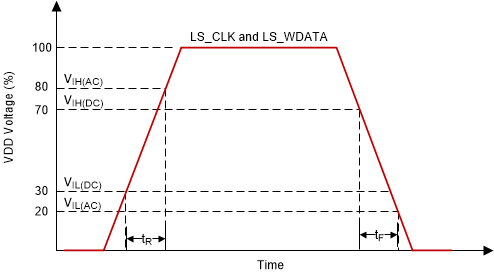 Figure 6-3 LPSDR
Input Slew Rate
Figure 6-3 LPSDR
Input Slew Rate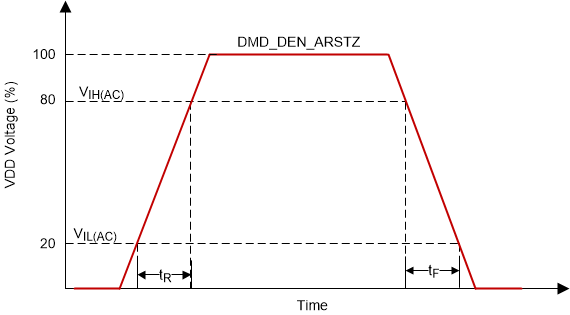 Figure 6-4 LPSDR
Input Slew Rate
Figure 6-4 LPSDR
Input Slew Rate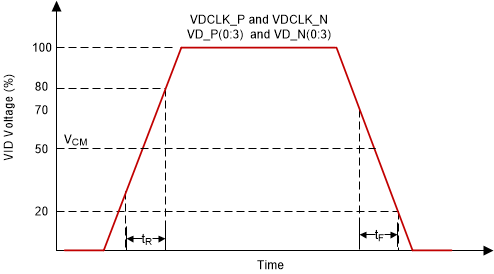 Figure 6-5 SubLVDS
Input Rise and Fall Slew Rate
Figure 6-5 SubLVDS
Input Rise and Fall Slew Rate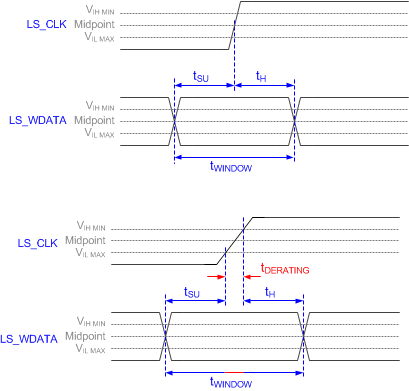 Figure 6-6 Window Time Derating Concept
Figure 6-6 Window Time Derating Concept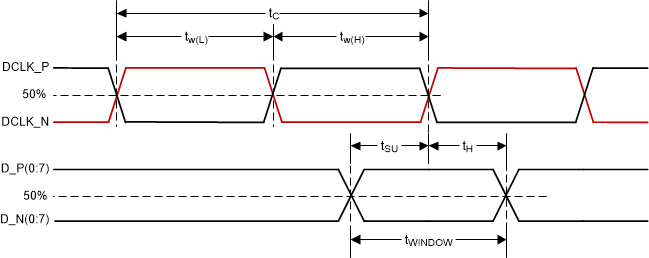 Figure 6-7 SubLVDS
Switching Parameters
Figure 6-7 SubLVDS
Switching Parameters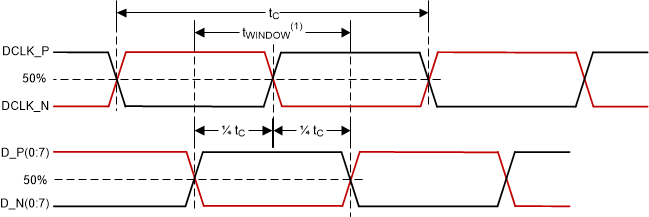
(1) High-speed
training scan window
(2) Refer to Section 7.3.3 for details
Figure 6-8 High-Speed Training Scan Window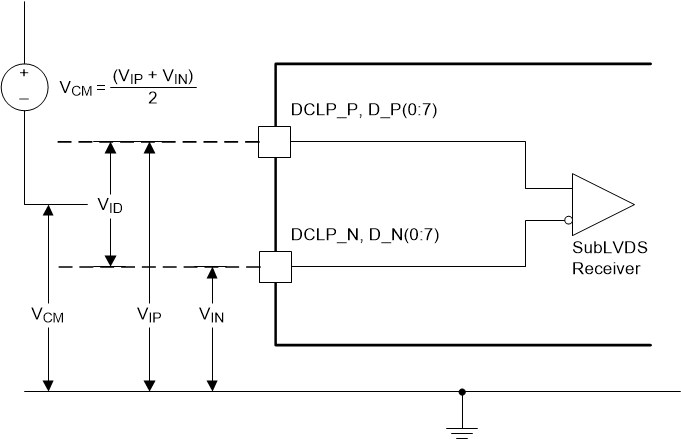 Figure 6-9 SubLVDS
