SBOS562G August 2011 – June 2020 INA826
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
- DRG|8
Orderable Information
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
at TA = 25°C, VS = ±15 V, RL = 10 kΩ, VREF = 0 V, and G = 1 (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INPUT | |||||||
| VOSI | Input stage offset voltage(1) | RTI | 40 | 150 | µV | ||
| vs temperature, TA = –40°C to +125°C | 0.4 | 2 | µV/°C | ||||
| VOSO | Output stage offset voltage(1) | RTI | 200 | 700 | µV | ||
| vs temperature, TA = –40°C to +125°C | 2 | 10 | µV/°C | ||||
| PSRR | Powersupply rejection ratio | G = 1, RTI | 100 | 124 | dB | ||
| G = 10, RTI | 115 | 130 | |||||
| G = 100, RTI | 120 | 140 | |||||
| G = 1000, RTI | 120 | 140 | |||||
| zid | Differential impedance | 20 || 1 | GΩ || pF | ||||
| zic | Common-mode impedance | 10 || 5 | GΩ || pF | ||||
| RFI filter, –3-dB frequency | 20 | MHz | |||||
| VCM | Operating input range(2) | V– | (V+) – 1 | V | |||
| VS = ±1.5 V to ±18 V
TA = –40°C to +125°C |
See Figure 41 to Figure 44 | ||||||
| Input overvoltage range | TA = –40°C to +125°C | ±40 | V | ||||
| CMRR | Common-mode rejection ratio | At dc to 60 Hz, RTI | G = 1, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V | 84 | 95 | dB | |
| G = 10, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V | 104 | 115 | |||||
| G = 100, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V | 120 | 130 | |||||
| G = 1000, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V | 120 | 130 | |||||
| G = 1, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V,
TA = –40°C to +125°C |
80 | ||||||
| At 5 kHz, RTI | G = 1, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V | 84 | |||||
| G = 10, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V | 100 | ||||||
| G = 100, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V | 105 | ||||||
| G = 1000, VCM = (V–) to (V+) – 1 V | 105 | ||||||
| BIAS CURRENT | |||||||
| IB | Input bias current | VCM = VS / 2 | 35 | 65 | nA | ||
| TA = –40°C to +125°C | 95 | ||||||
| IOS | Input offset current | VCM = VS / 2 | 0.7 | 5 | nA | ||
| TA = –40°C to +125°C | 10 | ||||||
| NOISE VOLTAGE | |||||||
| eNI | Input stage voltage noise(4) | f = 1 kHz, G = 100, RS = 0 Ω | 18 | 20 | nV/√Hz | ||
| fB = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz, G = 100, RS = 0 Ω | 0.52 | µVPP | |||||
| eNO | Output stage voltage noise(4) | f = 1 kHz, G = 1, RS = 0 Ω | 110 | 115 | nV/√Hz | ||
| fB = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz, G = 1, RS = 0 Ω | 3.3 | µVPP | |||||
| In | Noise current | f = 1 kHz | 100 | fA/√Hz | |||
| fB = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz | 5 | pAPP | |||||
| GAIN | |||||||
| G | Gain equation | 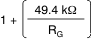 |
V/V | ||||
| Range of gain | 1 | 1000 | V/V | ||||
| GE | Gain error | G = 1, VO = ±10 V | ±0.003% | ±0.015% | |||
| G = 10, VO = ±10 V | ±0.03% | ±0.15% | |||||
| G = 100, VO = ±10 V | ±0.04% | ±0.15% | |||||
| G = 1000, VO = ±10 V | ±0.04% | ±0.15% | |||||
| Gain vs temperature(3) | G = 1, TA = –40°C to +125°C | ±0.1 | ±1 | ppm/°C | |||
| G > 1, TA = –40°C to +125°C | ±10 | ±35 | |||||
| Gain nonlinearity | G = 1 to 100, VO = –10 V to +10 V | 1 | 5 | ppm | |||
| G = 1000, VO = –10 V to +10 V | 5 | 20 | |||||
| OUTPUT | |||||||
| Voltage swing | RL = 10 kΩ | (V–) + 0.1 | (V+) – 0.15 | V | |||
| Load capacitance stability | 1000 | pF | |||||
| ZO | Open-loop output impedance | See Figure 56 | |||||
| ISC | Short-circuit current | Continuous to VS / 2 | ±16 | mA | |||
| FREQUENCY RESPONSE | |||||||
| BW | Bandwidth, –3 dB | G = 1 | 1 | MHz | |||
| G = 10 | 500 | kHz | |||||
| G = 100 | 60 | ||||||
| G = 1000 | 6 | ||||||
| SR | Slew rate | G = 1, VO = ±14.5 V | 1 | V/µs | |||
| G = 100, VO = ±14.5 V | 1 | ||||||
| tS | Settling time | 0.01% | G = 1, VSTEP = 10 V | 12 | µs | ||
| G = 10, VSTEP = 10 V | 12 | ||||||
| G = 100, VSTEP = 10 V | 24 | ||||||
| G = 1000, VSTEP = 10 V | 224 | ||||||
| 0.001% | G = 1, VSTEP = 10 V | 14 | |||||
| G = 10, VSTEP = 10 V | 14 | ||||||
| G = 100, VSTEP = 10 V | 31 | ||||||
| G = 1000, VSTEP = 10 V | 278 | ||||||
| REFERENCE INPUT | |||||||
| RIN | Input impedance | 100 | kΩ | ||||
| Voltage range | (V–) | (V+) | V | ||||
| Gain to output | 1 | V/V | |||||
| Reference gain error | 0.01% | ||||||
| POWER SUPPLY | |||||||
| IQ | Quiescent current | VIN = 0 V | 200 | 250 | µA | ||
| vs temperature, TA = –40°C to +125°C | 250 | 300 | |||||
(1) Total offset, referred-to-input (RTI): VOS = (VOSI) + (VOSO / G).
(2) Input voltage range of the INA826 input stage. The input range depends on the common-mode voltage, differential voltage, gain, and reference voltage. See Typical Characteristic curves Figure 9 through Figure 16 and Figure 41 through Figure 44 for more information.
(3) The values specified for G > 1 do not include the effects of the external gain-setting resistor, RG.
(4)
Total RTI voltage noise =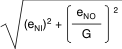 .
.
Total RTI voltage noise =
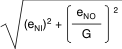 .
.