SNOSCS2D November 2013 – March 2019 LM3697
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Descriptions
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Register Maps
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
Package Options
Refer to the PDF data sheet for device specific package drawings
Mechanical Data (Package|Pins)
- YFQ|12
Thermal pad, mechanical data (Package|Pins)
Orderable Information
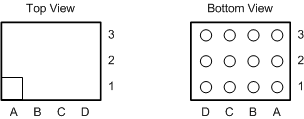
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
YFQ Package
12-Pin DSBGA