Voltage Parameters
Figure 6-9 SubLVDS
Voltage Parameters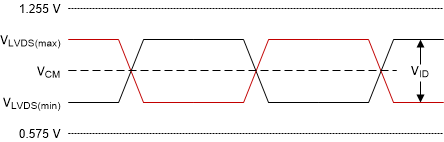 Figure 6-10 SubLVDS Waveform Parameters
Figure 6-10 SubLVDS Waveform ParametersVSubLVDS(max) = VCM(max) + ½ × |VID(max)|
VSubLVDS(min) = VCM(min) – ½ × |VID(max)|
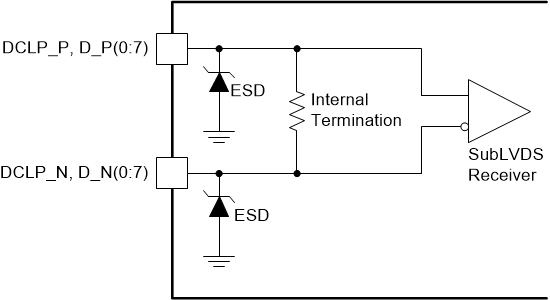 Figure 6-11 SubLVDS
Equivalent Input Circuit
Figure 6-11 SubLVDS
Equivalent Input Circuit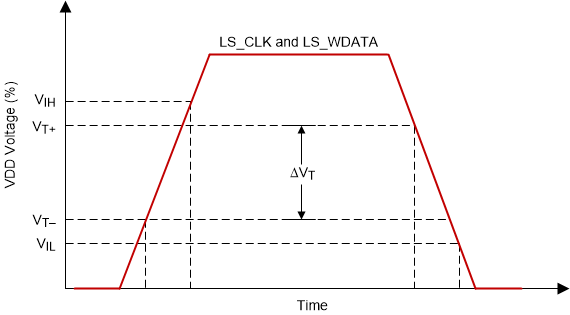 Figure 6-12 LPSDR
Input Hysteresis
Figure 6-12 LPSDR
Input Hysteresis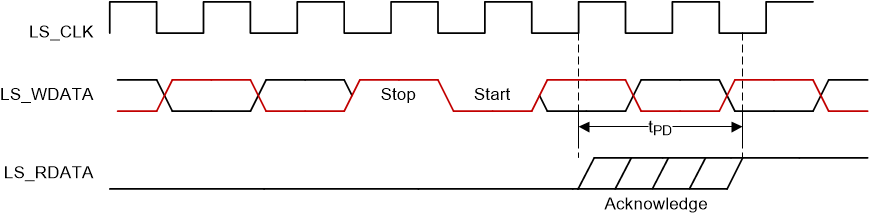 Figure 6-13 LPSDR
Read Out
Figure 6-13 LPSDR
Read Out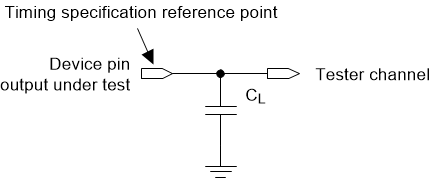
See Section 7.3.4 for more information.
Figure 6-14 Test Load Circuit for Output Propagation Measurement